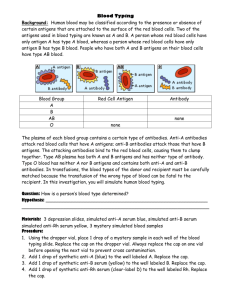
The word blood refers to a highly complex mixture of cells, enzymes
advertisement

Chapter 12 – Part 1 DNA is the abbreviation for ________________________________ and is_____________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ The word blood refers to a highly complex mixture of _______, _______, _______, and _______ substances. Plasma______________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ Suspended in the plasma are solid materials consisting chiefly of several types of cells. _________ _________ _______ also called ___________ _________ _________ _______ also called ___________ _____________________ The solid portion of blood accounts for _________ of its content. Blood clots when a protein in the plasma known as _________ traps and enmeshes the _________ _________ _______. If the clotted material were removed, a pale yellowish liquid known as __________ would be left. The blood components that are directly pertinent to the forensic aspects of blood identification are the _________ _________ _______ and the _________ _________ . Red blood cells transport _______ ________ ________ ______ ______ _____ _____ _____ and remove _______ ________ ________ ______ ______ _____ _____ _________ _______ ______ ______ , where it is exhaled. On the surface of each cell are millions of characteristic chemical structures called __________. Antigens impart specific characteristics to _________ ________ ________. Antigen______________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ Antibodies______________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ p.329 Blood antigens are grouped into systems depending on their relationship to one another. More than ______blood antigen systems have been identified to date; of these, the ____ , ____, ____ and ______ systems are the most important. If an individual is type A, this simply indicates that each rbc has ____ ______ on its surface. All type ____ individuals have B antigens, and rbc of type AB individuals contain both ____ _____ _____ antigens. Type O individuals have _______A nor B antigens on their cells. Therefore, the presence or absence of A and B antigens on the rbc determines _____ ______ _____ _____ _____ _____ ____ _____ _____ ______.. Another important blood antigen has been designated as the Rh factor, or ___ ________. Those people having the D antigen are said to be ___ __________, those without this antigen are ___ __________. In routine blood banking, the presence or absence of the three ______ ______ _______ _____ _____must be determined in testing compatibility of the donor and recipient. The fundamental principal of blood typing is that ______ _______ ______ ______ _____ _____ _____ ______. Each antibody symbol contains the prefix anti- followed by the ______ ______ ______ ______ ______ ______ _____ ______ _______. Anti-A is specific only for ____ _______, anti-B for __ _____, and ______ ____ for D antigen. The serum-containing antibody is referred to as the ___________, meaning a serum that reacts against something (antigens). Antiserum-__________________________________________. Pg. 330 p. 330 An antibody reacts only with its ________ _________ and no other. Thus, if serum containing ____________ is added to red blood cells carrying the B-antigen, the two will ___________, causing the antibody to ___________ ______ ______ _____ _____. Antibodies are normally __________-they have two reactive sites. This means that each antibody can ____________ be __________ to _____________ located on _________ different red blood cells. This creates a vast network of _________-________ _____ usually seen as clumping or _________________. Agglutination-________________________________________________________. p.330 In normal blood, __________ on red blood cells and ______________ coexist without destroying each other because the ____________ present are not _________ toward any of the _____________. However, suppose a foreign serum added to the blood introduces a new __________. This results in a _________ ______-_______ reaction that immediately causes the _______ _______ _____ to _______ ___________ or agglutinate. The serum of _______-____ ______ contains anti-B and no anti-A. Similarly, type B blood contains only ______-___, type____ blood has both anti-A and anti-B, and type AB blood contains ___________ ______-___ nor ______-___. Blood type A B AB O P330 Antigens on RBC Antibodies in Serum Anti-B B Neither A nor B Serology- Pg. 331 ______________________________________________________________________ The most widespread application of serology is ______ ______ _______ _____ _____ ____ ____ ___-____-___ _________. In determining the A_B_O blood type, only two antiserums are needed-______-____ and _____-___ _______. P331 To determine the identity of each of the four blood groups— 1. Type A blood is agglutinated by ________serum; type B blood is agglutinated by ________serum; type AB blood is agglutinated by both ________and ________; and type O blood is ________ agglutinated by either the anti-A or anti-B serum. 2. the identification of natural antibodies present in blood offers another way to determine blood type. Testing the blood for the presence of anti-A and anti-B requires using ____ ________ cells that have known ________. (Commercially available) When A cells are added to a blood specimen, ____________ occurs only in the presence of ________. Similarly, B cells agglutinate only in the presence of ________. All four A_B_O types can be identified in this manner by testing blood with known ________ and ________cells. The population distribution of blood types varies with location and race throughout the world. Pg. 332 O A B AB _____% _____% _____% _____% Immunoassay Techniques – pg. 333 The concept of specific antigen-antibody reaction is one that is finding application in other areas unrelated to blood typing. This approach has been extended to the ___________ of ________ in blood and ___________. Antibodies that are capable of reacting with drugs do ________ _____________ exist; however they can be _____________ in ____________ such as ______________. ______________-__________ __________ __________ (EMIT) has gained widespread popularity among toxicologists because of its ______ and high ___________ for detecting drugs in __________. One of the most frequent uses of the EMIT technique in forensic laboratories has been for screening the __________ of suspected _______________ _____________. The greatest problem associated with marijuana’s detection in urine is _________________. While smoking marijuana will result in the detection of _________ metabolite, it is very difficult to determine _________ the individual actually used the marijuana. In frequent smokers detection can be determined within _______ to ________ days after last use. However some individuals may yield positive results up to ______ days. What is an RIA? Why must analysts be careful when using immunoassay techniques to identify drugs? (pg. 334) Polyclonal Antibodies______________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ Monoclonal Antibodies______________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ Forensic Characterization of Bloodstains – pg. 336 The criminalist must be prepared to answer the following questions when examining dried blood: 1. _____ _____ __________? 2. ________________________________________________________________________ ______________? 3. If the blood is human, how closely can it be _____________ ____ __ _______________ _____________? Define hemoglobin – List five tests used for the determination of blood: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Which of the above is a known carcinogen and its use is generally discontinued? Which of the above four are based on the fact that blood hemoglobin possesses peroxidase-like activity? Name two other substances that can turn Kastle-Meyer test pink besides blood? Which of the above tests is designed as a urine dipstick test for blood? What color does the dipstick turn in the presence of blood? Which of the above tests results in a production of light when mixed with blood? Pg. 337 The _______________ test is extremely sensitive. It is capable of detecting blood stains up to ______________ times. Luminol will also _________ _____________ with any subsequent DNA testing. In order to determine if the stain is human or animal, the standard test used is the _____________________ test. How does the precipitin test work? Historically, forensic scientists used ___________________ to individualize bloodstains. They were particularly interested in enzymes that exist in different forms, or __________________________. The advent of DNA has reduced this approach for characterizing biological stains to one of historical interest only.