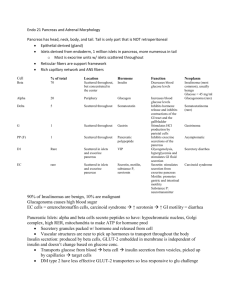
9/11/08 - Logan Class of December 2011
advertisement

1 1/14/09 Nutrition 2 (exam1) Clinical Nutrition Why? Who? How? -Philosophical considerations for nutrition practice The Scourge of Chronic Illnesses Seventy million American suffer from arthritis—or one in every three adults. That’s twice as many arthritis sufferers as there were twenty years ago. More than 20 million Americans have asthma today. It is the sixth most common chronic disease. More than 50 million Americans suffer every year from allergies, a number that has doubled in the past two decades. There has been a 100 percent increase in the prevalence of hay fever in developed countries in each of the last three decades. Allergic dermatitis affects us at triple the rate in 1960. Ten percent of young children are affected by allergic dermatitis. There were 18.2 million people in the United States with diabetes in 2002, almost a 50 percent increase from a decade ago--contributing to about two hundred thousand deaths in the United States each year. Cardiovascular disease is the number one killer of Americans. Almost 64 million Americans have it in some form, and it killed close to a million people in 2001. Eczema is the most common skin condition in children under eleven; an estimated 15 million Americans have inflammatory bowel disease. Almost one in two Americans (150 million) suffer from an inflammatory disease. Source: Inflammation Nation, Floyd Chilton Chronic Diseases: Cause Unknown How many of you think that there is a major health care crisis in the US today? For some reason unknown to the medical industry that there are so many of us decided to get all kinds of chronic illnesses these last twenty years or so. All they have to offer is symptomatic relief that comes with side effects that are worse than the problems in the first place. The Cause of Chronic Illnesses A major driving force of these diseases is our diet—the “toxic-waste spill”--leads to chronic inflammation The food industry is worth $1.4 trillion and we spent 1.6 trillion dollars in 2003 in “health” care Who is at risk? Every single one of us! There are no safe medical interventions or surgical procedures that will save us. The only way out is a fundamental change in the way we produce, deliver and consume our food. the guy with the bow tie 2 Diabetes Out of Control 1/3 US , ½ Hispanic children born since 2000 is expected to have diabetes It is fastest growing disease in the US, China, Japan and India Expected to grow from 20 million today to 50 million in 2025 in the US 50% of children Dx with diabetes today is type 2, age as young as 7 It causes more suffering and disability than heart disease and cancer and cost more to treat It is considered a health time bomb that threaten to destroy our economy 1/16/09 Nutritional Deficiency is Common It is estimated that our hunter-gatherer ancestors consumed about 7,778-11,083 mg/day of potassium. We are consumming 75% less today On average, we consume about 2500 mg of K per day RDA for K is 3500 mg/day BMJ 2001;323:497-501 Potassium Deficiency Increased risk of high blood pressure and stroke Increased risk of diabetes, fatigue, muscle weakness and heart conditions Increased PGE-2 and inflammation In severe cases, rhabdomyolysis the guy with the bow tie 3 Magnesium Deficiency Minerals work together Mg depletion affects K homeostasis—hypokalemia Kidney fails to conserve K during Mg deficiency Both minerals are severely lacking in our overly processed diet Fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds and healthy animal protein and dairy Vitamin D Deficiency -rickets (children) -osteomalacia (adults) -elevated serum PTH -decr serum phosphorus -elevated serum alkaline phosphatase -osteoporosis -epidemiological evidence of increased risk of colon, breast, and prostate cancer -increase rate of autoimmune, CV, endocrine problems Micronutrient Deficiency Linked to DNA damage, cancer risk Depressed immune system Impaired cognitive and mental functions Free-radical damages Developmental defacts Semin Arthritis Rheum 1997;27:180-85 Mutat Res 2001 Apr 18;475(1-2):7-20 Int J Vitam Res 1995;65(2):117-21 Nutrition 2001;17(9):709-12 Toxical Enviorn Health 2001;63(8):583-98 Pottenger’s Cat Study Diet can alter body physiology Improper diet can lead to physical degeneration that negative traits can pass onto the next generations These effects are cumulative upon the next generation unless the natural diet is restored Altering both physical and emotional wellbeing Culminate in infertility--extinction We have drifted into this deplorable position of national Malnutrition quite inadvertently. …It is the result of scientific research with the objective of Finding the best way to create foods that are non-perishable, that can be made by mass production methods in central factories, …and distributed so cheaply that they can sweep all local competition from the market… Then, after there develops a suspicion that these “foods” are inadequate to support life, modern advertising steps in to propagandize the people into believing that there is nothing wrong with them. That they are products of scientific research…intended to afford a food that is the last word in nutritive value …and the confused public is totally unable to arrive at any conclusion of fact, …and continues to blindly buy the rubbish that is killing them Years ahead of their time. --Royal Lee, DDS, June 1943 A Wonder bread culture With the advent of industrialized roller milling and mass refining of grains in about 1880, worldwide epidemics of pellagra and beriberi began because of loss of B vitamins during processing of grain to remove the bran and the germ for longer shelf life. -Am J Clin nutr 2003;78(suppl):508S-13S. -The grain passes through more than forty processes before it emerges as flour and bran. Sifters consist of a dozen large sieves, one below the other-just like the floors of a tall building. The top sieve has the coarsest mesh, the next not quite so coarse, and so on. These sieves are all made to swing briskly by machinery - in fact they swing continuously with a motion very like that of the ordinary sieve at home. The broken wheat comes first onto the top sieve, and then through the others in turn, each sieve helping to separate the material. Purifiers not only separate the broken parts of the wheat by sieving, that is, according to size, but it also separate those parts which are of the same size but of different weight. This is done by using currents of air. The skins are much lighter in weight than the inner white floury parts, and a current of air is drawn upwards through the mixture on the sieve, lifting up and 'floating' the skins, but allowing the heavier white parts to remain on the sieve and be separated by the sieving motion. www.botham.co.uk/bread/ the guy with the bow tie 4 A “WONDER BREAD” CULTURE OF INSTITUTIONALIZED SUPPLEMENTATION In 1937 scientists showed that nicotinic acid was the specific micronutrient deficiency for pellagra and thiamine for beriberi. These discoveries were so fundamental and startling that some believed that little remained to be investigated in the field of nutrition. One obvious solution, protecting health and satisfying the needs of industry, was to re-supply the deficient nutrients. There seemed to be no need to modify food production, because the only problem was a shortage of a few important vitamins. The net result of all these forces was over-reliance on several nutrients and food enrichment, what might be called a "Wonder Bread" culture of institutionalized supplementation. It is now clear that today’s chronic diseases, such as atherosclerosis, ischemic heart disease, and cancers, are complex diseases with multiple etiologies and not simple deficiency diseases. For example, findings of the strongly reduced risk of ischemic heart disease, diabetes, and some cancers among habitual consumers of whole-grain foods support the idea that food synergies play an important role in chronic disease prevention. Nevertheless, the over-processing of grains and other foods has worsened since the early 1900s....” -Am J Clin nutr 2003;78(suppl):508S-13S. Pasteurization of Milk The Lancet, page 1142, May 8, 1937 states that resistance to tuberculosis increased in children fed raw milk instead of pasteurized to the point that, in five years, only one case of pulmonary TB had developed, whereas in the previous five years, when children had been given pasteurized milk, 14 cases of pulmonary TB had developed. The Lancet, page 1142, May 8, 1937 says that in children the teeth are less likely to decay on diet supplemented with raw milk than with pasteurized milk. -Vitamin News, by Dr. Royal Lee, DDS, ifnh.org “…the response in height to raw milk was significantly greater than that to pasteurized milk. Their interpretation of the data led to the assertion that the pasteurized milk was only 66 percent as effective as the raw milk in the case of boys and 91.1 percent as effective in the case of girls in inducing increases in weight, and 50 percent as effective in boys and 70 percent in girls in bringing about height increases.” Milk protein is destroyed by heat. Therefore milk calcium cannot be assimilated. -Krauss, W.E, Erb, J.H. and Washburn, R.G., Studies on the Nutritive Value of Milk. Ohio Agricultural Experiment Station Bulletin 518, page 7, January 1933 -Soil to Supplements, op.cit. Standard American Diet 80% processed refined carbohydrate foods Commercial factory farm meats Chemical farming Genetically Modified Organism Fast-super-sized foods 30% calories come from sugar Man-made fat instead of traditional fats the guy with the bow tie 5 GM Soy Kills Rats 55.6% Mortality in Rats Whose Mothers Were Fed GM Soy -http://www.seedsofdeception.com/utility/showArticle/?objectID=293 • http://www.csa.com/discoveryguides/gmfood/overview.php Why nutrition? Chiropractors are in a responsible position to make a fundamental difference in people’s lives Clinical experience, epidemiological data and research support the need to change the ways we eat to halt the growth of chronic illness and suffering More teachers are needed To improve treatment outcome Mission Control The ongoing discovery of how we express our gifts to add life enriching value to the world. Nutrition and dietary counseling is an added value in our practice and patient’s treatment outcome Disease is a dynamic event in the life of an individual. Determined by disharmonies, imbalances, and pernicious influences. The goal of diagnosis is not to identify the disease entity, which has no independent reality, but to characterize the disharmonies of the particular case, so that they can be corrected. --Leo Galland, MD Cookbook Vs. Patient-Centered Symptoms relief Removing the causes Functional Health Care Functional Healthcare Health oriented Patient oriented Biochemical individuality Cost effective Holistic Look for true cause High touch high tech True prevention Conventional care Disease oriented Doctor oriented Same Dx=same Tx Cost prohibitive Specialization Dx from a set of symptoms High tech Early detection=prevention The Nutrition Care Process Assess nutrition status Analyze assessment data to determine nutrient requirements Develop a plan of action for meeting nutrition needs, include education Implement the care plan Evaluate the effectiveness of care plan through ongoing assessment and make changes as needed. Total Load Food allergies Mold allergies Structural lesion Intestinal pathogens Leaky gut Compromised detox Environmental toxins Hormone imbalance Polypharmacy Nutritional deficiencies Repressed emotion Functional disturbance and physical symptoms the guy with the bow tie 6 The Health Detective Get the whole picture Elucidate the underlying causes by first line and second line testing Respect biochemical individuality Focus on restoring normal functions Cause no harm to the patient Critical Questions What is the patient’s full story? Where does the symptoms come from? What does the symptoms mean? What keep the condition going? What is the major point of leverage? The Functional Health Care Workup Chief complaint History of present illness OPQRST Past medical history Review of organ systems Family history Dietary history Medication and dietary supplement history Social, lifestyle and exercise habits Physical exam Lab findings Radiology Assessment and diagnosis Fundamental clinical imbalances that underlie the diagnosis Who should I teach? Everyone is affected by the modern deficient diet and polluted environment. Patients with chronic pain Trauma, acute injuries Young athletes Children with learning problems, allergies Women in all stages of life Man in all stages of life Students under loads of stress We all need help in eating better How to practice nutrition? Technique: AK (CRA, MRT, Lebowitz’s Protocol), CMRT, BEST (pH balance), evidence based (Janet Lang, Datis Kharrazian) Philosophical: Weston A. Price Whole Food, Natural Hygiene, Macrobiotic, Vegan, lacto oval vegetarianism Macronutrients: Atkin’s, South Beach, Protein Power, USDA Food Guide, Zone Biochemical: using lab tests, symptoms surveys, and physical exam to guide and replace deficient nutrients, pH/acid-base balancing Supplements: mega-dose isolated, whole-food extracts, herbs, homeopathic, flower remedies What do I do? Start somewhere Using some supplements Experiment with different natural, organic foods Try a diet Detox program Nutrition classes and seminars Learn about special lab tests Saliva test, hair analysis, functional tests the guy with the bow tie 7 Dangerous Rx, FDA Inaction Rosiglitazone is taken by about seven million people worldwide and brings in sales of more than $3 billion for GlaxoSmithKline. Analysts have warned that these new safety concerns could cut sales by 50%, and shares in GlaxoSmithKline have plummeted Was the NEJM right to publish? FDA: No action recommended at this time www.medscape.com www.nejm.com Nutrition Assessment History Physical exam Symptoms surveys: paper or computer pH: saliva, urine Lab tests Blood, Urine, stool, Hair Analysis, Saliva AK Others Nutrition Companies Standard Process Thorne Research Biotic Research Design For Health Apex Energetics Orthomolecular Nordic Natural fish oils Premier Research Labs Healthforce Nutritionals Pure Encapsulations Tropical Tradition Coconut oil Many others, call and get info, catalogs, sponsored seminars, newsletter, freebies Discount for Chiropractic students Websites Great Smokies: www.gsdl.com www.doctorsdata.com www.diagnostechs.com www.westonaprice.org www.newstarget.com www.nytimes.com, health section www.mercola.com www.medscape.com/drugchecker www.curezone.com the guy with the bow tie 8 Diet For Optimal Health http://journeytoforever.org/farm_library/price/pricetoc.html 1/20/09 Nutrition and health among people on traditional diets in the 1930s 14 human groups From isolated Irish and Swiss, to Eskimos and Africans Almost every member enjoyed superb health Free of chronic diseases Free of dental decay Free of mental illness Strong, sturdy and attractive Produced healthy children with ease ”Civilized” humans in comparison groups Members of the same racial/ethnic groups who had become ”civilized” who ate the food products of commerce: Refined grains Canned foods Pasturized milk Sugar Infectious disease Degenerative illness Infertility Tooth decay Children with Crowded an crooked teeth Narrow faces Deformities of bone structure Susceptibility to many medical problems Malnutrition affects all human groups in similar ways Historical experience of indigenous/traditional peoples No cancer, cardiovascular diseases, type 2 diabetes or dental caries Independent observations of anthropologists, physicians, missionaries, explorers, etc. E.g. !Kung San people in the Kalahari desert Chronic diseases appear as soon as such humans change environment and lifestyle, particularly diet Characteristics of Traditional Diets 1. The diet of healthy, nonindustrialized peoples contain no refined or denatured foods such as refined sugar or corn syrup; white flour; canned foods; pasteurized, homogenized, skim or low fat milk; refined or hydrogenated vegetable oils, protein powders; artificial vitamins; or toxic additives and colorings Modern American Diet The fattest nation on earth 64.5% of Americans are overweight or obese. Source: JAMA, 2002;28:1723-1727 Obesity is now the number 1 preventable cause of death in the US. Source: JAMA, 1996;276:1907-1950 “Low fat” foods often high in sugar and low in nutrients Convenience foods usually high in refined carbs, highly processed, and super-size portions Trans fats are found in most processed foods and may disrupt fat and cholesterol metabolism. 80% supermarket offerings are carbohydrate foods, Increased carbs lead to: Increased blood glucose and insulin output Decreased glucose and increased food cravings, especially more carbs and sweets Excessive calories lead to fat storage and obesity Fortunately there seems to be a reverse of this trend due to the success of Atkin’s and other high protein diets. 2. All traditional cultures consume some sort of animal food, such as fish and other seafood; land and water fowl; land and sea mammals; eggs; milk and milk products; reptiles; and insects. The whole animals is consumed—muscle, organs, bone and fat. the guy with the bow tie 9 The Importance of Meat Two important parts of human evolution The progressive incorporation of more meat into the early human diet Going from scavenging to hunting Meat provides easy access to the full complement of nutrients our body needs More closely adapted to a meat based than a plant based diet 3. The diets of healthy, indigenous peoples contained at least four times the calcium and other minerals and ten times the fatsoluble vitamins found in animal fats (vitamin A, vitamin D and activator X) as the average American diet. Modern American Diet Low-fat diet consists of processed low-fat food. Avoid sunshine lead to lack of vitamin D synthesis Avoid animal fat—the only source of vitamin A and vitamin D Wide-spread deficiency of fat-soluble nutrients Protein deficiency Mineral deficiency 4. In all traditional cultures, some animal foods are eaten raw: Meats and organ tissues Seafood Dairy products Eggs 5. Primitive and traditional diets have a high food enzyme content from raw dairy products, raw meat and fish, raw honey; tropical fruits; cold-pressed oils; wine and un-pasteurized beer; and naturally preserved, lacto-fermented vegetables, fruits, beverages, diary products, meats, and condiments. 