General Ecology syllabus448
advertisement

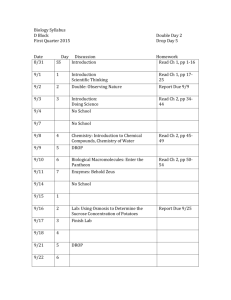
Syllabus: General Ecology (Bio-448), Spring Semester 2013 Yarmouk University Biology Dept Faculty of Science office room: 117 first floor Lecturer: Dr. Emad Malkawi office hours: 11-12 Sun, Tue. -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Lecture time: 9:30-11:00 Mon, Wed. Office Hours: Please contact me by email to make an appointment. You are also welcome to just stop by my office or lab, but I may not be available unless you have an appointment. Official Office hours will be from 11-12 Sun, Tue. Email: shussein5@yahoo.com Course Objectives and description: This course is an introductory for the study of environment and its inhabitants. It aims for introducing the students to the basic principles of ecology, comprising evolutionary, physiological, behavioural, population and community ecology. Moreover, this course concentrates on the conditions of the physical environment, adaptation and responses to variation in the environment. Develop a more comprehensive understanding of the relationships that exist between organisms and their environment, and understand how changes in the environment affect the distribution and abundance of organisms. It also deals with energy flow in the ecosystems and the regulation of ecosystem functions. Attendance: Students are expected to attend classes. Consequently, students are responsible for ALL material presented or assigned during the scheduled class period and are expected to obtain such information on their own should a class period be missed. Whenever possible, absences will be discussed with the instructor in advance. Class attendance will be taken in lecture. Students will be allowed three absences (with acceptable reasons) between every mid-term exam, and a total of six absences before the final. Absences in excess of that stated above will result in the student failing in the course. Policy on academic dishonesty and Make-up examinations: University regulations and rules will be strictly implemented. Refer to University's student information book for more details about exams, exam make up and absence rules; If you are absent from one or more of your examinations for medical or other reasons, you must provide documentary evidence to justify your absence for the consideration of a make up exam within one week or else no make up exam will be permitted. Assessment: First exam: 15% Second exam: 15% Final exam: 40%. Lab work: 30% Course outline Week No Topic 1 Introduction to ecology: What is ecology? Why to study ecology? How to study ecology? Where to study ecology? How will we learn about ecology? Organization of life: species, populations, community and ecosystems. Ecosystems, biomes and habitats: Ecosystems of the world, terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems. Ecosystem productivity. The input of energy, gross and net productivity, energy flow in ecosystems and production efficiency. Biochemical cycles. 2 3 4 5 6 7 Community ecology: Concept of community and basic terms, community structure, function (Terrestrial and aquatic (fresh water and marine) communities), succession and limnology. First Exam: wed 20/3/2013 Biological interactions in ecological communities including the predator-prey interactions-Lotka-Volterra equations and competition theory. Population ecology: population density, concept of population, biotic potential and natality, mortality, age structure. Population growth forms, populations’ fluctuations, interactions, concept of densitydependent and independent action in population control, human population growth. Dispersal mechanisms, types of population dispersion, population pyramid types. Second exam: wed 17/4/2013 Natural resources ecology: concept and classification, non-renewable and renewable ones, conservation and resources management. Pollution (air, water and soil) types, measurements and testing, control of pollution. References: 1) Molles,M.C. (2008). Ecology: concepts and applications, 4th ed. 2) Chander Kanta.(2004). Ecology. 3) Charles. J.Krebs. (1999). Ecological methodology. 2nd ed. 4) Paul Colinvaux.(1993). Ecology 2. 5) Pomeroy, L. R and J.J. Alberts. (1988). Concepts of ecosystem ecology. 6) Paul Colinvaux. (1986). Ecology. 7) Kumar, H.D. (1995). General ecology. 8) Robert,E. Ricklets. (1992). Ecology.