CO AS115
advertisement

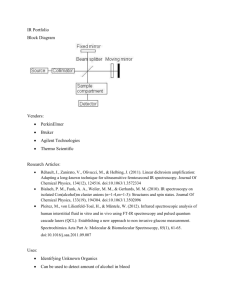
COURSE OUTCOME CHM 260 Basic Instrumental Analysis Semester: July – Oct 2007 Text: Principles of Instrumental Analysis, 5th edition, Skoog, Holler & Nieman, Saunders, 1998 Goal: Enable students to understand and apply scientific principles and methods of chemical analysis. Learning outcomes: On completion of this course, students should be able to do the following: 1. 2 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Identify and explain the different types of spectroscopic methods of analysis. Identify and explain the different types of chromatographic methods of analysis. Identify and explain the different types of electromagnetic radiation. Explain the principles and the working mechanism of Ultraviolet visible(UV) Absorption Spectroscopy, Infrared Absorption (IR) Spectroscopy, Atomic Absorption (AA) Spectroscopy, Flame Emission (FE) Spectroscopy, Gas Chromatography (GC) and High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC). Draw the schematic diagram of the related instruments in separation and identification techniques and able to explain the function of each components of the instrument. Differentiate between different instruments in terms of parts and functions. (For example: radiation sources and sample cells, detectors) Identify, distinguish and apply the appropriate chemical analysis methods in determining unknowns. Be able to use different instrumental methods of analysis to solve for specific analytical problems. The student should be able to choose the appropriate instrumental method for a particular investigation. Interpret and evaluate analytical information from spectral data and diagnose a physical problem and decide the most appropriate instrumental method for further investigation and quantify the known compound graphically and numerically. Operate the UV, IR, AA, FE, GC, HPLC instruments with minimal supervision. Acquire the science skills related to spectroscopic and chromatographic analysis. LESSON PLAN Week Total Hours 1 1 Contents Diagnostics and Learning Skills • Conceptual Survey in Chemical Concept Inventory• Learning Styles • Concept Mapping Introduction to Spectroscopic Methods of Analysis 1 1 Fundamental principles Properties of electromagnetic radiation Introduction to Spectroscopic Methods of Analysis 1 1 Molecular absorption spectroscopy. Terms employed in absorption spectroscopy: Transmittance and Absorbance Beers’ Law: Application of Beer’s Law to mixtures, limitations to the applicability of Beer’s law 2 Ultraviolet/Visible Spectrometry and Photometry 3 1 1 Molecular species that absorb UV/Vis radiation: Organic and inorganic compounds Instrumentation for UV spectroscopy Ultraviolet/Visible Spectrometry and Photometry 4 1 1 Application of absorption measurement to qualitative analysis Quantitative analysis by absorption measurement Test 1 Infrared Absorption Spectroscopy 5 1 1 Molecular species that absorb IR radiation Instrumentation and sample handling techniques Infrared Absorption Spectroscopy 6 1 1 Qualitative applications: Structural Analysis Qualitative applications: Structural Analysis Atomic Spectroscopy based on Flame Atomization 7 1 1 Fundamental principle Sample atomization, interferences Atomic Spectroscopy based on Flame Atomization 8 1 1 Instrumentation: Hollow cathode lamp Quantitative analysis Flame Emission Spectroscopy 9 1 1 Fundamental principles Comparison with atomic absorption Test 2 Introduction to Chromatographic Separations 10 1 1 Migration rates of solutes, column efficiency and resolution Qualitative/quantitative analysis Gas Chromatography 11 1 1 Principles of GC Instrumentation: Carrier gas, sample injection system, column temperature (isothermal & thermal programming), types of columns. Gas Chromatography 12 2 Detectors: principles and application for flame ionization detector, thermal conductivity detector, electron capture detector High Performance Liquid Chromatography 13 Principles of HPLC Instrumentation: Mobile phase reservoirs and solvent system (isocratic and gradient elution), pumping systems, detectors 1 1 High Performance Liquid Chromatography 14 Types of Liquid Chromatography (Adsorption, Partition – normal and reverse phase, ion exchange and size exclusion); Principles and applications 2 Test 3 15 Revision 16 FINAL EXAMINATION Assessment: Tests (3x) Practical Reports Final Examinations : : : 30% 20% 50% References: a) Spectrochemical Analysis, James D. Ingle, Jr. and Stanley R. Crouch b) Introduction to Spectroscopy, 3rd edition by Pavia, Lampman, Kriz c) Analytical Chemistry 6th edition , Gary D. Christian John Wiley &Sons, Inc.