6. Seeds, grains and nuts are soaked, sprouted, fermented or naturally leavened to neutralize naturally occurring antinutrients such as enzyme inhibitors, tannins and phytic-acid. Always soak grains overnight with a tablespoon of acid, preferably in a warm environment before cooking. Food enzymes content greatly increased by fermenting, soaking and sprouting What happens when you can’t digest your food? You immune system has to take that job of your digestive system The only thing the immune system does is to promote inflammation The results are symptoms of gut distress Two of the top OCT drugs are laxatives and acid blockers -eating untreated corn can block our body from absorbing niacin -eating food that cannot be properly digested will create food allergies 7. Total fat content of traditional diets varies from 30% to 80% of calories but only about 4% of calories come from polyunsaturated oils naturally occurring in grains, legumes, nuts, fish, animal fats and vegetables. The balance of fat calories is in the form of saturated and monounsaturated fatty acids. -10% of our calories come from polyunsaturated fat, leading to the formation of more cytotoxic free radicals 8. Traditional diets contain nearly equal amounts of omega-6 and omega-3 essential fatty acids—1:1 ratio Why Do We Need Essential Fatty Acids? EFA are not made by the body and must be included in our food. All processed oils are devoid of intact EFA. EFA deficiency is severe in American diets. EFA is essential for health and the maintenance of very cells, organ, tissues in our bodies. The brain and nervous system are especially in need of EFA for normal functions. the guy with the bow tie 10 Characteristics of Traditional Diets These nutrient-rich fats have nourished healthy peoples for thousands of years: Butter; tallow and suet; lard, chicken, goose and duck fat; coconut, palm and palm kernel oils; cold pressed olive, sesame, flax and peanut oils; fish and cod liver oils. Newfangled Fats All hydrogenated oils, industrially processed oils such as soy, corn, safflower, cottonseed and canola, fats and oils heated to a very high temperature in processing and frying are associated with cancer, heart disease, immune system dysfunction, sterility, learning disabilities, growth problems and osteoporosis. 1/21/09 Characteristics of Traditional Diets (cont) 9. All traditional diets contain some unrefined salt. 10. All traditional cultures make use of animal bones usually in the form of gelatin-rich meat and bone broths. The Salt of Life The theory that salt causes high blood pressure and other heart problems is not supported by sound scientific studies. Cells need salt to become fully hydrated. Without salt, cells get thirsty, sluggish and unable to produce enough energy. Avoid too much salt if you suffer from kidney disease or congestive heart failure. For more information, read You Body’s Many Cries for Water, by F. Batmanghelidji Sodium: As all body fluids contain sodium, it can be said that sodium is essential to life. It is needed for many biochemical processes including water balance regulation, fluid distribution on either side of the cell walls, muscle contraction and expansion, nerve stimulation and acid-alkaline balance. Sodium is very important to the proper function of the adrenal glands. However, excessive sodium may result in high blood pressure, potassium deficiency, and liver, kidney and heart disease; symptoms of deficiency include confusion, low blood sugar, weakness, lethargy and heart palpitations. Meat broths and zucchini are excellent sources. Potassium: Potassium and sodium work together--inner cell fluids are high in potassium while fluids outside the cell are high in sodium. Thus, potassium is important for many chemical reactions within the cells. Potassium is helpful in treating high blood pressure. It is found in a wide variety of nuts, grains and vegetables. Excessive use of salt along with inadequate intake of fruits and vegetables can result in a potassium deficiency. 11. Traditional cultures make provisions for the health of future generations by providing special nutrient-rich foods for parents-to-be, pregnant women and growing children; by proper spacing of children; and by teaching the principles of right diet to the young. the guy with the bow tie 11 Paleolithic diet: Variations Variations due to differences in geography, season and glaciations Paleolithic diet Meat, fish, fowl, vegetables, berries, fruits, nuts, roots, insects and seafood Approximately 20% more energy More nutritious food More protein-rich food Less carbohydrates (from <5 E% to 40 E%) (E=energy) High intake of fiber/phytochemicals Paleolithic diet: Fats Fats of high quality Between 10% and 80% of Energy More long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids C20-C22 Much lower n-6:n-3 ratio 1-2:1 Paleolithic 10:1 USA 6-7:1 Norway? 1:1 optimal? What Paleolithic people didn’t eat Cow’s milk, cereal grains (after 10 000 BP) Table salt (NaCl) White sugar (after 1800) Potatoes (after 1750) Highly processed foods (mostly after 1800) Pesticide residues (after 1930), radioactive foods (after 1945) Artificial/synthetic additives (mostly after 1950) Genetically modified food (since the 1990s) ”High-Fiber Diet May Not Guard Against Cancer: Study shows no effect on colorectal disease” -”our findings do not support the notion that fiber is protective against colon cancer.” "Until all the factors lost in milling are known and it is known that each of the others is adequately supplied by other foods, the logical solution of the problem presented is the restoration of the grain embryo itself to the diet." -MARKS, H. E., Vitamin Deficiencies and Re-stored Foods, Letters to the Editor of the Journal of the American Medical Association, 114, 6:512, February 10, 1940 The Traditional Diet Foods that are natural, unrefined, least processed, without additives, chemicals, hormones All natural meats, fats, vegetables, fruits, grains, legumes, nuts, seed, herbs, and fermented foods are part of a optimal diet for health. the guy with the bow tie 12 1/23/09 Nutrition Controversies “If people let the government decide what food they eat and medicine they take, their bodies will soon be in as sorry a state as souls under tyranny.” -Thomas Jefferson “In medicine, we are often confronted with poorly observed and indefinite facts which form actual obstacles to science, in that men always bring them up, saying: it is a fact, it must be accepted.” -Claude Bernard “A colleague once defined an academic discipline as a group of scholars who had agreed not to ask certain embarrassing questions about key assumptions.” -Mark Nathan Cohen, Health and the rise of civilization, 1989 “All men by nature desire to know. Perhaps, but men of science by culture desire to know that what they know is really so.” -Robert Merton, Behavior patterns of Scientists, 1968 “Avoid saturated fats.” Saturated fats are important: • Maintaining cell membrane integrity • Promote normal metabolism of essential fatty acids • Enhance the immune system • Protect the liver, kidneys and lung functions • Promote strong bones • Preferred fuel for the heart and skeletal muscles • Body makes saturated fats from excess carbohydrate and protein http://www.westonaprice.org/knowyourfats/oiling.html http://www.hsph.harvard.edu/nutritionsource/fats.html “Limit cholesterol.” Cholesterol contributes to: • Strength of the intestinal wall • Healthy brain and nervous system development • High cholesterol foods are also nutrient-dense foods • Used as antioxidants in the body, only oxidized cholesterol contribute to CVD – Powdered milk, powdered eggs contained oxidized cholesterol www.westonaprice.org/moderndiseases/benefits_cholest.html “Saturated fat and cholesterol caused CVD.” • • During the period of marked increase in heart disease from 1920-60, American consumption of animal fats declined with the concomitant dramatic increased consumption of refined vegetable fats and hydrogenated oils. (1) The fatty acids found in plaque arteries are mostly unsaturated (74%). (2) • 1. USDA-HNIS, 2. Lancet 1994, 344:1195 • www.ravnskov.nu/cholesterol.htm Good Things in Butter Vitamin A Vitamin D Vitamin E Vitamin K Copper Zinc Chromium Selenium Iodine Shorter Chain Fatty Acids Essential Fatty Acids Lecithin Wulzen Factor (anti-stiffness) Price Factor or Activator X Cholesterol Glycosphingolipids Conjugated Linoleic Acid (CLA) -since the mid 1920’s butter consumption has dropped dramatically while CVD and cancer have increased dramatically -the conclusion is that butter is not the cause of CVD and cancer “So switch to butter and profit from the many nutrients in this natural, healthy fat.” Butter contains fat-soluble vitamins. We have discussed the important benefits of vitamins A and D (which will only be in the butter if the cows are on green pasture). But vitamins E and K are also important. Vitamin E protects our cells against free radicals and is essential for normal reproduction; vitamin K is needed for healthy blood and bones. Butter is a good source of many trace minerals, including copper, zinc, chromium, selenium and iodine. the guy with the bow tie 13 The combination of vitamin A and iodine makes butter an excellent food for the thyroid gland. In mountainous regions where the soil is deficient in iodine, butter concentrates what little is available 9or is provided in salt licks) and helps prevent thyroid problems. Once, after listening to this lecture, a young man told me that his mother grew up in Romania. She was the only one in her village who developed a goiter. She hated butter, never touched it. But everyone else ate plenty of butter. Butter contains important shorter chain fatty acids and a nice balance of essential fatty acids. It contains lecithin, which helps the body use cholesterol properly, and the Wulzen factor, which helps prevent arthritis. If the cows are on rapidly growing green grass, butter will contain the X Factor. It contains cholesterol, which is a nutrient, and glycosphingolipids, which aid digestion. Finally, if the cows are on green grass, butter will contain CLA, a strong, anti-cancer substance. All of these factors are rather stable and survive pasteurization except the Wulzen factor, which is destroyed by pasteurization. The best butter, of course, is raw butter from cows on green pasture, but if you only have access to pasteurized butter, be sure to get butter from cows that graze on pasture.” (Source: www.westonaprice.org) While butter consumption in the US has plummeted, cancer and heart disease rates have risen dramatically. We do not know all the reasons for these epidemics, but one thing for sure, they are not caused by butter consumption because the trends are going in opposite directions. “Serum cholesterol should be less than 180 mg/dl.” • • The all-cause death rate is higher in individuals with serum cholesterol values lower than 180 mg/dl. This study merit the caution of putting patients on cholesterol blocking drugs • Circulation 1992, 86:3 • http://www.nytimes.com/2008/01/17/business/17drug.html “Polyunsaturated oils are good for you.” • Increased use is associated with increase cancer, CVD, autoimmune diseases, learning disability, GI problems and premature aging. • Consume in large amount, vegetable oils and even, olive oil can lead to imbalance at the cellular level. http://www.bmj.com/cgi/content/full/311/7015/1239 http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/butter-vs-margarine/AN00835 Int J Toxicol. 2001;20 Suppl 2:21-9. Links Final report on the safety assessment of Hydrogenated Cottonseed Oil, Cottonseed (Gossypium) Oil, Cottonseed Acid, Cottonseed Glyceride, and Hydrogenated Cottonseed Glyceride. [No authors listed] Hydrogenated Cottonseed Oil, Cottonseed (Gossypium) Oil, Cottonseed Acid, Cottonseed Glyceride, and Hydrogenated Cottonseed Glyceride are cosmetic ingredients derived from Cottonseed Oil and used as skin-conditioning agents and surfactants. Nonoils known to be toxic that may be found in cottonseed oils include gossypol, aflatoxin, and cyclopropenoid fatty acids (CPFA). Toxic heavy metal and/or polychlorinated biphenyl (PCB) or other pesticide contamination is also possible. Cottonseed Oil was nontoxic in acute oral toxicity studies in rats. In a short-term study, rabbits that had been fed 2% Cottonseed Oil for 7 weeks had significantly lower blood chemistry parameters (compared to wheat bran controls) and significantly more stored hepatic vitamin A (compared to rabbits fed other fats). Cottonseed Oil controls used as vehicles in two parenteral studies produced negative results. Hydrogenated Cottonseed Oil tested in formulation did not produce dermal or ocular irritation in rabbits. An oral-dose reproductive study tested up to 30% Cottonseed Oil (with 1% CPFAs) and reported no adverse effects on sexual maturity and reproductive performance of the F0 generation; changes were noted in the F1 generation but reproductive capacity was not altered. Parenteral-dose reproductive studies reported no adverse effects. Cottonseed Oil was not mutagenic. Cottonseed Oil did not induce aberrant crypt foci when given orally to mice, but in other studies, it increased the incidence of spontaneous mammary tumors in rats and mice. Mice fed 20% Hydrogenated Cottonseed Oil during induction and promotion of photocarcinogenesis had significantly lower tumor incidence compared to mice fed 20% sunflower oil. Hydrogenated Cottonseed Oil in formulation (up to approximately 21%) was neither an irritant nor sensitizer in clinical studies. Limited clinical data indicated that Cottonseed Oil does not contain allergic protein. Based on the available data, it was concluded that these ingredients may be used safely in cosmetic formulations if established limits on gossypol, heavy metals, and pesticide concentrations are not exceeded. Scand J Work Environ Health. 1999 Aug;25(4):309-16. Links Risk of developing lung cancer in relation to exposure to fumes from Chinese-style cooking. Zhong L, Goldberg MS, Parent ME, Hanley JA. Joint Department of Epidemiology, McGill University, Montreal, Quebec, Canada. In an evaluation of the association between exposure to indoor air pollution from Chinese-style cooking and the risk of lung cancer, epidemiologic and experimental studies were reviewed. The 9 case-referent studies that were identified showed consistent positive associations between the risk of lung cancer and a variety of indices of exposure to indoor air pollution arising from Chinese-style cooking. Three experimental studies showed that volatile emissions from oils heated in woks are mutagenic in several in vitro short-term test systems. Several toxic agents, including some accepted or suspected carcinogens, have been detected in the emissions of the heated cooking oils. While experimental data support the epidemiologic data, it may be premature to conclude that the association is causal. However, simple precautions can be taken to reduce the risk in the event that exposure to indoor air pollution arising from Chinese-style cooking is indeed a cause of lung cancer. the guy with the bow tie 14 This graph illustrates the changes in the types of fats we are consuming over the course of the last century. Butter consumption has gone down from 18 grams per person per day to 5; hardly anyone uses lard anymore. Shortening consumption had increased almost threefold. And the shortening in 1909 was made from coconut oil and lard, it was a natural product. Today the shortening is made from partially hydrogenated vegetable oil. Margarine consumption had increased over five-fold. And the consumption of liquid vegetable oils had increased over 15-fold. Most people are not aware of these changes, changes which are contributing to widespread disease and infertility. The situation is similar to that in Roman times, with lead from lead pipes contaminated the drinking water and contributed to a decline in fertility in the Roman Empire. U.S. Dietary Fat Animal and Vegetable Sources 35 32 30 28 Grams/Capita/Day 25 20 18 15 15 11 10 10 5 5 3 2 2 0 Butter Lard Shortening 1909 Margarine Oils 1985 Source: HNIS-USDA Margarine Manufacture Soy beans, corn, cottonseed or canola seeds Oils extracted by high temperature & pressure Remaining fraction of oils removed with hexane and other solvents Remaining fraction of oils removed with hexane and other solvents Oils mixed with a nickel catalyst Oils with catalyst subjected to hydrogen gas in a high-pressure, high-temperature reactor. Soap-like emulsifiers mixed in Oil steam cleaned again to remove horrible odor Gray color removed by bleaching Artificial flavors, synthetic vitamins and natural color added Mixture is packaged in blocks or tubs Advertising promotes margarine as a health food Good Fats Butter, beef tallow, lamb tallow, lard Chicken, goose and duck fat Cold pressed olive oil, sesame oil and flax oil Tropical Oils—Coconut Oil and Palm Oil Marine Oils, such as cod liver oil Bad Fats All partially hydrogenated fats including margarine and shortening used in processed foods Industrially processed vegetable oils, especially soy, safflower, corn, cottonseed, and canola All fats, especially polyunsaturated oils, heated to very high temperatures To summarize, eat the traditional fats your ancestors ate and avoid modern processed vegetable oils. “Animal fats cause cancer and CVD.” • • • Animal fats provide numerous nutritive factors that protect against cancer and CVD. Natural vitamin A and D can only be found in animal fats Consumption of large amount of vegetable oils is associated with increase incidence of cancer and heart disease/ • Federation Proceedings July 1978, 37:2215 “Avoid red meat.” • Organically grown, free-range, grass-fed red meat is a rich source of: – Vitamin B12, B6, zinc, phosphorus, carnitine, CoQ10 and essential fatty acids -These nutrients protect the heart and nervous system. -commercially grown red meats: animals are extremely diseased the guy with the bow tie 15 “Cut back on eggs.” • • • Eggs provide high quality protein and nutrients: – Iron, vitamin A, D, essential fatty acid Americans had less CVD with higher egg consumption in the past Egg substitute consumption lead to rapid death in experimental animals. www.westonaprice.org/knowyourfats/oiling.html “Restrict salt.” • • Salt is important to digestion and absorption of nutrients Necessary for the development and function of the nervous system, maintaining blood pressure and proper function of the kidneys www.westonaprice.org/moderndiseases/prehypertension.html -potassium and magnesium are the counterbalancing nutrients to sodium This is an excerpt from an article from Weston Price Foundation website: “COMMERCIAL