Saponification Lab: Soap Making Experiment
advertisement

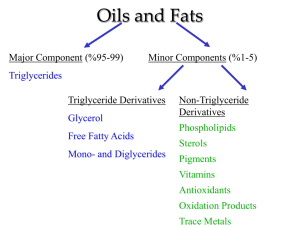
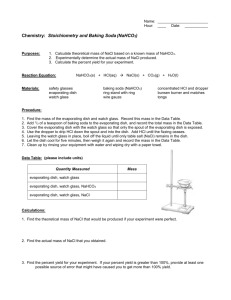
SAPONIFICATION Pre-Lab Discussion Fats are esters formed from glycerol (an alcohol) and a long-chain organic acid (a long-chain fatty acid). The formation of a fat can be represented by the equation: *Diagram* Soaps are metallic salts of fatty acids. Soaps are made by boiling solid fats or liquid fats (oils) with a solution of a strong base. This reaction is called saponification. If the fat from the equation above reacts with a strong base, such as NaOH, a soap and glycerol are formed: *Diagram* In condensed form, this equation can be written: (RCOO)3C3H5 + 3NaOH 3RCOONa + C3H5(OH)3 In this experiment, soap will be made by reacting a liquid fat with sodium hydroxide dissolved in ethanol. Purpose Prepare soap from liquid fat and a strong base. Equipment beaker, 50-mL graduated cylinders, 10-mL and 100-mL evaporating dish ring stand iron ring wire gauze microspatula test tube, 13x100-mm glass stirring rod funnel burner safety glasses Materials oil, cottonseed or olive saturated NaCl solution ethanol 30% NaOH solution distilled water litmus paper filter paper Procedure 1. 2. Measure out 8.0 mL of cottonseed or olive oil and pour it into a clean, dry evaporating dish. Add 8.0 mL of ethanol and 4.0 mL of 30% NaOH solution to the oil. CAUTION: Handle this solution carefully. Set up the ring stand, wire gauze, evaporating dish, and burner as shown in Figure 50-1. Heat the mixture gently with a very low flame. CAUTION: Keep the flame away from the ethanol, which is highly flammable. *Diagram* Figure 50-1 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Continue heating for 10-15 minutes, stirring constantly to prevent spattering. Stop heating when the odor of fat has dissappeared and the oil has dissolved. Allow the mixture to cool. During this time, place 20.0 mL of distilled water in a 50-mL beaker and heat to just below boiling. When the evaporating dish is cool enough to touch, add the hot water to the mixture in the dish. Then add 25.0 mL of saturated NaCl solution and stir the mixture. Filter the mixture, collecting the liquid in the beaker. Discard the liquid and keep the solid on the filter paper. In a test tube, dissolve 2 microspatulas of your soap in 20.0 mL of distilled water. Test the solution with litmus paper and record your observations. Add about 1.0 mL of tap water to the soultion in the test tube. Place your thumb over the mouth of the tube and shake vigorously. Record your observations. Observations Litmus test: Shaking test: Conclusions and Questions 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. What do the processes of saponification and esterfication have in common? How do these processes differ? To what class of compounds do fats belong? Soaps? Describe the contents of the test tube after shaking it (step 8). Did any white precipitate (scum) appear? If so, explain its prescence. The formula for the hydrocarbon radical (R-) in the fat glycerol stearate is C17H35. Write an equation showing the reaction of glycerol stearate with sodium hydroxide to produce the soap sodium stearate. How are soaps treated commercially before they are marketed?