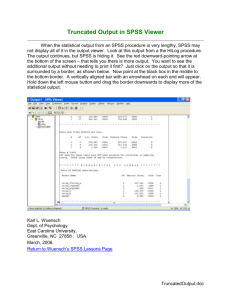
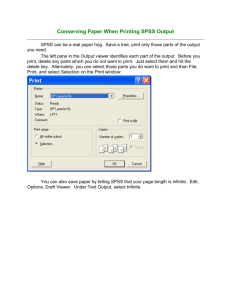
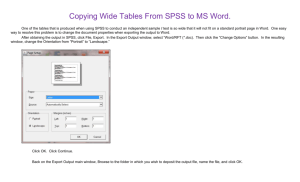
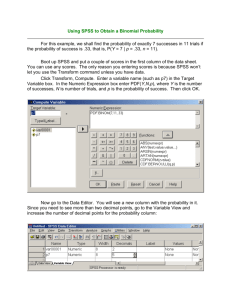
Instructor: Dr - Jordan University of Science and Technology
advertisement

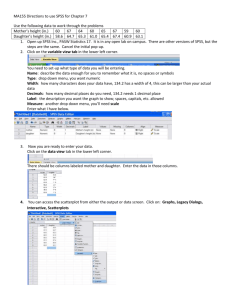
JORDAN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY Faculty of Medicine - DEPT. of Public Health. Use of Computer (PH 701) - 2 Credit Hours Instructor: Dr. Yousef Khader Office: Department of Public Health Course Objectives: This course is designed to provide you with an introduction to the practice of statistics. By the end of the course, you should be able to: Use the statistical software package SPSS for analyzing statistical data: 1. Catalog description: The student will learn to execute three major steps in the data analysis process: (a) identify the appropriate statistical technique for a given research problem; (b) conduct analyses using the SPSS for Windows computer software (one-sample, dependent-samples and independentsamples t tests, one-way ANOVA, two-way ANOVA, correlation, simple linear regression, multiple linear regression, chi-square tests, logistic regression, and factor analysis); and (c) interpret the statistical values generated by these various analytical tools. 2. Course content: In this course students will learn specific statistical techniques as applied to various research problems found in a variety of fields of study. The topics contained in the course include the following: 1. Introduction to the SPSS for Windows software 2. Hypothesis testing [one sample case] 1. steps used to construct and test a set of hypotheses designed to determine whether the population mean has changed 2. use of SPSS to conduct a one-sample t test and the interpretation of the results 3. types of errors encountered in hypothesis testing 4. power analysis and sample size determination for a one-sample t test 5. 6. practical significance versus statistical significance calculation and classification of an effect size 3. Two types of t tests used to test the difference between two means 1. use of SPSS to conduct a paired-samples t test and the interpretation of the results 2. use of SPSS to conduct an independent t test and the interpretation of the results 4. One-Way ANOVA 1. use of SPSS to conduct a one-way ANOVA and the interpretation of the ANOVA table 2. reason for conducting multiple comparisons tests 3. use of SPSS to conduct various types of multiple comparisons tests and the interpretation of those tests 5. Two-way ANOVA and interaction effects 1. use of SPSS to conduct a two-way ANOVA and the interpretation of the ANOVA table 2. using SPSS to plot the interaction effect and identify whether it is ordinal or disordinal 3. construction of an SPSS syntax file to conduct simple effects tests 6. Bivariate correlation analysis with SPSS including the scattergram 7. Construction of simple linear regression model, analysis of the models with SPSS, and the interpretation of the results 8. Construction of multiple linear regression models, analysis of the models with SPSS, and the interpretation of the results 1. 2. 3. 4. the use of continuous independent variables the use of dummy independent variables the use of a series of dummy independent variables the construction and analysis of models that contain two-way interaction effects 9. Chi-Square test [two group case] 10. The use of SPSS to analyze logistic regression models [two group case] and the interpretation of the results 1. evaluating the statistical significance of the independent variable coefficients 2. assessing the model's prediction accuracy 3. the calculation and interpretation of Delta-p values 11. The use of SPSS to conduct factor analysis and the identification of the factors 3. Student learning objectives: The student will learn to execute three major steps in the data analysis process: (a) identify the appropriate statistical technique for a given research problem; (b) conduct analyses using the SPSS for Windows computer software (one-sample, dependent-samples and independentsamples t tests, one-way ANOVA, two-way ANOVA, correlation, simple linear regression, multiple linear regression, chi-square tests, logistic regression, and factor analysis); and (c) interpret the statistical values generated by these various analytical tools. 4. Student assessment criteria: The degree of student mastery of the material presented in this course will be evaluated through two methods: (a) three tests, and (b) a paper that addresses the statistical analyses presented in a research article selected by the student.