SALT The salt that you find in table salt and most processed foods is sodium chloride. Salt in this form has been processed at high temperatures, which changes the molecular structure and removes vital minerals from the salt. Table salt also contains additives, anticaking agents, and even sugar. Excess salt consumption is associated with high blood pressure, fluid retention, heart and kidney disease. Trash It: Dump out your salt shaker and toss out all other packaged or processed foods with a high sodium content. Stash it: We have been told for years to avoid salt, but following this advice can lead to even more problems. We are all salty on the inside--our blood, sweat, tears, and even our urine--it's all salty. It's important to replenish the salt in our body, using the right salt is what makes all the difference in the world. The best way to put salt back into your body is to use Celtic sea salt. This high quality salt contains over 80 balanced minerals from the sea. Celtic sea salt is essential for maintaining proper fluid balance and utilization in the body. It also normalizes blood pressure, enhances digestion, and nourishes the adrenal glands. Celtic sea salt is available at many natural food stores or can be ordered through The Grain and Salt Society, call 1-800-TOPSALT.” Source: http://www.westonaprice.org/transition/kitchen.html “Eat a low fat diet.” • Lean meat and low-fat milk lack fat-soluble vitamins and essential fatty acids, they are needed for proper assimilation of protein and minerals in the meat and milk. • Low fat diet can lead to vitamin A and D deficiencies. http://www.westonaprice.org/brochures/wapfbrochure.html “We benefit from a low-fat diet.” • • Low-fat diet for children is linked to growth retardation, failure to thrive and learning disability. • Chemistry News 10/3/1994 Low-fat diet is linked to increase risk for depression, mental problems, fatigue, violence and suicide in adults. • Lancet, 3/21/92 vol 339 “Low-fat diet prevent breast cancer.” • The is no difference in breast cancer rate found in women consumed either low-fat (<20%), or high-fat diet. • New England Journal of Medicine 2/8/96 “Limit fat consumption to 30% of calories.” • • • • Too low for most people Too much polyunsaturates lead to increase free radical damages Low blood sugar and fatigue may result. Traditional diets contribute between 30% to 80% of calories from healthy fats, mostly animal origin. “Eat 6-11 servings of grains per day.” • • Majority of grains products are from refined white flour. – Devoid of nutrients – Synthetic vitamins added as “enrichment”, can actually cause vitamin deficiency. Whole grain products, if not prepared properly, can lead to mineral deficiencies and intestinal distress the guy with the bow tie 16 Low Carb Diet More Reducing • • • • Objective To compare 4 weight-loss diets representing a spectrum of low to high carbohydrate intake for effects on weight loss and related metabolic variables. Intervention Participants were randomly assigned to follow the Atkins (n = 77), Zone (n = 79), LEARN (n = 79), or Ornish (n = 76) diets and received weekly instruction for 2 months, then an additional 10-month follow-up. Result and conclusion: Weight loss was greater for women in the Atkins diet group compared with the other diet groups at 12 months At 12 mo., secondary outcomes for the Atkins group were comparable with or more favorable than the other diet groups. • JAMA. March 7, 2007;297:969-977. Good Things in Whole Grains B Vitamins Vitamin E Essential Fatty Acids Bad Things in Whole Grains Macro and Trace Minerals Protein Fiber -sprouting grains diminishes the anti-nutrients Phytic Acid (if not neutralized) Enzyme Inhibitors (if not deactivated) Fiber (irritating if not properly prepared) Rancid Essentials Fatty Acids (if grains are subjected to oxygen & high heat) Altered Proteins (if grains are subjected to high heat & pressure) Proper Preparation of Seed Foods Imitates natural factors that neutralize the grains and seed’s “preservatives” and allow it to sprout: Moisture, Warmth, Slight Acidity, Time 1. Soak rolled oats in warm water and 1 tablespoon of something acidic (whey, yoghurt, vinegar or lemon juice) overnight. 2. Next morning, bring water and salt to a boil. 3. Add soaked oatmeal, bring to a boil and cook, stirring, for one minute. 4. Cover and let sit several minutes. http://www.gaia-movement.org/files/Booklet%204e%20%20Malted%20Grain,%20Fermented%20Food.pdf Serve oatmeal with plenty of butter or cream and a natural sweetener. Sprinkle coconut and/or crispy nuts on top if desired. -carbs should be eaten with fats to help slow down digestion, otherwise too much sugar will enter the system at one time “Eat 5 servings of fruits and vegetables per day minimum.” • Most commercially grown fruits and vegetables receive about 10 applications of pesticides, from seeds to storage.* • Choose organic, locally grown produce *http://www.eartheasy.com/eat_pesticides_produce.htm *http://www.foodnews.org/walletguide.php “Eat more soy foods.” • • • http://www.westonaprice.org/soy/index.html Modern soy foods are not a safe to eat for human at any age. It blocks mineral absorption, inhibits protein digestion, suppresses thyroid function. It contains potent carcinogens, hormone agonist. – May lead to feminization of boys and infertility “Drink Only Pasteurized Milk” http://realmilk.com/ • Drinking ‘raw’ milk could reduce children’s risk of suffering allergy-related conditions such as eczema and hayfever, new research suggests. Untreated milk cuts children's allergies • • • There has been a huge increase in the number of children suffering allergies in the past 30 years. One in three is now affected by eczema, hayfever or asthma — double the level 20 years ago. British academics investigating why farmers’ families suffer fewer allergies than others found that even occasional consumption of raw — unpasteurised — milk had a powerful effect. Just a couple of glasses a week reduced a child’s chances of developing eczema by almost 40 per cent and hayfever by 10 per cent. http://www.dailymail.co.uk/pages/live/articles/health/healthmain.html?in_article_id=399520&in_page_id=1774 2/3/09 the guy with the bow tie 17 Raw Milk Studies • • • • • • • • • Children fed raw milk have more resistance to TB than children fed pasteurized milk. (Lancet, p 1142, 5/8/37) Pathological organisms do not grow in raw milk but proliferate in pasteurized milk. (The Drug and Cosmetic Industry, 43:1:109, July 1938) Raw milk prevents scurvy and protects against flu, diphtheria and pneumonia. (Am J Dis Child, Nov 1917) Raw milk prevents tooth decay. (Lancet, p 1142, 5/8/37) Raw milk promotes growth and calcium absorption. (Ohio Agricultural Experiment Station Bulletin 518, p 8, 1/33) Raw cream prevents joint stiffness. (Annual Review of Biochemistry, 18:435, 1944) Raw milk protects against asthma and allergic skin problems. (Lancet 353:1485, 1999) After three generations on pasteurized milk, cats developed numerous health problems and pathologies of behavior. At four generations, all reproduction ceased. (Pottenger’s Cats, 1983, Price-Pottenger Nutrition Foundation) Pasteurization destroys vitamin A, B complex, C, D, enzymes and whey proteins. (See numerous abstracts listed at www.realmilk.com) Veganism in Principle • humans can convert carotenes to vitamin A • humans can convert sunlight to vitamin D • humans can manufacture all needed cholesterol • humans can obtain all needed minerals from plant foods • humans can produce all superunsaturated long chain fatty acids from essential fatty acids in plant foods • vitamin B12 is available from dark green algae • human conversion to vitamin A is difficult, and humans require dietary vitamin A from animal sources • humans require additional vitamin D from animal sources • dietary cholesterol protects the intestinal tract, reduce need for internal synthesis • humans absorb minerals more easily from animal foods • most humans benefit from dietary intake of superunsaturated longer chain fatty acids from animal sources • humans do not absorb vitamin B12 from blue green algae http://www.westonaprice.org/healthissues/ethicsmeat.html http://www.westonaprice.org/tour/vegtourindex.html Genetically Modified Foods -it is potentially a health and environmental disaster -GMO industry is operating without proper oversight The institutionalized vigilance, “this unending exchange of critical judgment,” is nowhere to be found in the study of nutrition, chronic disease, and obesity, and it hasn’t been for decades. -Gary Taubes Resource • • • • • • • • • • • • • www.mercola.com Nourishing Traditions, Sally Fallon Nutrition and Physical Degeneration, Weston A. Price Know Your Fat, Mary Enig The Cholesterol Myth, Uffe Ravnskov www.realmilk.com Dr. Weil Endorses Gary Taubes' Good Calories, Bad Calories Charlie Rose - NUTRITION PANEL Oiling of America – http://www.westonaprice.org/knowyourfats/oiling.html The benefits of high cholesterol – http://www.westonaprice.org/moderndiseases/benefits_cholest.html Untreated milk cuts children's allergies http://www.dailymail.co.uk/pages/live/articles/health/healthmain.html?in_article_id=399520&in_page_id=1774 Vegetarianism: What the Science Tells Us – http://www.westonaprice.org/basicnutrition/vegetarianism.html The Pollution Within – http://www3.nationalgeographic.com/ngm/0610/feature4/index.html the guy with the bow tie 18 Use of Enzymes to Counteract Inflammation Modern Diet Highly refined and processed foods Chemicalized Eat in a hurry But the most damaging part is the removal of enzymes inherent in food. Enzymes help digest the food that contains them. Enzymes Catalysts that speed up chemical processes in the body. Use in digesting foods and many metabolic functions in the body There will be no life without enzymes Enzymes composed of a protein part and a vitamin (co-enzyme) or mineral part (co-factor) http://bioactive.mrkirkscience.com/06/ch6intro.html THERE ARE MANY DIFFERENT TYPES OF ENZYMES Metabolic Enzymes Over 4000 known enzymes involved in synthesis, detoxification, movement, and cellular regulation Usually found within cells May be active orally Digestive Enzymes Involved in food degradative processes Found primarily in the pancreas and GI tract http://www.loomisenzymes.com/articles.asp?article=2 Enzymes Decrease the Energy of Activation (Ea) for Chemical Reactions Fletcherization Promoted by Horace Fletcher, in the mid 1850’s Chew each bite of foods at least 100 times until there is no lumps, liquidfy. Release enzymes in raw food Reduce particle size for enzymes to act on and improve digestion What Happen When You Can’t digest Your Meals? Bacterial, parasitic and fungal fermentation in the gut producing toxins Inflammation of gut wall lead to leaky gut syndrome Large food molecules and microbial toxins enter into the blood stream lead to inflammation in the blood stream Initiates immune system action and stress http://www.allergyescape.com/leaky-gut-syndrome.html http://www.leakygut.co.uk Stress A specific biochemical reaction in the body Increase the body’s need to nutrients When there is a failure to deliver nutrients to meet increased needs during stress—> dis-ease Dis-ease—Inability of the body to maintain normal function—homeostasis—during prolong stress http://findarticles.com/p/articles/mi_m0860/is_n11_v51/ai_8097915 Three Stages of Stress Humoral phase—can be corrected with improve nutrition and digestion Matrix phase—body recruits immune, endocrine and autonomic systems to help out—inflammation in the weakest areas of the body, hormonal imbalance and autonomic system imbalance Cellular phase—body depleted, toxins enter lymphatic and cells, causing DNA damages—chronic degenerative disease http://www.heel.com/download/6-phase-table.pdf the guy with the bow tie 19 Stress is the only cause of diseases Three types of stress: emotional, physical and chemical/nutritional The body react to stress the same way Increased stress causes increase nutritional needs When nutritional needs is not able to supply the body’s needs symptoms The bottom line cause of chronic degenerative disease—malnutrition Homotoxicology Excretion phase--In this phase the body's defensive system is intact and can excrete toxins in various ways such as through diarrhea or rhinitis (a runny nose). Inflammation phase--If excretion is not sufficient, the body has an inflammatory response (such as a fever) in an attempt to neutralize toxins. Deposition phase--If toxins are not sufficiently excreted and continue to flow into the body, the toxic products are stored in the extracellular space. This phase often occurs without symptoms. Impregnation phase--Once toxins have invaded the cell and the toxins themselves become part of the connective tissue and matrix. Increasingly severe symptoms are typical of this stage and indicate damage to organ cells. Degeneration--Abundant toxins within the cells destroy large cellular groups within an organ, resulting in organ degeneration. Differentiation--Illnesses in this phase are characterized by the creation of undifferentiated, non-specialized cell forms. Malignant diseases lie at the end of this phase. http://www.healingfocus.org/Homotoxicology.pdf Inflammation The most commonly bought over-the-counter drugs in the United States: Pain killers Digestive aides Sleep aides 2/4/09 Drugs It function by ways of blocking a normal physiological function Poisoning biological pathways Symptoms suppressing Do not address the underlying causes of diseases Allow the causes of diseases to develop further—leads to side effects Drugs will never restore HEALTH! Ten reasons why people seeks alternative health care 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Back problems Anxiety Headache Sprains or strains insomnia 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Depression Arthritis High blood pressure Digestive problems Allergies -Typically, these are conditions that conventional MDs have no answer for. RA More than 50% of patients who are working at the start of RA are disabled after 5 years. 5 year survival rate with more than 30 joints - 50% (similar the coronary artery disease of stage IV Hodgkin’s disease) Average loss of 18 years of life in patients who develop RA before age of 50 Autoimmune Abnormal bowel permeability Food Allergies Microorganisms (EBV, measles virus, amoebic organisms, mycoplasma) Decreased DHEA levels the guy with the bow tie 20 OA Age-related changes in collagen-matrix repair mechanisms Fractures and mechanical damage Genetic predisposition Hormonal and sex factors Hyper-mobility/joint instability Inflammation Inflammatory joint disease Can be halted and reversed Aspirin and other NSAIDS may contribute to osteoarthritis by inhibiting cartilage repair. Nightshade family vegetables may trigger Antioxidants protect Glucosamine sulfate most thoroughly researched Lack of correlation between severity of OA (degenerative changes apparent on X ray) and the degree of pain $100 BILLION Arthritis and other rheumatic conditions are the primary cause of disability in the US with direct and indirect costs over $116 billion – 1.4 % of the U.S. gross domestic product 38 Million American suffer ALLOPATHIC PAIN MANAGEMENT NSAIDS OPIOIDS EPIDURALS MORPHINE PUMPS ELECTRICAL IMPLANTS TENS UNITS CORTICOSTEROIDS METHOTREXATE (rheumatologists) elevates homocysteine Antibiotics (mycoplasma) in RA http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/hp.asp VIOXX Pulled from market in September 2004 after studies showed twice the risk of heart attack http://www.usatoday.com/news/health/2004-10-12-vioxx-cover_x.htm BEXTRA RISK MAY BE HIGHER THAN VIOXX Sept. Bextra replaced Vioxx as the current anti-inflammatory of choice. Clinical trials showed patients taking the drug were twice as likely to have a heart attack or stroke. Not as persuasive as a blind clinical trial but so significant that warranted thorough examination of entire class by FDA http://www.usatoday.com/money/industries/health/drugs/2005-04-07-bextra_x.htm ALEVE, ASPIRIN, IBUPROFEN Aleve – first non-prescription NSAID to be added to the list of painkillers associated with heart attacks and strokes. Patients taking for nearly 3 years have been advised to stop and new users no more than bid for no longer than 10 days OTC has 200 mg of naproxen…prescription recommends more than twice the dose and has 500 mg. (1,500 mg). 