Deforming the Earth`s Crust
advertisement

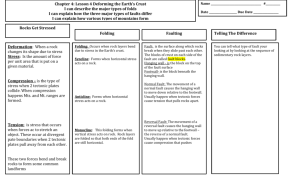
Deforming the Earth’s Crust Faults and Folds Deformation • • • • The process by which the shape of a __________________________________________________________ There are __________ types of stress that occur in rocks: C______________ T______________ Compression • Compression occurs when rock is _______________. • Compression happens when two plates ___________ at a convergent boundary. • Compression occurs and forms large __________ ranges. Compression/ Mountain Building The __________, for example, were raised by the compression that accompanied collision of the Indian plate with the Eurasian plate. Another example is Europe's _______ and _______ mountains which were also formed by horizontal compression, generated in their case by collision with the African plate and the Eurasian plate. Tension • Tension occurs when an object is ___________. • Tension occurs when plates move ________ from each other at plate boundaries. • At the ______ ____________ ridge the seafloor is spreading at a rate of about 3cm per year. The frequency of earthquakes at a mid-ocean ridge will depend on how much tension is happening at that point. The more tension means the more seafloor spreading, resulting in a higher frequency of earthquakes at a particular mid-ocean ridge. Folding Folding is the bending of rock layers due to _________ in the Earth’s crust. Depending on how rock layers deform, different types of ________ occur: ___________ ___________ ___________ Anticline • • An anticline is an _________ _________ fold. An anticline is formed when there is __________stress on rock layers. Syncline • Synclines are ____________ folds. • They are also caused by __________ stress. Monocline Monoclines are rock layers that are folded so that both ________ of the fold are horizontal. Faults • Some rock layers __________ when stress is applied to them. • The surface along which rocks break is called a ___________. • The ________ of crust on each side of the fault are called fault __________. • A fault has a __________wall and a __________ wall. Hanging Wall and Footwall 3 Types of Faults • N__________ Fault • R__________ Fault • S___________Fault Normal Fault Rocks are pulled apart because of ____________ o In a normal Fault, the hanging wall slides ________ the footwall. Reverse Fault In a reverse fault the hanging wall is pushed ___________due to compression. Strike-Slip Fault Opposing forces cause rocks to move _________. __________ occur along these faults. 3 Most Common Types of Mountains • • • • • Mountains exist because tectonic plates are continually moving around and _________ with each other. There are _______ types of mountains, named for how they form: F_____________ Mountains _________ __________ Mountain V______________ Mountain Folded Mountains Folding is a process in which the Earth's plates are pushed ___________ in a roller coaster like series of high points and low points. Folding ________ many layers of rocks without breaking them. The _________ Mountains and Rocky Mountains of the United States, and the Alps of Europe are examples of mountain ranges that were formed by folding. Fault- Block Mountains Mountains sometimes form when many layers of the Earth's crust are moved vertically ________ at fault lines by pressures caused by plates colliding. Fault lines are great cracks in the crust. The mountains that are formed in this way are called fault-block mountains. The Sierra Nevada mountains in California and Nevada, and the Grand Teton range of Wyoming are examples of fault-block mountains. Volcanic Mountains • • • Volcanic mountains are forms when magma erupts from a ________ boundary and hardens. Many volcanic mountains exist ________ the sea. Some volcanic mountains rise above the surface of the ocean to from islands, _________ for example.