4X’s the recommended FDA dose FDA Announces Series of Changes to the Class of Marketed NSAIDS April 2005 FDA asked Pfizer, Inc. to withdraw Bextra and include a boxed warning to the Celebrex label. FDA asked manufacturers of all other prescription NSAIDs to revise labels and include boxed warnings highlighting the potential for increased CV events and GI bleeding. FDA asked manufacturers of all OTC NSAIDs to revise their labels and to include possible skin reactions as well as CV and GI the guy with the bow tie 21 Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2002 99: 13926-13931 Ibuprofen, aspirin and other NSAIDs work in part by targeting COX-1 and COX-2. Acetaminophen, unlike NSAIDs, doesn’t target COX-1 and COX-2 and therefore has only a weak anti-inflammatory effect COX-3 detected (variation of COX-1). COX-3 is strongly inhibited by acetaminophen. May shed light on the link between genetics, pain and fever. http://www.pnas.org/content/99/21/13926.full.pdf http://www.pnas.org/content/99/21/13371.full.pdf The New England Journal of Medicine Dec. 20,2001 Pts. with kidney disease or other ailments who take aspirin or acetaminophen 2x’s week for 2 months increase risk of chronic kidney failure two to three times. Diabetics have increased risks of kidney failure. ½ - 1/3 diabetic don’t know they have it. http://content.nejm.org/cgi/reprint/345/25/1801.pdf DOUBLES RISK OF URINARY RETENTION Dutch study of 72,000 men implicated NSAIDs in doubling the risk of acute urinary retention. Inhibits the production of prostaglandin essential to muscle function http://www.associatedcontent.com/article/371014/study_nsaids_increase_risk_of_acute.htm NSAID RISKS 15% of dialysis patients today may be a direct result of Tylenol and/or aspirin use. May also be associated with diverticular disease http://www3.interscience.wiley.com/cgi-bin/abstract/112185987/ABSTRACT?CRETRY=1&SRETRY=0 Increases chance of relapse in patients with Heart Failure Not linked to a first case of congestive heart failure Aspirin may reduce the risk of heart attack however, patients who take other NSAIDs for chronic illness may increase the risk of heart failure (causes fluid retention and high blood pressure) Investigators found that patients who filled at least one NSAID prescription were nearly 10 times more likely to have a relapse of CHF http://archinte.ama-assn.org/cgi/content/full/160/6/777 IMPAIRED BONE HEALING Reports for over 20 years of impaired bone healing in patients taking NSAIDs. The new NSAIDs block healing where ibuprofen and indomethacin only delay healing by a few weeks (25 to 50%). Aspirin decreases pain without this side effect. COX-2 may be crucial in bone-forming stem cells and growth factors http://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/481998 http://query.nytimes.com/gst/fullpage.html?res=9805E5D6113AF93AA25751C0A9639C8B63 Key to Health Remove road blocks of healing When the cause of a symptom is known, the treatment becomes obvious. Prevention of disease and maintaining health by improved nutrition the guy with the bow tie 22 Functional Assessment of Stress Muscle contraction due to organs dysfunction—Dermatome referral pattern Chapman’s reflexes Hair analysis Saliva tests Blood, urine, stool analysis Energy Meridian stress analysis Supplemental enzymes Improve digestion Resolve inflammation Reduce microbial growth in GI Overall effect—reduces stress ENZYMES ARE SAFE No toxicity at any dosing level FDA classifies as GRAS (safe) Work on food as well as pathological microbs in the gut Enter into the body and reduce inflammation in the blood and lymph circulation the guy with the bow tie 23 Pancreatic Vs. Plant-Derived Digestive Enzymes Animal-based - Enzymes extracted from pig and cow pancreas Work only in intestinal tract, produce exorphin peptides Function in narrow pH range (not as useful) Plant-based - Isolated from papaya, pineapple, and fungi Similar function as pancreatic, but different structure Work in stomach and intestinal tract Classified as dietary supplements (no prescription needed) Function in broad pH range Whole Food Supplements Food naturally contains: carbohydrates, protein, lipid, vitamins, minerals, enzymes and other synergistic factors such as phytochemicals Supplements processed by concentrating whole foods contain all of these factors Synthetic supplements lacks enzymes and other synergistic factors How to use enzymes? For reducing pain and inflammation: proteases are most effective, should be taken on empty stomach For acute inflammation, take large doses several times a day until symptoms subside For digestion, take them with meals Enzyme Products on the Market Most supplement companies produce enzyme products Look for reputable companies Companies that specialized in enzymes Condition specific products Refer to company literature and training information the guy with the bow tie 24 Natural Vs. Synthetic Supplements Are there any difference? What kinds of supplements to use in practice? “One of the first duties of the physician is to educate the masses not to take medicine.” — William Osler, considered to be the “Father of Modern Medicine”, The Principles and Practice of Medicine (1892) "My scientific career was a descent from higher to lower dimensions led by a desire to understand life. I went from animal cells to bacteria, from bacteria to molecules, and molecules to electrons. The story has its irony, for molecules and electrons have no life at all. On my way, life ran out between my fingers." ~ Albert Szent Gyorgyi The Living State, Academic Press 1972 FOOD CONSUMPTION IN THE U.S.A. Between 1900 and 1980 • Fresh fruit and vegetable consumption decreased from 40% to less than 5% • Butter consumption decreased 75% • Lard consumption decreased 66% • Unprocessed potato and sweet potato consumption decreased 40% • Processed potatoes comprise 33% of all white potatoes consumed. The majority of these are in the form of french fries • Whole grain consumption decreased 50% • • • • • • • Beef (feedlot variety) consumption increased 75% Dairy (confinement cows) product consumption (other than butter) increased 25% Cheese (processed) consumption increased 400% Fat and oil consumption increased 150% Margarine consumption increased 800% Corn syrup consumption increased 400% Sugar consumption increased 50% (the average person consumes 150 pounds of REFINED WHITE SUGAR per year) Between 1910 and 1980 • Poultry (factory farm) consumption increased 350% • Fresh apple consumption decreased 70% • Fresh fruit consumption decreased 33% Between 1930 and 1980 • Processed citrus fruit consumption increased 2500% • Fresh citrus fruit consumption decreased 50% Between 1940 and 1980 • Egg consumption decreased 25% • Food coloring consumption increased 90% Between 1960 and 1980 • Soft drink consumption increased 300% Each person consumes 38 gallons of soft drinks annually (one fifth of our sugar intake is in soft drinks) • *Statistics compiled by the United States Department of Agriculture What is a vitamin? A vitamin is a complex mechanism of biological, functional, interrelated, interdependent components. It consists of not only the organic nutrients identified as the vitamin, but also enzymes, coenzymes, antioxidants, and trace element activators. Since enzymes are proteins, they must contain amino acids and trace minerals. Enzyme activators may include trace elements such as manganese, cobalt, zinc, copper, molybdenum, selenium, vanadium, etc. These components are effective only when left in the proper organic state. “A vitamin is a complex biological “Wheel within a wheel”, of functional, interrelated, interdependent components.” “Every mineral needed by the living cell is commonly found in a natural assemblage of vitamin concentrates” - Royal Lee the guy with the bow tie 25 Two Points of View Synthetic -isolated -vitamin fractions manufactured in chemically ‘pure’ form in high concentrations “high potency” Natural -the whole is greater than the sum of the parts -vitamins are complex and come with other substances in a synergistic nature -if taken apart they cannot operate in their intended organized and functional manner Whole food supplements contain the total complex family of micro-nutrients (known and unknown) just as they are found in nature. Synthetic vitamins (isolates) lack this supporting family. Supplements on the Market Today NATURAL: • Natural means vitamins as found in natural foods, untampered with any way that might change their molecular, their biological or biochemical combinations, or their action. This usually means that only the fiber and moisture are removed. All labels of truly NATURAL food concentrates should indicate the exact food source from which the vitamin is obtained. CRYSTALLINE: • Means it had a natural food as its original source but was treated with various high powered chemicals, solvents, heat and distillations to reduce it down to one specific, pure crystalline vitamin or amino acid and hence is no longer natural. Sometimes it goes through a fermentation process. It no longer has its synergistic components, that is ,its enzymes, co-enzymes, minerals, mineral activators, and co-vitamin helpers. Sometimes it comes with contaminants such as the d-form of a vitamin. It has been reduced to a pure crystalline powder with one definite simple chemical structure. SYNTHETIC: • Means that in the laboratory the scientist has reconstructed the exact structure of the CRYSTALLINE molecule by "putting together" or chemically combining the same molecules from other sources. Chemically, therefore, there is no difference between the two. The Crystalline may have a slight advantage in that it is difficult to reduce any natural product to an absolute pure state and any impurities would be "synergists" hence giving a little added value to the Crystalline over the Synthetic. On the label for either Synthetic or Crystalline only the chemical name of the single vitamin is usually given. Legally it is not necessary to give the source from which the synthetic chemical is derived. • 90% of synthetic vitamins are made in China these days. http://seattletimes.nwsource.com/html/nationworld/2003732744_vitamins03.html?syndication=rss 2/6/09 Are Synthetics the Exact Mirror Image of the Natural? Vitamins manufactured in the laboratory, using artificial synthetic techniques come in the dextro- and levo- forms (so-called "right" and "left handed" molecules, which are the mirror images of each other), and the body can only use the levo- forms. Science’s form of “Natural” vitamin C 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Corn Starch refined to refined sugar (Glucose) C6-H12-O6 Refined Sugar is hydrogenated into sorbitol Sorbitol is fermented into sorbose Sorbose + Acetone reacted with Sulfuric Acid yielding 2-keto-L-gulonic acid 2-keto-L-gulonic acid washed in an alcohol bath creating crude Ascorbic Acid C6-H8-O6 Common Knowledge in the Isolated Vitamin Industry • • • Use of isolated vitamins/minerals as single nutrient for long-periods is not recommended as it causes imbalances and deficiencies of other vitamins/minerals. For example: giving folic acid on its own masks a vitamin B12 deficiency, which can lead to neurologic problems. When you combine a single vitamin with a vitamin/mineral complex, the risk of overdose symptoms is reduced. Supplementation with synthetic vitamins creates deficiencies In the Journal of the American Dietetic Association (March 21, 1940) it was reported that "…synthetic vitamins should be used with caution in order to prevent the development of deficiencies more serious than the deficiency we set out to control." -excessive amounts of any single nutrient could potentially cause an imbalance in the body the guy with the bow tie 26 Some dangers of isolated vitamins Nature’s version of Vitamin C -in nature, vit A and vit D always work together -therefore, if supplement with vit D, then need to add vit A with it “Vitamin C supplements may promote atherosclerosis” Vitamin C supplementation [ascorbic acid] appears to promote intima-media* thickness (IMT) in a dose-dependent manner. Men who took 500 mg of vitamin C daily had an increase in IMT progression that was 250% greater than men who did not use supplements. In an interview with Reuters Health, Dr. Dwyer said the effect was observed regardless of disease-state at baseline. “Even men with no evidence of thickening at baseline who were regular supplement users had an increase in intima over the 18 months,” he said. (intima is the innermost membrane/lining of the artery) Mar 3, 2000 (Reuters Health) Does vitamin C have a pro-oxidant effect? Nature. 1998 Sep 17;395(6699):231-2. Vitamin C exhibits pro-oxidant properties. Nature. 1998 Apr 9;392(6676):559. Ascorbic Acid Content in Whole Food • A small apple contains only 5.1 mg of Vitamin C. But the same contains polyphenols and flavanoids-beneficial food compounds that equal the effect of 1,500 mg of vitamin C. • Antioxidant activity of fresh apples. Nature. 2000 Jun 22;405(6789):903-4. the guy with the bow tie 27 The Lancet, Volume 358, Number 9275; 07 July 2001 Plasma ascorbic acid in heart disease • • Sir Kay-Tee Khaw and co-workers' findings (March 3, p657) contrast strikingly with the frequently disappointing, and sometimes disconcerting, results of molecularly based cancer chemoprevention trials. For example, ß-carotene, administered alone or together with vitamins A, E, or ascorbic acid, for the prevention of cancer in heavy smokers or asbestos workers, does not lower cancer risk (and in some cases incidence increases). These supplementations are, therefore, suspected of having harmful as well as beneficial effects. Epidemiological data firmly linking high fruit and vegetable consumption to health benefits have prompted efforts to reproduce these effects with a single industrially derived molecule. In-vitro and in-vivo models show frequently the expected biological activity of single nutrients. The trouble comes when these do not arise after consumption in human beings. Khaw and co-workers remark that benefits from ascorbic acid supplements remain to be seen. However, dietary supplementation of 500 mg ascorbic acid daily (ie, a common commercial dose) to healthy volunteers for 4-6 weeks causes substantial oxidative DNA damage in circulating lymphocytes. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 2002 Spring;32(2):193-200. Antioxidant properties of fruit and vegetable juices: more to the story than ascorbic acid. Leonard SS, Cutler D, Ding M, Vallyathan V, Castranova V, Shi X. Pathology and Physiology Research Branch, Health Effects Laboratory Division, National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health, Morgantown, West Virginia 26505, USA. Dietary supplements such as vitamin C have become popular for their perceived ability to enhance the body's antioxidant defenses. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) have been shown to cause a broad spectrum of damage to biological systems. Scavenging of ROS is part of a healthy, well-balanced, antioxidant defense system. The present study used the Fenton reaction as a source of hydroxyl radicals and xanthine/ xanthine oxidase as a source of superoxide radicals to investigate the scavenging capabilities of various fruit and vegetable juices against these radicals. Electron spin resonance (ESR) spin trapping was used for free radical detection and measurement. Using a colormetric assay, the present study also investigated the protective effects of fruit and vegetable juices against lipid peroxidation induced in cell membranes by hydroxyl radicals. The present study showed that the free radical scavenging capability of each individual juice, but not its ascorbic acid content, is correlated with its protective effect on free radical induced lipid peroxidation. The results indicate that ascorbic acid is only one facet of the protective effect of fruit and vegetable juices. It appears that consumption of whole fruits and vegetables would be superior to an ascorbic acid supplement for antioxidant effectiveness. The antioxidant paradox Lancet 2000; 355: 117980 Interest in the use of antioxidants for the treatment of human disease, and in the role of dietary antioxidants in the prevention of disease development, has been sustained for at least two decades. Development in both therapeutic and nutritional fields has been punctuated by some successes, but also by some spectacular failures. For example, people with diets rich in fruit and vegetables have a decreased chance of getting cancer and an increase in the concentration of ß-carotene in the blood. Supplements of ß-carotene, however, do not have an anticancer effect, rather the opposite in smokers. Fruit and vegetable consumption decreases the amount of free-radical damage to DNA in the human body (a risk factor for cancer development), but supplements of ascorbate, vitamin E, or ß-carotene do not decrease DNA damage in most studies. As research continues, paradoxical effects accumulate; vitamin-E supplements were protective against cardiovascular disease in the CHAOS9 study, but not in the GISSI-Prevenzione trial. Intakes of vitamin C below the recommended daily allowance are associated with increased free-radical damage to DNA4,11 but, paradoxically, so is supplementation with high-dose vitamin C. Antioxidant activity of fresh apples • Vitamin C is used as a dietary supplement because of its antioxidant activity, although a high dose (500 mg) may act as a pro-oxidant in the body. Here we show that 100 g of fresh apples has an antioxidant activity equivalent to 1,500 mg of vitamin C, and that whole-apple extracts inhibit the growth of colon- and liver- cancer cells in vitro in a dosedependent manner. Our results indicate that natural antioxidants from fresh fruit could be more effective than a dietary supplement. • • Department of Food Science, 108 Stocking Hall, Cornell University, Ithaca, New York 14853-7201, USA MARIAN V. EBERHARDT, CHANG YONG LEE & RUI HAI LIU The Lancet, Volume 358, Number 9275; 07 July 2001 • The surprisingly healthy outcomes associated with an increase of just one serving per day of fruit and vegetables 1. are in keeping with the observation that whole-apple extracts exert much greater (>263-fold) total antioxidant activity and stronger inhibitory effects on growth of colon and liver cancer in vitro than does synthetic ascorbic acid, presumably because of their high content of nutrients and phytochemicals.5 Khaw and co-workers themselves considered the possibility that the measured plasma ascorbic acid might only be an indicator of other protective factors. They give the association of ascorbic acid with numerous other components present in foods as the most likely alternative explanation. The overall combination of substances (holistically) present in fruit and vegetables could be the true cause of the overall biological benefits of green vegetables. the guy with the bow tie 28 Alpha-tocopherol (vit E) supplementation is dangerous • A study in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (Vol. 94, April 1997) suggests that it could be dangerous to take high doses of Vitamin E (alpha tocopherol) without also consuming gamma tocopherol. The study showed that high doses of alpha tocopherol on its own displaces gamma tocopherol in tissues. -Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, Vol. 94, April 1997 Gamma tocopherol is as important as alpha tocopherol • As shown in a 1993 study published in the Proceedings of The National Academy of Sciences (Vol. 90, March 1993)(1), gamma tocopherol is superior to alpha tocopherol in the detoxification of nitrogen dioxide (NO2). Nitrogen dioxide is a highly reactive free radical that has been linked to increased cancer risk in humans. A revealing epidemiologic study on the populations of Fiji and the Cook islands, showed that the serum gamma tocopherol levels in the Fiji population was 2 fold higher than the Cook Islanders, while the Fijian's lung cancer rate was 10-20 times lower. Both groups had similar alpha tocopherol levels and both groups had similar smoking patterns. • Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, Vol. 90, March 1993 • Gamma tocopherol is the predominant tocopherol in natural oils, and it is gamma tocopherol that is being reevaluated for its role in human nutrition and disease prevention. In a more recent study, also published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (Vol. 97, October 2000), scientists have shown that gamma tocopherol plays a critical role in the defense against cancer and cardiovascular disease by inhibiting the process of inflammation more effectively than alpha tocopherol • Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, Vol. 97, October 2000 Innate Intelligence “The first thing that is destroyed in the laboratory when a nutrient is isolated from a food, is the delicate web of intelligence that binds the components of food together. When a blood cell rushes to a wound site and begins to form a clot, it has not traveled there at random. It actually knows where to go and what to do when it gets there, as surely as a paramedic - in fact, more surely, since it acts completely spontaneously and without guesswork. Even if we break down its knowledge into finer and finer bits, looking for the secret in some minute hormone or messenger enzyme, we will not find a protein strand labeled ‘intelligence’, and yet there is no doubt that intelligence is at work.” ~ Deepak Chopra, M.D Quantum Healing How to choose supplements? Read and understand the label • • • • • • • What form is the mineral in? Citrate, acetate, gluconate, oxide, etc Chelated forms (citrates, acetates etc) generally better than inorganic forms (oxides, carbonates etc) Whole food, herbal concentrates Enzymes, homeopathic, flower remedies How many capsules / tablets are there? What is the potency per tablet? What are the additional (non-active) ingredients? Additional Ingredients • • • • • • Fillers, binders, lubricants, emulsifiers, preservatives, coating agents, anti-caking agents – eg, Lactose, sucrose, corn starch, sodium chloride, talc, soap, waxes, dicalcium phosphate, magnesium stearate, stearic acid, microcrystalline cellulose, etc Introduces undesirable substances into the body Can upset the mineral balance of the preparation May be difficult for the digestive system to break down and obtain the nutrients Capsules have less additional ingredients Capsules easier broken down by digestive system Which is Better? -15mg Zinc Citrate only about 4-5mg zinc -15mg Zinc as Citrate 15mg zinc (bound in the citrate form) the guy with the bow tie 29 Beware of Marketing • • • • • • Marketing literature may not be written by qualified nutritionists Clever wording designed to sell / make profit Beware of vague wording such as “complex” “formula” or “blend” Patented products not necessarily effective Several companies may buy products from the same manufacturer and repackage MLM/Network marketing Other Types of Supplements Timed Release Supplements • May be useful for water soluble vitamins • Coatings may hinder absorption • Generally more expensive and benefits not always clear Food Form • Mineral is delivered with natural co-factors to enhance absorption and utilization • “Scientific” evidence is lacking in this area Chelated minerals • Metallic minerals usually chelated with an amino acid • Better absorbed within the body than inorganic minerals • Scientific evidence comparing them to organic forms is lacking Liquid Supplements • Often low potency – poor value for money • Likely to be destroyed by stomach acids • May be beneficial to those who are unable to swallow tablets Independent testing • • • • • • Potency Stability Contamination (heavy metals) Yeasts / Moulds / Bacteria Chemical solvents / pesticide residues If in doubt ask the company if they can provide independent test results for their products Signs of a good company • • • • • Check the company website for details of manufacturing processes / quality assurance etc Trained nutritionists will be available to answer any questions you have about their products Products should have been independently tested and chemical assays available A good company will provide scientific research to back up the claims for its products Some companies run seminars or workshops which are educational – not just a sales technique Problems with cheap products • • • • • • • Fillers and binders may upset the mineral balance or hinder absorption Could contain impurities which result in allergic reactions May contain heavy metals / chemicals which increase toxic load in the patient May not contain as much of a particular nutrient as is stated on the label Potency not adequate for therapy Likely to use cheap forms of minerals with lower absorption Storage may not be adequate, e.g. for fish oils / probiotics Implications for therapy • • • • • Lack of results reduce confidence in the practitioner – patient is less likely to stick to the diet or take further advice Results may be slower than expected – the patient may become impatient, lose motivation and give up the treatment Allergies may be triggered Mineral imbalances may be caused or worsened Toxic load may be increased the guy with the bow tie 30 What do practitioners use? Brands / suppliers used by some of the practitioners include: • Allergy Research Group • Borlean (flax oil) • Biopathica (Homoeopathic remedies) • Biotics Research Corp (sublingual free-form amino acids) • Bach Flower Remedies • Boiron remedies • Enzymatic Therapy • DC Nutritionals • Design For Health • Douglas Labs • Garden of Life (PRIMAL DEFENSE) • Gaia Herbs • Innate Response • • • • • • • • • • • • Heel Remedies Loomis Institute Metabolics Metagenic Nutriwest Nordic Natural fish oils Orthomolecular Solgar (selected products) NOW Standard Process Thorne Research Vitacost (recommended by Dr. Lee) Do not assume that all products from these companies would be suitable, it is up to your professional judgement to evaluate the products on the market and select the ones you are going to use for your patients or in practice!! Summary • Check labels carefully • Use reputable suppliers • Beware of fillers and binders • Beware of allergens • Don’t be fooled by clever marketing • Beware of excessively cheap or expansive products • You generally get what you pay for • Ask for research to support claims for products • If in doubt ask for independent test results If it seems too good to be true it probably is! Decisions, Decisions, Decisions • • • • • • • • There is a place for both crystaline and whole food concentrate supplements. Treat synthetic mega-dose forms of nutrients as drugs, use only short-term if deem necessary. Avoid synthetic vitamin-like substances. Choose chelated minerals rather than inorganic salt: Calcium citrate vs. calcium carbonate. Choose naturally extracted nutrients over synthetic source: Acerola cherry extract vs. ascorbic acid from corn syrup. Choose whole food complex for long-term support. Always initiate dietary change as soon as patient’s willing, at least bring that to patient’s attention. Use you professional judgment and experiences. the guy with the bow tie 31 2/10/09 Nutr2 - Exam 2 Nutrition and The Digestive System: Part 1 Introduction to GI Disorders A web-like link of systemic disorders to the GI tract “Symptoms of gastrointestinal tract disorder existed with no known structural, pathological, radiological, and laboratory findings comprised forty-one percent of the membership’s practice” according to a survey conducted by the American Gastro-enterological Association. Traditional treatment of GI problems relies on drugs such as anti-inflammatory agents, antacids, enteric nervous system inhibiting agents. These approaches do not seek to uncover the underlying causes or triggers. Suppressing symptoms rather than improving functions of the GI tract often lead to further deterioration. Close interrelationship the GI tract plays with every major system in the body http://advan.physiology.org/cgi/content/full/31/4/329 http://www.fdhn.org/user-assets/Documents/awards_documents/Future_Trends_Effect_of_Aging.pdf http://www.gi.org/patients/gihealth/functional.asp http://www2.niddk.nih.gov/NR/rdonlyres/276BFB7C-B9AB-402B-9FA2-706AF8580F1D/0/DDICC_Sept_26_2003_Minutes.pdf GI-Immune, Pain, Inflammation Over 60% of human immune system is in the GI tract 99% of the body’s neurotransmitters Any adverse antigen that interacts with the gut-associated lymphoid tissue (GALT) will trigger an inflammatory response Lead to production of inflammatory mediators causing pain, inflammation and vasoconstriction GI dysfunction is commonly found in patients with any chronic pain. Complex inflammatory response lead to free radicals, interrupting the electron transport chain uncoupling of oxidative phosphorylation, damage DNA and perpetuates a viscous cycle of oxidative stress and inflammation http://www.ualberta.ca/~drayner/475_lt/lt_MALT1.htm The Enteric Nervous System -The central autonomic nervous system (hypothalamus and brain stem) mediates its influence on the gastrointestinal function via the intrinsic, enteric nervous system http://www.vivo.colostate.edu/hbooks/pathphys/digestion/basics/gi_nervous.html Cutting, Sheaving (bundling), and Stooking (shocking) Grain from ancient Egypt (7000 BC)--to medieval Europe (1568)--to 20th century United States -Since the beginning, each kernel of grain ripened in shocks in the field producing nutrients essential to the life of the plant AND the life of the people. THRESHING After the grain had ripened sufficiently in the shocks, it was threshed. Threshing removes the grain from the stalks, winnows and collects the grain, and stacks the straw. For millennia, farmers did this by hand, flailing and pounding the bundles of grain by hand; or with devices powered by horses or other animals. In the late 19th and pre-WWII 20th century, individual farmers usually did not own threshing machines but hired a crew or depended on a communal arrangement to do the job. I-A Cutting, Bundling and Shocking Grain The cradle consisted of a broad scyth with a light frame of four wood fingers attached to it. The advantage of the cradle was that by a turn to the left the operator could throw the grain into a swath, ready to be raked and bound into sheaves. This improvement was introduced in America about 1776 and was the common instrument of grain harvesting as late as 1840. For cradling grain, two acres was considered a hard day's work for each man. Threshing: A steam engine was set up in or near the grain field and was belted up to the threshing machine. A team of workers called "bundle haulers" went out into the field and loaded shocks onto a horse-drawn wagon. The filled wagon was brought up to the spot where the threshing machine was set up. Men standing on top of the wagon pitched the grain bundles down into the feeder which conveyed the bundles to the threshing cylinder where most of the grain was separated from the stalks. The separated grain fell to the bottom of the threshing machine, while chaff and dust was removed by a fan as it descended. An elevator on the threshing machine then transported the loose grain into a grain wagon parked nearby or into individual bags, depending on the method preferred. After the straw went through the cylinder, it was continually battered as it progressed along, ensuring that all the grain was removed from the stalks. At the rear of the threshing machine, after the straw had passed over the straw walkers, it was deposited in a fan housing which propelled the straw through the blower and into the straw stack. the guy with the bow tie 32 Sheaves (bundles), Shocks (stooks) and Stacks Shocks stood in the field for several weeks before threshing. Grain seeds were exposed to rain and dew which soaked into the sheaves. This moisture, combined with heat from the sun, germinates the seed. Germination neutralizes enzyme inhibitors and releases the enzymes. Germination increases the enzyme activity as much as six times. Use of the modern combine harvester results in a mature but dormant (resting) seed. The modern method for germinating seeds is soaking before cooking. -Edward Howell MD: Enzymes for Health and Longevity Like “Industrial Agriculture,” Processed Whole Foods is an Oxymoron Last week, the federal government released its Dietary Guidelines for Americans 2005…. Most media reports focused on the guideline’s emphasis on weight loss…. Emphasizing weight loss conveniently puts the onus for dietary change on the individual and avoids talk of refining in the food industry’s multibillion-dollar marketing budget for unhealthy foods…. Americans have become accustomed to eating highly processed foods that come in a package – the antithesis of whole foods that come from nature. The very definition of food has been transformed by industry, yet the dietary guidelines don’t reflect that. If they did, it would be a major threat to a fivehundred-billion-dollar-a-year processed foods industry whose voice is heard loud and clear in Washington…. But “processed whole foods” is an oxymoron. -Michele Simon, San Francisco Chronicle, January 19, 2005 Civilization vs Nutrition Readjustment of our chemical apparatus to changed conditions takes thousands of generations. A general change in dietary habits taking place in one or two hundred years partakes of the nature of sudden disaster. By adopting a standardized diet of refined and devitalized foods, we have thrust upon our endocrine system an insufferable task of rapid adaptation. -Melvin E. Page, D.D.S., Body Chemistry in Health and Disease, 1953,54, distributed by: www.price-pottenger.org Gut Associated Lymphoid Tissue Lymphoid tissue in the gut, the gut part of MALT , which is comprised of the following: Tonsils . Adenoids (Waldeyer's ring). The tonsils and adenoids are made of lymph tissue and help to fight off infection. Largest in childhood and gradually shrink throughout life. Peyer's patches . Lymphoid aggregates in the appendix and large intestine. Lymphoid tissue accumulating with age in the stomach. (?) Small lymphoid aggregates in the oesophagus. Diffusely distributed lymphoid cells and plasma cells in the lamina propria of the gut. http://www.healthonnet.org/Library/Theme/Allergy/Glossary/galt.html Processed Foods Lack of enzymes Removal of nutrients Addition of synthetic chemicals Practically un-digestible Stimulate immune reactions Lead to inflammation the guy with the bow tie 33 The Vicious cycle of GI dysfunctions and pain, Inflammation and oxidative Stress www.clevelandclinic.org/health/health-info/docs/1600/1678.asp http://biochemgen.ucsd.edu/mmdc/ep-3-10.pdf Functional Hypothyroidism and the GI Tract Dysbiosis 20% of active T3 is dependent upon a healthy gut microflora Imbalance gut flora can cause a decrease in T3 Gut dysbiosis put stress on the adrenal glands cortisol Cortisol can shift T4 into a higher percentage of inactive rT3 rather than the active T3 There are functions served by rT3—a break on the thyroid. http://www.healthyeatingclub.com/info/articles/func-foods/probioticsupdate.htm Reverse T3 The thyroid gland is the body’s metabolic thermostat controlling body temperature, energy use, growth rate, and affecting the operation of all bodily processes and organs. Thyroid hormone production is centrally regulated: Thyroxine (T4) from the thyroid gland is peripherally converted in the liver and kidney cells into T3 and reverse T3 (rT3). T3 is the active hormone and is five times as potent as T4, but rT3 is almost biologically inactive. RT3 can also be included into the Total Thyroid Screen on request or carried out separately. RT3 is primarily produced from monodeiodiation of thyroxin in the peripheral tissue rather than by direct secretion by the thyroid gland. Physical, mental and environmental stresses can inhibit the deiodinating enzyme, causing less T4 to be converted to T3, thus decreasing the amount of active thyroid hormone available to the cells. More T4 is then shunted towards rT3 causing an elevation in rT3. Measuring rT3 levels is useful when ‘sick euthyroid’ conditions are suspected. When a patient produces excessive levels of rT3 they will usually present with hypothyroid symptoms. Factors that can elevate rT3 levels: Selenium deficiency Potassium and Zinc deficiency High stress levels especially high cortisol Chronic illness Cadmium, mercury and lead toxicity High simple carbohydrate intake Low protein intake / poor protein digestion Starvation diets, fasting Compromised liver or kidney function GI Dysfunction and Autoimmune Disorders Antigen exposed to GALT Inflammation Increase intestinal permeability; Absorb middle and large molecular particles; Leaky Gut Up-regulate immune system Auto-antibody Autoimmune Disease the guy with the bow tie 34 GI Disorders and Adrenal Stress HPA axis involvement when the GALT is activated Adrenal alarm response Decrease DHEA reduce other steroid hormone production Potential shift of physiology away from anabolic state to a catabolic state Sub-clinical GI sensitivities to food antigen are major cause of adrenal stress and often undetected, unsuspected Elevated cortisol suppress GI mucosal cells regeneration, decrease sIgA increases dysbiosis http://www.schwarzbeinprinciple.com/pgs/newsletters/SP_Newsletter_InfDig_Part2.pdf GI Dysfunction and Adrenal Stress 2/11/09 GI Dysfunction and Estrogen Dominance Dysbiosis increase Beta Glucoronidase activity Uncoupling the conjugated estrogen Reactivate estrogen and increase total estrogen load and liver stress Ratio of 2-OH and 16-OH estrogen imbalance toward increase risks of reproductive organs cancers Friendly flora can further metabolize estrogen, prevents re-absorption into body http://www.ei-resource.org/articles/candida-and-gut-dysbiosis-articles/intestinal-dysbiosis-and-the-causes-of-disease/ the guy with the bow tie 35 GI Dysfunction and B-12 Deficiency Megaloblastic anemia B12 absorption is dependent on adequate HCl in the stomach, pancreatic enzymes and healthy brush border. Increase serum homocysteine , an inflammatory marker Emotional and psychological signs and symptoms http://www.hkgerisoc.org/Vit%20B12%20and%20Metformin%2025.2.05.pdf http://findarticles.com/p/articles/mi_m0ISW/is_252/ai_n6160495 GI Dysfunction on Moods and Depression Decreases neurotransmitters synthesis and glucose absorption Adrenal stress, cortiscolinsulin resistance The enteric system produces 99% of the body’s serotonin (5HT) Abnormal glucose absorption may cause glycemic dysregulation and impact on mood, behavior and emotion controls http://www.gdx.net/home/assessments/finddisease/depression/digestive_function.html http://www.ahealthyme.com/topic/mindbodygut GI Dysfunction and Weight Control GI inflammation can disrupt intercellular communication and make weight loss very difficult Gut inflammation cytokines can prevent lipolysis and increase lypogenesis the guy with the bow tie 36 Gut and Weight Leaky Gut and Food Sensitivities Healthy GI tract has tight junctions between enterocytes to prevent absorption of large food molecules. During chronic inflammation or stress, tight junctions may be breached allowing large food molecule to enter bloodstream Triggering histamine, leukotrienes, postanoids and PGs leading to food allergies. Healthy Gut Leaky Gut GI Dysfunction and CVD the guy with the bow tie 37 GI Dysfunction and Neurodegenerative Disorders Antigen exposure to GALT Global alarm reaction Glial cells of brain release inflammation cytokines and nitric oxide Neuronal apoptosis Neurodegenerative diseases GI Dysfunction and Chronic Fatigue When Do You Need to Change Diet? GI Laboratory Tests Stiff, sore joints Headache Heartburn Gas pain – bloating Constipation – diarrhea Anxiety – irritability Restlessness – insomnia Depression Dr. Howard Loomis Intestinal permeability test, aka lactulose and mannitol challenge test -If lactulose in urine, then leaky gut SIgA Food Sensitivity Test Helicobacter pylori Test Comprehensive Digestive Stool Analysis Oxidative Stress Test http://www.gdx.net/home/assessments/findsystems/gastro.html GI Dysfunction and Liver Detox Any form of GI imbalance will impair hepatic detoxification Dysbiosis, leaky gut, antigen overload, inflammation reaction increase demands on the liver Pathogenic intestinal bacteria release lipopolysaccharides which goes to the liver and down-regulate the Cytochrome P450 enzymes Beta glucoronidase up-regulation deconjugation of hormones and chemicals Increase total liver workload 2/13/09 GI Laboratory Tests Blood test: increase liver enzymes, antibodies Urine: Increase indican level Genova Diagnostic Labs: CDSA www.gdx.net Diagnos-Techs, Inc: CDSA http://www.diagnostechs.com/main.htm Reference The information in this presentation is based on the “Functional Endocrinology” seminar by Datis Kharrazian, DC. Dr. K had done extensive literature research on this subject. For more information on Dr. K’s seminars on functional endocrinology, contact Apex Energetics — www.apexseminars.com http://www.lef.org/protocols/prtcl-044.shtml the guy with the bow tie 38 Nutrition and the Digestive Tract—Part 2 Gut Facts The GI tract is considered another brain, it works in conjunction with the cerebral cortex to help maintain homeostasis About 60% of the total force of the immune system is in the gut. That makes the gut our most important immune organ Before the brain was developed, the gut was the original brain in invertebrate animals. The Second Brain, Michael Gershon 95 % of the total serotonin production in the body is from the GI tract. SSRI reduces serotonin to the GI tract and can cause nausea, vomiting and constipation. One half of all our neurons of the peripheral nervous system are located in our digestive tract. The state of the GI tract has a profound impact on our health. From the healthy gut, we enjoy health, neurologically, psychologically, as well as immunologically. The GI tract has as many neural connections as the spinal cord. Has more neurons than the rest of the peripheral nervous system Forms the Enteric Nervous System Connected to the brain via the vagus nerve Can function independently—brain dead patients can continue to digest and absorb intubated feeding indefinitely The gut produces all of the neurotransmitters and hormones that the brain does plus more. The GI tract is highly susceptible to stress of any kind—emotional, physical and toxins There are more than 10000 different kinds of microorganisms in the gut. Half of fecal weight is bacteria. Probiotic or normal flora in the gut contributes numerous health benefits Bacteria Citizens in Our Gut Common Human Intestinal Bacteria Approximate Concentrations Bacteriodes ~1010 / gram intestinal contents Bifidobacteria ~109 / gram intestinal contents Eubacteria ~109 / gram intestinal contents Streptococci ~109 / gram intestinal contents Lactobacilli ~108 / gram intestinal contents Function of Friendly Gut Flora Produce vitamins such as folic acid, K, B12 Nourish the lining of colon by feeding on dietary fiber and produce butyric acid an essential fuel for the gut cells, reduce risk of colon cancer Limit the growth of pathological microbes Break down toxins Assist in digestive process GI Blues Two of the top five most widely prescribed prescription drugs in this country are for digestive disorders. Colorectal cancer is the second leading cause of cancer deaths. More than 60 million Americans experience heartburn at least once a month, and about 25 million are daily sufferers As many as 37 million episodes of diarrhea occur annually among America’s 16.5 million children under five, leads to three million physician visits each year and 163,000 hospital visits; accounts for 13 percent of all hospital stays for children in this age group. Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) alone affects almost 20 percent of the adult population in America. One million Americans suffer from AIDS Eight million have cancer Twelve million battle heart disease. Thirty-eight million Americans are victims of digestive disorders, including Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis, diverticulitis, celiac disease, IBS, constipation, diarrhea, GERD, candida and food allergies. the guy with the bow tie 39 Functions of the GI System Reduce complex nutrients into small units for absorption Absorb subunit of nutrients into the blood and lymph Remove toxins and germs that come in through the mouth or excretes via the bile Chewing Protein digestion and breaking down large food particles in the stomach Carbohydrates and lipids digestion in small intestine--duodenum Nutrients absorption in the small intestine--ileum Immunity provided by HCl, SIgA, GALT Nutrients manufacturing by friendly flora—vitamin K, biotin, short chain fatty acids, minerals released by fermentation of fibers—large bowel Hormone conversion—rT3 to T3, vitamin D Toxins disposal via bile Immune Protective Factors in Saliva Lactoferrin—fungicidal and bactericidal protein Lysozyme—enzyme that digest bacterial cell walls Hypothiocyanate—strong oxidizing agent against cell walls Secretory Ig A– primary mucosal immunoglobulin Digestion and Absorption Protein digestion starts in the stomach and requires strong stomach acid. Carbohydrate digestion starts in the mouth and finishes in the small intestine, by pancreatic enzymes. Fat and fat soluble vitamins require bile to digest and absorb Bile is produced by the liver, stored in the gall bladder, release during food digestion Medium and short chain fatty acids do not need as much bile for digestion The Second Brain (book by Michael D. Gershon, MD) “A hundred million neurotransmitters line the length of the gut, approximately the same number that is found in the brain..." Nearly every chemical that controls the brain in the head has been identified in the gut, including hormones and neurotransmitters. http://psychologytoday.com/articles/pto-19990501-000013.html http://www.behealthy.org.uk/gaps.pdf 2/17/09 The Brain Gut Connection Patients with bowel problems tend to have abnormal REM sleep. Poor sleep has been reported by many perhaps a majority of, patients with irritable bowel syndrome (lBS) and nonulcerative dyspepsia (also known as "sour stomach") who complain of awakening tired and unrefreshed in the morning. -http://www.immunesupport.com/library/showarticle.cfm/ID/1404/t/CFIDS_FM -http://rheumatology.oxfordjournals.org/cgi/content/abstract/30/3/220 The Brain Gut Connection Abnormal REM sleep is reduced by low-dose treatment with the anti-depressant amitryptiline, which has also been shown to be effective in treating lBS and non-ulcerative dyspepsia. About 25% of people taking fluoxetine (Prozac) and other types of similar-acting antidepressants experience gastrointestinal problems such as nausea, diarrhea and constipation. http://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/434526 -feeding friendly bacteria with poor-quality food can change them into pathological bacteria (they release toxic metabolites) -antibiotics can also turn them into pathological forms -chickens with pineal gland removed will often produce scoliosis (reduced melatonin) -book “In Defense of Food” by Michael Pollan the guy with the bow tie 40 Four Underlying Causes of Gastrointestinal Dysfunction Pathogen associated GI complaints caused by: Parasitic Infestations Yeast Overgrowth (kids with autism or ADHD often have yeast pblm) Fungal Infections Normal Flora Imbalances Bacterial Overgrowth/Infections Neuroenteric related complaints caused by: Dystonia of GI smooth muscle Dysrhythmia of GI smooth muscle Sympathetic to parasympathetic imbalance Non pathogen related GI complaints caused by: Acquired or genetically determined functional and structural GI complaints External Stressors: Dietary intolerances & allergies Environmental factors Pharmacological factors Factors Affect GI Health Toxins such as petrochemicals, heavy metals, organic compounds, food additives and drugs Trans fatty acids Pathological organisms overgrowth—yeast, fungi, virus, bacteria Extreme Emotions—anger, fear, excitement, anxiety Overeating Other Factors affect GI Health Malnutrition—protein, fat, vitamin, mineral, essential fatty acids Food or drinks in extreme temperatures Lack of sleep—affect the balance of GI flora and hormones Dehydration—The GI tract produces more than 4 liters of digestive fluid daily Lack of or excessive dietary fiber Refined sugars in the diet—damage enzymes by glycation Dysbiosis and Asthma Is there a link between the explosive increases in asthma and allergies over the past four decades that have occurred in tandem with widespread increases in antibiotic use? Antibiotics weaken natural bacteria in the gut and, stimulate overgrowth of the yeast Candida albicans. Previous studies have shown that overgrowth of yeast adversely affects the body's mucosal immunity. The result: A weakened immune system that becomes vulnerable to allergies and asthma. http://www.mdheal.org/parasites.htm http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/health/4801118.stm Allergy and Immune Stress Study In a University of Michigan study, mice were given antibiotics in their drinking water for five days to weaken their gut bacteria. They were then injected with candida yeast, to mimic the response that antibiotics produce in humans. Finally, the mice's nasal passages were exposed to aspergillus, a mold spore that is a common allergy trigger in humans. The mice that received antibiotics showed increased sensitivity to the mold spore in their respiratory systems, whereas mice that did not receive antibiotics did not develop the sensitivities to mold. http://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2005/01/050111174539.htm This study reaffirms the concept that what goes on in the gut can play an important role in regulating immune responses--even in the lungs, since they too secrete mucus. And, to take the concept one step further, if a problem in the lungs is found to originate at another site in the body, there is possibility that other chronic diseases have their roots in the gut or other parts of the body not thought of previously. -Increased incidence of pneumonia with the use of acid blocking drugs the guy with the bow tie 41 Leaky Gut and Food Allergies The widespread use of antibiotics and dramatic changes in the diet in industrialized countries have been accompanied by a striking increase in the incidence of allergies and asthma. The natural flora of our bodies plays a significant role in regulating immune responses. When normal flora in our GI fall out of balance, the body responds in imbalanced ways symptoms. http://www.mold-survivor.com/leaky_gut_syndrome.html Drugs and Gut Twenty percent of the patients received prescription drugs experience side effects The drugs that most often caused complications were antibiotics, antidepressants, and NSAIDs. The most often reported side effects were GI symptoms, sleep difficulties, fatigue and mood changes. -Journal of General Internal Medicine 2000;15:149-154 http://www.ibsgroup.org/main/medications.shtml SSRI-Prozac, Effexor, Celexa, Zoloft and paxil—have a threefold greater risk of upper GI bleeding than those who do not take these drugs Alain Li Wan Po. Antidepressants and upper gastrointestinal bleeding, British Medical Journal, Oct. 23, 1999;319:1081-1082, 1106-1109 http://www.bmj.com/cgi/eletters/331/7516/529 http://www.webmd.com/depression/news/20030117/antidepressants-tied-to-stomach-bleeding Cox2 Inhibitors Anti-inflammatory (pain killers) medications—Vioxx, Celebrex, Bextra Thought to prevent GI bleeding, but recent data shows that they are not protective of the GI tract. Increases the incidence of heart attacks. Vioxx may have caused anywhere between 400 to 11000 heart attacks in older men according Dr. David Grahm’s report to the FDA panel. Vioxx was voluntarily pulled out of the market by Merck, September, 2004, but a FDA panel of “experts” was recommending that it be put back on the market because the other two drugs—Celebrex and Bextra— were still being sold and they have the same problem as Vioxx?!? (New York Times, Feb, 18, 2005) Disorders of the Upper GI Tract (May interfere with chewing and swallowing) Achalasia AIDS Alzheimer’s disease Broken jaw Cancer Chemotherapy Congenital defects Dental caries Dry mouth Gullain-Barre syndrome Head injury Ill-fitting dentures MS Missing or no teeth Myasthenia gravis Oral surgery Parkinson’s disease Peridontal disease Radiation therapy Temperature sensitivity Strokes Surgery ulceration Disorders of the Stomach GERD (Gastro-esophageal reflux disease) Indigestion, dyspepsia Gastritis Hiatal Hernia Peptic ulcers Nausea and vomiting the guy with the bow tie 42 GERD Prevention Eat small meals and drink liquids an hour before and after meals, avoid stomach distension Relax at mealtime, chew thoroughly, avoid swallow air Limit foods that relax the LES Avoid foods that are acidic, too hot or too cold Maintain healthy weight Avoid tight-fitting clothing Avoid bending down lower than stomach Stop smoking Avoid spicy foods 2/20/09 Treatment of GERD Most common cause of GERD is insufficient stomach acid production and delayed gastric emptying Betaine HCl Proteolytic enzymes Active Manuka honey (helps to kill h. pylori) Address ligament laxative problem Address emotional stress Don’t eat large meals when upset Treat hiatal hernia with soft tissue manipulations, diaphragm C3,4,5, mid thoracic, Psoas http://www.manukahoneyusa.com/gerd.htm The Lower Esophageal Sphincter AKA cardiac sphincter, gastroesophageal sphincter Substances that relax the cardiac sphincter: ●Alcohol ●Anticholinergic agents ●Calcium channel blockers ●Chocolate ●Diazepam ●cigarette ●Garlic ●high-fat foods ●Meperdine ●Onions ●Peppermint and spearmint oils ●theophylline Hydrochloric Acid Secretion Very energy dependent process—1500 Kcal per liter of gastric juices to concentrate the hydrogen ion to that concentration in the stomach HCl produced in the parietal cells at pH 0.8 pH reaches 1.0—2.5 after mixing with the other gastric juices at the gastric lumen HCl production Chloride ion is actively transported into the parietal cells from the blood Water is dissociated into hydrogen ion and hydroxyl ion Carbon dioxide combines with the hydroxyl ion to form bicarb ion with the aide of carbonic anhydrase Hydrogen ion combines with chloride ion to from HCl. http://hopkins-gi.org/multimedia/database/intro_247_Parietal.swf Signs and Symptoms of Hypochlordydria Bloating, belching or gas w/in 1 hour of post eating upper GI Bad breath (halitosis) Fingernails chip, peel or break easily Anemia unresponsive to iron Sense of fullness after meals Indigestion, diarrhea or constipation Multiple food allergies Nausea after taking supplements Itching around the anus the guy with the bow tie 43 Nutritional Physical Exam Findings Adult acne Dilated capillaries on nose and face Dandruff Soft, poor growth of fingernails Brittle and splitting nails White spots on nails (sign of zinc deficiency, Zn needed for HCl production) Loss of taste or smell (sign of Zn def.) Simple In-office Testing Zinc taste test—use 2% zn sulfate solution, positive if can’t taste HCl reflex—tenderness 1 inch below and to the left of xyphoid to the left edge of the rib cage HCl Chapman Reflex—tenderness in the 6th intercostal space on the left rib cage in the mid-clavicular line Other Tests Urine Indican—Increased level is an indication of protein mal-digestion, increase microbial fermentation of protein in the lower bowel Urine Sediment—Elevated uric acid residue due to poor protein digestion and hypochlorhydria H. pylori infection Other indications can be noted in blood chemistry test. Blood Chemistry Hypochlorhydria possible—Increased globulin level (>2.8 or 28 g/L) with a normal or decreased total protein (<6.9 or 69 g/L) Hypochlorhydria probable—Increase globulin (>2.8 or 28 g/L) with increase BUN (>16 if 40g/L) decreased or normal total protein and or albumin and or decreased serum phosphorous Other Blood Chemistry Indicators Increased or decreased gastrin Increased MCV and MCH Decreased calcium Decreased iron Decreased chloride Increased anion gap http://www.globalrph.com/anion_gap.htm AG=[Na+] - [Cl-] - [HCO3-] Decreased alkaline phosphatase Diseases Associated with Hypochlorhydria Chronic dysbiosis Diabetes mellitus Childhood asthma Thyroid problems Skin problems Hepatitis Osteoporosis Gallbladder Ds Chronic autoimmune disorders Myasthenia gravis Urticaria Adrenal exhaustion Chronic atrophic gastritis Chronic candida 2/24/09 Natural Therapy for Hypochlorhydria Betaine HCl—150 mg with meals to begin with, build slowly to max of 1500 mg with each meal. If experience burning, neutralize with 1 tsp of baking soda in water or milk, cut back to comfortable level Vinegar —start with 1 tsp of apple cider vinegar in water with each meal, build up to 10 tsp. Back off to comfort level if experience burning in the stomach Vitamin B12 and folic acid (see note) MVM Digestive enzymes Digestive Bitters Herbs: Gentian, Scutelaria, Goldenseal the guy with the bow tie 44 Patients with hypoHCl are more often than not deficient in B12 because of a decrease in HCL production from the parietal cells which lead to a drop in intrinsic factor production. Intrinsic factor is important for B12 absorption. An MCV greater than 89.9 is common finding in B12 deficicency. Look for other indicator of B12 deficiency such as MCHC and RDW. If these levels are elevated above normal. Methylmalonic acid and homocysteine levels are more sensitive B12 status tests. If suspect B12 deficiency, 1000 mcg of B12 injection weekly for 4 weeks and retest. Long term treatment, use sublingual B12 lozenges to prolong the effects of B12 shots. Hypersegmented neutrophils is sign of folic acid deficiency if found in microscopic blood smear. If you see there is a concomittant high serum B12 and a high MCV and other signs of B12 deficiency, suspect a decreased function of MTHFR (methylenetrahydrofolate Reductase) which is essential for the methylation of folate and the conversion of cobalamin into methylcobalamin, an essential step in converting homocysteine into methionine. Dietary Advise for Hypo HCL Chew food thoroughly Eat small frequent meals Avoid drinking liquids with meals The Myth of Acid Indigestion 95% of the times, people with GERD does not produce enough stomach acids--hypochlorihydria Rotten food in the stomach produces organic acids that are regurgitated into the esophagus--heartburn Conditions Associate with N/V Pregnancy GERD Esophagitis Peptic ulcer Gallbladder disorders Pancreatic disorders Kidney disorders Cancer, chemo therapy Delayed gastric emptying (diabetics) Carbonate beverages Minimize Nausea and Vomitting 1-2 teaspoons of apple cider vinegar Orthophosphoric acid Avoid overeating Use gallbladder support supplements—beet extract, bile salt replacement Ginger tea, mint tea B6 may be helpful for pregnancy related N/V Lemon, Ume plum Hiatal Hernia Another reason for acid reflux Overweight, smoking Certain foods such as coffee, chocolate, hot spices, mint can relax the lower esophageal sphincter allowing acid to get up into the esophagus Related to chronic ICV problem Gastritis, Peptic and Duodenal Ulcer Delay gastric emptying (gastroparesis) Decreases mucous protection due to complex hormonal changes Increases inflammation Presence of Helicobacter pylori Drugs that blocks acid production may lead to parietal cells atrophy. the guy with the bow tie 45 Signs and Symptoms of H Pylori Infections Discomfort in the upper GI especially the LUQ Bloating Nausea Vomiting possible Burning or pain int the upper abdomen an hour or so post prandial or in bed Patient may have—Crohn’s disease, gastritis, peptic ulcers, rosacea Associating Factors of Gastritis Regular use of pain relievers—NSAIDS, aspirin, ibuprofen, naproxen Excessive alcohol use—irritate and erode mucosal lining Stress—suppress parasympathetic system, reduce mucosal integrity Bile reflux disease—incompetent pyloric valve allows bile to flow into the stomach, neutralize acid and irritate lining lead to inflammation and chronic gastritis Complications of Chronic Gastritis Long-term effect: B12 deficiency mimic senile dementia Test for serum B12, MCV, MCHC, homocysteine and methylmalonic acid levels Signs and Symptoms of Gastritis Normal or very frequent stools Weak appetite Epigastric pain worse or better with eating Unexplained N/V Fever at any temp Blood in stools Weight loss Vomiting blood Bloating Belching Hiccups Intolerance to spicy foods Feeling of fullness in upper abdomen after eating Treatment for H. pylori Medication: antibiotics Natural treatments: Gum Mastica (Pistacia lentiscus), 1-2 g per day for 2 weeks Sulforaphane: Broccoli sprout concentrates Deglycerized licorice (DGL): heal stomach lining Herbs: myrrh, clove, anise seed, barberry bark, oregon grape root, wild indigo, cinnamon, oregano Manuka honey Probiotics Bismouth Treatment for hypo-HCl Natural Treatment for Gastritis Neem: antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, reduce stomach discomfort Slippery Elm: soothing mucilage coats GI tract, part of “Roberts Formula” Water: 4-6 glass during the pain DGL: heal stomach lining Aloe vera: sooth and heal GI lining Gamma-oryzanol: in rice bran oil, heals GI lining, affects ANS to normalize gastric secretion Cabbage juice: folk remedy for heartburn and ulcers, vitamin U for anti-ulcerative actions. 1 qt daily for 2 weeks Zinc: 50-100mg per day the guy with the bow tie 46 Robert’s Formula Although it has never fully studied in placebo-controlled trials, it has long been used by natural doctors treating suspected inflammation in the GI tract. It sometimes contains bismuth, which kills H. Pylori, usually found in upper GI ulceration, as well as other microorganisms. Sooths inflamed mucosa, heals ulcers and reliefs dysbiosis Cabbage leaf Geranium Marshmallow root Slippery elm Echinacea Goldenseal http://curezone.com/forums/fm.asp?i=280027 The 6R Program to Restore GI Health Supplements and dietary change to “Remove” pathological factors “Reduce” negative dietary factors “Restore” proper transit time “Re-inoculate” Beneficial factors “Replace” missing enzymes “Repair” damages done to the GI tract, mucosal lining the guy with the bow tie 47 Nutrition and The Digestive System—Part 3 Disorders of the Lower GI Tract Diarrhea Short-bowel syndrome Constipation Celiac Disease Irritable Bowel Syndrome Diverticulosis Gallbladder disorder Diverticulitis Fat malabsorption Inflammatory bowel disease—ulcerative colitis Pancreatitis Cancer Cystic Fibrosis Resections of large intestine Crohn’s Disease Dysbiosis http://www.jr2.ox.ac.uk/bandolier/booth/booths/gi.html Inflammation and Gut Health Inflammation is linked to all of these gut problems Controlling inflammation is paramount in controlling these GI troubles What are the causes of inflammation? A typical American diet is pro-inflammatory Stress-filled lifestyle for all ages Stress cause the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemicals Effects of Stress on the Body Endocrine system: Adrenalin and other stress hormones are secreted. Cause sympathetic hyperactivity: - Heart rate speeds up. - Muscles tension increases - Breathing rate speeds up - Brain becomes extra alert!! - Non-essential systems (immune and digestive) shut down temporarily - Cortisol, causes more sugars to go into the circulation, by converting fat and proteins. Increased risk for heart disease due to continued presence of stress factors Immune system can become depressed increasing risk of diseases, and decreasing the body’s resistance Digestive system: cramps, stomach aches, increased risk for ulcers, constipation, diarrhea Mental Health the guy with the bow tie 48 Immediate Response to Stress The brain becomes more alert. Heart rate increases. Adrenal glands produce stress hormones. Muscles tense. Breathing quickens. Digestive system slows down. Effects of Chronic Prolonged Stress Stress hormones can damage the brain’s ability to remember and cause neurons to atrophy and die. Baseline anxiety level can increase. Persistently increased blood pressure and heart rate can lead to potential for blood clotting and increase the risk of stroke and heart attack. Cortisol and other stress hormones can increase appetite and thus body fat. Cortisol increases glucose production in the liver, causing renal hypertension. Other Effects of Stress Stress can contribute to headaches, anxiety, and depression. Sleep can be disrupted. Stress can contribute to menstrual disorders in women. Stress can contribute to impotence and premature ejaculation in men. Muscular twitches or “nervous tics” can result. Mouth ulcers or “cold sores” can crop up. The lungs can become more susceptible to colds and infections. Immune system is suppressed. Skin problems such as eczema and psoriasis can appear. Stress can cause upset stomachs. Stress, HPA dysregulation and GI Problems Stress sympathetic over-activity depressed parasympathetic influence of the GI tract multiple GI disorders. Reduced gastric acid production reduce secretin and CCK gallbladder suppression fat malabsorption Gallstone fat soluble nutrients deficiency depress normal physiology and indigestion due to digestive enzyme deficiency. Malnutrition lowered immune function chronic infection and increase internal stress and maintain vicious cycles of illness S/S Digestive Enzyme Deficiencies Loose watery stool Maldigestion Post prandial abdominal pain Stool with undigested food Protein in stool Acne (toxic liver) Food allergies and intolerances Hypoglycemia Abnormal weight gain or loss GERD Bloating Dysbiosis (abnormal population of flora) IBS UC Diseases Associated with Pancreatic Enzyme Deficiencies Diabetes Cystic fibrosis Chronic pancreatitis Malabsorption IBS UC IBD Dysbiosis the guy with the bow tie 49 Irritable Bowel Syndrome IBS is a poorly understood condition relating to functional abnormality of the lower GI tract, 20% of the adults in the US suffered from it. Symptoms: abdominal cramps, painful and explosive diarrhea, and/or constipation, mucous in the stool, bloating, gas, not able to completely empty bowel or feel like it is not completely empty Diagnosed by ruling out physical causes Since there is no known cause, there is no known cure—medications for symptomatic relief--antispasmodic, laxative, antidepressants Certain foods can cause symptoms—sub-clinical gluten intolerance Food sensitivity and dysbiosis are considered suspects by many alternative health professionals Stress’ also considered as a major trigger Symptoms of IBS Abdominal distention, spasm and pain Abdominal pain relief with defecation Increase stool frequency Alter stool consistency Mucus in stool Incomplete evacuation Bloating and gas Diarrhea and constipation alternate 2/25/09 Testing To rule out organic disease such as Crohn’s, UC, cancer or parasitic infections Work up for hypochlorhydria Allergy and food sensitivity Fatty acid profile: n-3 to n-6, imbalance linked to inflammation response Lactose intolerance test--([hydrogen] in breath) Disaccharides intolerance—mannitol. Sucrose, sorbitol, maltose Tests Highly level of methane in hydrogen breath test, indicates Clostridium difficile infection CDSA with parasitology Intestinal permeability test Hormonal imbalance Genetic factors Psychological trauma or depression IBS Imbalance of gut hormones especially serotonin may be a key to solve the mystery. Prozac can cause diarrhea and constipation depends on the dose. The drug, Zelnorm acts as a serotonin agonist, stimulates GI tract motion What in nature can cause an imbalance of the serotonin system? Any addictive stuff. Sugar is universal. http://www.bioterrain.co.uk/IBS.html http://www.drugs.com/zelnorm.html Natural Therapy for IBS Antimicrobial substances and herbs such as Grapefruit seed extract Probiotics Improve digestion Avoid antigenic foods Low-fat, high fiber diet Natural anti-inflammatory herbs and functional food supl. Herbal pain management Repair the GI the guy with the bow tie 50 Dysbiosis Abnormal population of flora in GI tract The overgrowth of harmful microbes in the oral cavity, GI tract or vaginal cavity Common criminals: yeast, bacteria, parasites E. coli, salmonella, giardia, blastocytisis, cryptosporidium, candida sp. http://mdheal.org/parasites.htm Dysbiosis Induces Diseases Inhibit normal flora leads to nutrients deficiencies Cause inflammation in the GI, vagina or sinus Compromise nutrient absorption Produce toxins increase liver burden Decrease short chain fatty acid in colon thus increase risk of colon cancer Produce trans fatty acids in colon Leaky gut syndrome Deplete B12 and some amino acids Interfere with bile acid and estrogen elimination by deconjugating metabolites in bile and increase breast and uterine cancer risks Causes of Dysbiosis Antibiotics Hypo-HCl Presence of xenobiotics, chemicals and heavy metals Parasitic and yeast infections Pancreatic insufficiency Slow GI transit time or stasis Poor GI immune fxn, low SIgA Nutrient deficiencies Low fiber diet Alkaline GI pH S/S of Dysbiosis Unexplained abdominal symptoms Frequent stools Intolerance to sugar, starch, fiber or probiotics Odiferous flatulence Bloating Chronic fatigue Headaches Skin problems Vaginal yeast infection Diseases and disorders linked to dysbiosis IBS, UC, IBD Inflammatory and autoimmune dz Food allergies and intolerance Breast and colon cancer Chronic fatigue and fibromyalgia Atopic eczema Pancreatic insufficiency Leaky gut Candidiasis Endocarditis Malnutrition the guy with the bow tie 51 Conventional Treatment Antibiotics Antifungals: Diflucan Antiparasitics: Flagyl Probiotics Natural Therapies Grape fruit seed extract Oregano oil Olive leaf extract Black walnut hull Goldenseal Wormwood Bayberry Enzymes Probiotics—restore normal flora http://mdheal.org/articles/word2/gastrointestinalisorder2.htm Leaky Gut Syndrome S/S Diarrhea Allergies Cramping Eczema, psoriasis Bloating Migraine headache Flatulence Malnutrition Weight loss Depression and anxiety Steatorrhea http://mdheal.org/leakygut.htm http://www.anapsid.org/cnd/diffdx/leakygut2.html Tests for Leaky Gut Syndrome The Intestinal Permeability Test: pre and post urine recovery samples with mannitol and lactulose challenge (Genova Diagnostics) Mucosal Barrier Test (ImmunoSciences, Inc, Bio-Health labs) SIgA (Diagnos-Tech, Bio-Health, Genova, Doctor’s Data) Stool and saliva samples http://www.genovadiagnostics.com/ http://www.doctorsdata.com/home.asp http://www.diagnostechs.com/ http://www.biodia.com/ Natural Tx for Leaky Gut Syndrome Restore Bowel Flora Heal the GI lining: L-glutamine, butyric acid, fatty acid supplements Biliary Insufficiency/Stasis S/S Pain between shoulder blades Greasy food upset Steatorrhea, loose, bulky, odorus stools Nausea Motion sickness Morning sickness Dry itchy skin, peels on heels Headache over eyes Gallbladder attacks Hx Bitter taste in mouth after meals Dark orange urine the guy with the bow tie 52 Physical Findings of Biliary Insufficiency Dry scaly hyperemic ear canal with dark wax Dry skin, hair Red bumps on the elbow Follicular hyperkeratosis Xanthelasma on the eyelids Xanthomas Clubbing of the fingers Murphy’s sign Tenderness and nodulation on right thumb web Pain over the gallbladder area at 6th intercostal space Nutrients to thin the bile Bile salt Taurine Pancreatic lipase Vitamin C Phosphatidylcholine Lecithin (raw egg yolk is the best source of lecithin) Choline and methionine (lipotropic factors) Pancreatic enzymes Cholagogues and antispasmotic Artichoke leaf extract Beets Spanish black radish (high is sulfur – methyl glycine) Dandelion root Celandine Milk thistle Peppermint oil (enteric coated)—use on empty stomach, or use topically for difficulty passing stools with spasm The Effects of Fat Malabsorption the guy with the bow tie 53 Lactose Intolerance Your Gut—The Drug Maker According to a research from the University of Michigan, the human brain contains receptors for benzodiazepine, a drug that relieves anxiety, suggesting that the body produces its own internal source of the drug Patients with liver failure, fell into a deep coma. The coma can be reversed, in minutes, by giving the patient a drug that blocks benzodiazepine. Could depression be caused by a distressed gut releasing too much benzodiazepine? Restore and Maintain Gut Health The body is a self-regulating organism There are lots more that our body can do than our conscious mind can ever comprehend Innate intelligence Our ancestors did not have to study what to eat or what medications to use All they had to do was eat whatever mother nature provided for them—they stayed healthy 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. Eat wholesome natural, organically grown foods Avoid all forms of processed foods, refined sugars and carbohydrates Minimize exposure to toxic chemicals and metals Get enough sleep, in total darkness Eat enough, but not excessive fiber: vegetables, nuts, seeds, whole grains and fruits Drink adequate but not excessive clean water, but don’t drink too much water with meals Chew slowly and thoroughly (Fletcherizing) Eat until only 80% satisfy Do not eat while upset, worry or angry Do not eat within three hours of bed time Do not use drugs unnecessarily Use probiotics or lacto-fermented foods to replenish friendly flora Use coconut oil, raw cream or butter for their antimicrobial short and medium chain fatty acids Avoid eating raw foods if any GI ailments present Eat with relaxing music and with loved ones, in silence Use nutritional, herbal and homeopathic supplements Exercise regularly, but not after 5 pm Avoid foods you are sensitive to Sleep between 10pm to 6am regularly The 4R Program Jeffrey Bland, PhD, has outlined a natural course of care for these digestive complaints, called the 4R approach. It involves: Removing infective organisms, which can be properly diagnosed with a stool analysis (CDSA Labs); Reinnoculating the gut with friendly bacteria to completely reset the digestive and repair function. Repairing the GI lining, often using proteins and fats; Replacing digestive enzymes and acids to give your digestion a “help” initially the guy with the bow tie 54 2/27/09 -theory behind homeopathy: -in tiny quantities, an herb eliminates the symptoms that it would otherwise cause in a large quantity -for example, in large quantities an onion causes cold-like symptoms (runny nose, eyes, etc) -therefore, in very small quantities, onion can remove cold-like symptoms The 6R Program to Restore GI Health Supplements and dietary change to “Remove” pathological factors “Reduce” negative dietary factors “Restore” proper transit time “Re-inoculate” Beneficial factors “Replace” missing enzymes “Repair” damages done to the GI tract, mucosal lining The 6R Program--Remove Elimination of pathogenic microbs—yeast, parasites, bacteria, virus etc. that may be present, with plant enzymes, herbs, homoeopathic preparations, bioresonance therapy (Rife frequency generator) and ozone therapy. Reduce sugar, refined carbohydrates, saturated fat, red meat. Increase dietary fiber and water. Coconut oil, olive oil have antimicrobial activities Research for herbs and nutrients that can remove microbial infestation Antimicrobial herbs Zymex (SP)—yeast Zymex II (SP)—parasites Articin (Thorne), Wormwood—parasites Black walnut hull--parasites Garlic—fungus, parasites, virus (soak garlic in apple cider vinegar for a few weeks) SF722 (Thorne)— yeast Enzymes, Cat’s claw, Olive leaf extract, coconut oil, grapefruit seed extract, oregano oil Goldenseal, andrographus The 6R Program--Reduce Reduce negative dietary factors Refined sugars Refined flours Additive and preservatives Food antigens—gluten, dairy, lactose, soy Specific diets Specific carbohydrate diet Anti-inflammatory diet GFCF The 6R Program--Restore Restore proper intestinal transit time Fruits and vegetables Dietary fiber supplements Essential fatty acid Acidifying GI pH—lacto-fermented vegetables, vinegars and dairy Home-made pickles, chutneys the guy with the bow tie 55 The 6R Program—Re-Inoculate Reintroduction of desirable gastrointestinal microflora Lacto-fermentation A good source of beneficial microbs: Lactobacillus, bifidobacterium Lactobacillus sporogenes Hemostatic soil organisms (HSO) Lacto-fermented dairy, vegetables, vinegars, Kombucha Lactic acid yeast, Saccharomyces boulardii http://www.blackwell-synergy.com/doi/abs/10.1111/j.1523-5378.2007.00516.x?journalCode=hel Kombucha has been used for centuries in eastern lands as a valuable aid to good health. One of the earliest records goes back to approx. 447AD when a Korean physician named Kombu treated the Japanese nobleman Inkyo with the tea elixir. Such was its success that it rapidly spread from Japan to Manchuria, and into Russia. The name Kombucha is derived from Kombu, (the Korean physician) and Cha an eastern name for tea. The Kombucha fungus (it is actually a lichen) has the unique ability to turn tea and sugar into a highly beneficial drink producing many essential acids whilst only producing a minute amount of alcohol. Kombucha elixir has the ability to de-tox the body, boost the immune system and improve energy levels. It produces Glucuronic Acid useful for de-toxing and boosting the immune system, Usinic Acid useful in cases of Uria (gout) to rid the body of impurities, Lactic Acid, essential for a healthy digestive tract and Acetic Acid useful as an antiseptic and for inhibiting harmful bacteria. It can also produce Citric Acid, Malic Acid, Butyric Acid, Amino Acids and almost all of the B complex vitamins. Kombucha brewing has gained in popularity in recent years in the west either by the batch method or more recently by the continuous fermentation process. 3/3/09 The 6R Program—Replace Replacement of digestive factors and or enzymes whose intrinsic function maybe limited or inadequate. These substances facilitate the breakdown of foods to the basic molecular compositional units and/or their preparation for absorption. Probiotics The 6R Program--Replace Betaine HCl Bile salt Beet root and leaves extract Plant enzymes—bromelain, papaya enzyme, mold enzymes Proteolytic/pancreatic enzymes Pancreatic or plant enzymes, bile salts digestive herbs, Betaine HCI. (hydro-chloric acid) are some of the main replacement items. To aide digestion while repairing the GI tract, support digestive enzymes activities and gallbladder function. The 6R Program--Repair Repair refers to the provision of nutritional support for regeneration of the intestinal mucosa. The G.I. mucosal cells represent the largest mass of rapidly proliferating cells in the body of normal individuals. Damage can occur through chronic dietary insufficiency, food allergens, pathological infections, parasites, viruses, candidasis etc. Damaged mucosa leads to the syndrome we generally call "leaky gut". Think of the gut wall as a one-way fence, with small "holes" in it to allow the passage of nutrients. If they enlarge due to damage, toxins can pass through as well, thus damaging liver function, increasing bile, carcinogens, free radicals, ending up with systemic toxic overload, eczema, pancreatitis, gallstones, I.B.S., fatigue, arthritis, shortness of breath, poor exercise tolerance. Treatment includes vitamin therapy, Vitamin C, E & A, Beta-carotene, Aloe Vera, Glucosamine and the remedies mentioned under the "Remove" section. Anti-inflammatory and Pain management Gamma-oryzanol EPA/DHA Artichoke leaf extract Boswellia Peppermint oil Ginger Turmeric Antispasmodic herbs—chamomile, melissa, rosemary, valerian, skullcap, passion flower the guy with the bow tie 56 The 6R Program--Repair Herbs or nutrients that speed the healing of damaged gut mucosa Slippery Elm bark Aloe vera Colostrum Coconut oil N-acetyl-cysteine (a precursor to the antioxidant glutathione) L-glutamine Quercitin (a bioflavanoid) Folic acid Gamma-oryzanol Antioxidant vitamins—A, C, E MVM Zinc Clear digestive problems first Patients with marked GI symptoms Lab test: stool analysis, food intolerance Dietary recommendations Supplements: Antimicrobial herbs Digestive enzymes Probiotics Nutrients that protect and heal mucous membrane Caution Do not recommend a liver detox for patients with severe GI disturbance Patients must have normal bowel movements before engaging any detox program Emotional Stress Relief Techniques for emotional problems—NET, EFT (www.emofree.com, www.tapping.com) Time management Get together with friends Practice forgiveness Volunteering and reach out to others Exercise—yoga, Taichi, breathing exercise Hobbies To learn more… www.westonaprice.org www.mercola.com The Second Brain, Michael Gershon Natural Ways to Digestive Health, Stephen Holt. http://www.whyagain.com/book.htm -- an ebook of taking responsibility of our lives. Google “Inverse paranoid” *always take care of the GI problem first -herbs, nutrition, adjust, acupuncture, and soft tissue the guy with the bow tie 57 Functional Approach to Endocrine Disorders (part 1) 3/4/09 Foods as Hormonal Signals from Nature • • • • Foods provide the chemical signals from nature to coordinate our micro-endocrine system Nutrients from real foods connect humans to the macro-endocrine system of the earth We are all One—children of Gaia Our ancestors had to eat according to seasons. (Isotopic Evidence for Dietary Variability in the Early Hominin Paranthropus robustus. Science, Nov 10, 2006, Vol. 314. no. 5801, pp. 980 - 982 ) -vegetables and fruits (foods high in water) tend to be yin (cooling) -animal proteins (and cooked foods) are yang (warming) -when we eat winter foods in the summer (like barbecue), then we’re more likely to get overheated Clinical Endocrinology • • The branch of medicine dealing with the endocrine glands and their hormones Identify organs or glands that are deficient or non-functioning and use some type of pharmaceutical agent or hormone to replace, suppress or support the dysfunction glands • Specific for certain genetic disorders and disease patterns that alter hormone production or functions pathologically http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/bv.fcgi?rid=endocrin.TOC&depth=1 Functional Endocrinology • • • • • • Identifies alterations in the endocrine systems at subclinical states prior to the point of clinical diagnosis Typically not considered for treatment by conventional/allopathic medicine Subclinical problems are not considered diseases and left untreated Conventional blood and urine tests and reference ranges may not detect functional endocrine imbalances Left untreated, functional imbalance will progress to disease states Patients typically suffer from multiple organ dysfunctions, fatigue and depression for prolong period of time until objective measurements are evident in lab tests • Increased risks for many disorders • Example: Insulin Resistance • Elevated blood pressure, dyslipidemia, • Treated with statin for symptoms • Increase risks for multiple organ disorders • Culminate in diabetes, heart failure, obesity, CVD, PVD, eyes and kidney damages • The sick gets sicker with more and more suffering before disease state is reached and thus “diagnosed” • Understand and support a complex series of vicious cycles that feed each other • Identify these pattern • Provide nutritional support and counseling to unlock these vicious cycles • Look for the root causes • Not just identify symptoms and supply a magic pill to manage them http://hormoneseminars.com/seminar.htm What is Functional Endocrinology? Endocrinology is the branch of medicine dealing with the glands and their hormones. Functional endocrinology identifies abnormal alterations in the endocrine systems that are not in a diagnosible disease state. This is done by narrowing the blood work from the laboratory's normal range to the true "healthy" range which is a smaller margin within the lab range. For example, the normal lab range for thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) is 0.5-4.5 however the 'healthy' range lies between 1.5-2.5. If your TSH is less that 1.5, and along with other clinical correlations, an astute clinician with the knowledge of functional endocrinology can suspect sluggish thyroid function with or without obvious symptoms to the patient! People suffer from with many alterations in the endocrine systems that are not in a disease state, if not treated at the early signs of dysfunction may lead to pathology down the road. If these functional endocrine disorders are not diagnosed as abnormal and therefore are left untreated in the standard healthcare, these people will continue to suffer until manifestations of disease become apparent. These patients typically suffer from wide ranges of symptoms from, digestive problem, fatigue to severe depression. Allopathic doctors are trained to diagnosed condition by look for signs and symptoms and then prescribe medicine for “it.” Functional endocrinology, however requires the detective work necessary to find the main culprit that leads to the signs and symptoms that the allopath prescribes medication for. For example, in the traditional endocrine model, patients that present with elevated blood pressure or cholesterol will be placed on pharmaceutical agents to alter the secondary changes that may take place from insulin resistance. In functional endocrine model, factors that change metabolism, altering physiological response will be evaluated first. An example of this is managing the primary concern of insulin resistance and looking for improvements in blood pressure and cholesterol values. the guy with the bow tie 58 Functional endocrine disorders also increase risk for many disorders if untreated. In order to practice functional endocrinology, the clinician must understand the depth of human physiology and metabolism. Functional endocrinology involves understanding and supporting a complex series of vicious cycles that feed each other; therefore, the range of ailments assessed is wide and includes but is not limited to slow working thyroid (hypothyroidism), hypertension to high cholesterol, PMS to perimenopause, menopause to depression, fatigue to fibromyalgia, IBS to GERD, etc. Steps in Managing Functional Endocrine Disorders 1. 2. 3. 4. Understand the complex interactions of hormone metabolism Select the appropriate laboratory test and follow up from the patient’s first visit and history Understand the latest scientific research in the field of diet, nutrition, lifestyle and other non-invasive therapies Properly educate patients to assure compliance to diet, lifestyle changes and supplement protocols Vicious Cycles of Endocrine Imbalance Primary Physiology - Endocrine Hormones and neurotransmitters are the first control system for homeostasis response – lifestyle and dietary stress can cause system-wide breakdown in hormonal balance • Amino Acid based: – Endocrine – Insulin, Glucagon, Somatohormone, Insulin-like growth factor (IGF), Thyroxin… – Paracrine, pineal & neurotransmitters– Melatonin, Acetylcholine, Dopamine, Serotonin… • Cholesterol based: – Steroid endocrine – Cortisol, DHEA, Estrogen, Progesterone, Testosterone, • Fat based: – Autocrine – Eicosanoids, Prostaglandins the guy with the bow tie 59 3/6/09 Different mechanisms of cell signaling Prostaglandin synthesis and related compounds Chemical structures of the three major classes of human hormones the guy with the bow tie 60 Functional Endocrine Analysis • • • • • • • Hormone Synthesis Hormone transport Hormone peripheral conversion Hormone detoxification Hormone receptor binding Intercellular transduction Transcription and proteomic response Hormone Synthesis • • • • Secondary defects to hypothalamus pituitary function Drugs and synthetic compounds that inhibit synthesis Antibody reaction that inhibit function Lack of nutrients or cofactors that impact synthesis or release Hormone Peripheral Conversion • • • • Synthetic compounds and drugs that impact binding hormones Hormones that impact binding proteins Natural compounds that alter binding proteins Organ dysfunction impairs hormone conversion and activation Hormone Detoxification • • • • • Phase I—oxidation/reduction Phase II—hydroxylation, sulfation, sulfoxidation, glucoronidation, methylation, glutathione conjugation, amino acid conjugation Drugs and synthetic compounds that impact detoxification Natural compounds that alter detoxification polymorphisms Polymorphism (Biology). The occurrence of different forms, stages, or types in individual organisms or in organisms of the same species, independent of sexual variations. (genetics)The existence of a gene in several allelic forms Hormone Receptor Binding • • • • • • Drugs and synthetic compounds that alter binding Natural compounds that alter binding Polymorphism Hormones and intercellular mediators that alter binding Intercellular mediators that alter transduction Transcription and proteomic response to cell response Laboratory Analysis for Hormones • Saliva tests – less expansive – non-invasive – free fraction of hormone – measure circadian rhythms and entire menstrual cycle – unable to test for binding globulin – not available for all hormones – Lack of general understanding of their application and interpretation by the allopathic community • Serum tests – More expansive – Required the service of a blood draw – Measure all hormones bound to protein which do not give the amount of free active hormones – Do not differentiate the bound and free hormones—no information on the actual hormone activity – Serum free hormone tests are costly – Reference ranges varied between labs and includes patients with pathological levels calculate as averages the guy with the bow tie 61 Lab Analysis cont… • Urine tests – Measure hormone metabolites after they have passed detoxification – Not reliable to determine the amount or rate of hormone produced by the organs or glands – Amounts detected is altered by the rate of liver detox and kidney clearance in the individual – Estrogen metabolites can be used to determine the risk for estrogen proliferative disorders – Bone markers for assess bone metabolism – Neurotransmitters • Hair Analysis – Measure physiological minerals in hair – Magnesium, calcium, potassium, sodium, zinc, copper and phosphorus – Ratios of specific minerals indicate endocrine functions – Intracellular assessment – Indication of disease process in the making or imbalance in endocrine function before reaching disease state – Non-invasive and inexpensive – Provides easy monitoring on an ongoing basis www.Drlwilson.com Hair Mineral Ratios • • • • • • Ca/Mg (6.67:1) indicates pancreas function Ca/K (4:1) indicates thyroid function Na/Mg (4.17:1) indicates glucocorticoid function Na/K (2.50:1) indicates mineral corticoid function Ca/P (2.5:1) indicates protein utilization and absorption balance Zn/Cu (8:1) indicates sexual hormones balance Types of Salivary Hormone Profiles • • • • • • • • Adrenal Stress Index (ASI)—circadian cortisol rhythm in a single day Short Post Menopausal Panel (PHP1)—baseline female hormones levels of one random sample, for those on HRT Long Post Menopausal Panel (PHP2)—two saliva samples separated by 5-7 days Expanded PHP1—include the measurement of pituitary hormones, for those that are NOT on HRT Pre Menopausal Female Hormone Profile (FHP)—11 samples during one menstrual cycle Expanded Pre Menopausal Female Hormone Profile (eFHP)—include pituitary hormones Male Hormone Panel (MHP) Expanded Male Hormone Panel (eMHP) Prioritizing Patient Evaluation and Management 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Identify and manage any and all gastrointestinal disorders, food sensitivities and bowel dysfunctions Identify and manage adrenal and blood sugar disorders Identify and manage any alterations in liver detoxification Identify and manage any imbalances in essential fatty acid metabolism Identify and manage any significant deficiencies in B-complex, trace minerals and magnesium—indicated by the amount of refined carbs consumption by patients. the guy with the bow tie 62 Growth of Physicians and Administrators 1970-2005 This chart helps us explain why we can spend so much more for so much less. Among the nations we just looked at, all of them have take the fundamental step of rejecting the financing of care by for-profit insurance companies, except for the United States. The natural market behavior of insurance companies is to compete to cover healthy, profitable people while shunning anyone who actually needs care. To do this, they erect massive bureaucracies with no purpose other than to fight claims, issue denials and screen out the sick. They consume care dollars, but their main output is paperwork headaches. In response, hospitals and doctors’ offices must employ armies of administrators to deal with the separate payment bureaucracies of thousands of different insurance companies. U.S. businesses are saddled with the costly burden of administering their own health benefits. Co-payment collection and processing, eligibility determinations, utilization reviews: the scope of the bloat is staggering. This slide begins to give a idea of the explosion of administrative waste within our health system. Adrenal Stress Syndrome The stressed-out-burned-out dragged-out-all-frazzled syndrome What Do These Diseases Have in Common? • • • • • • Multiple Sclerosis Ulcerative Colitis Atherosclerosis Hydrochloric Acid Deficiency Constipation Periodontal Disease • • • • • Sugar Craving Estrogen Dominance Weakened Immune System Obesity Coronary Disease American Psychological Association • • • Forty-three percent of adults suffer adverse health effects from stress. Two-thirds of all office visits to family physicians are due to stress-related symptoms. Stress is linked to the six leading causes of death—heart disease, cancer, lung ailments, accidents, cirrhosis of the liver, and suicide. Foundation for Integrated Research In Mental Health • Globally, more than 3 out of 5 doctor visits are for stress related problems. Endocrine System • • • HPA axis is the key to health and resilience, which is another word for health It should be called the “HPTPAG” axis as the entire endocrine system that organized core health Foundational health rests upon this endocrine axis as the most important element of a stable resilient system capable of modulation in response to need/stress the guy with the bow tie 63 What Is Stress? • A physical, chemical, or emotional factor that causes bodily or mental tension and may be a factor in disease causation. 3/10/09 How We React To Stress • • • • • • • • What We Eat How We Digest How We Assimilate How We Eliminate What We Do How We Breathe shallow breathing mimics the stress mechanism (signals brain that we are stressed) What We Think What We Inherit the guy with the bow tie 64 Adrenals Hormones Adrenal hormones/actions: Medulla - Epinephrine/Norepinephrine – fight/flight Zona Reticularis – DHEA, Pregnenelone, Progesterone, Estrogen, Testosterone, Androstenidione – Antioxidant, repair, sex hormones, cortisol balance, anti-aging Zona Fasciculata – Cortisol – glycemic regulation, anti-inflammatory, immune response, vasculature tone, CNS stimulation, stress reaction normalization Zona Glomerulosa – Aldosterone – Regulation of Na, K, and fluid Adrenal Functions • • Hormone production—stress response – Adrenal cortex hormones: cortisol, aldosterone, progesterone, DHEA – Adrenal medulla hormones: epinephrine and norepinephrine The ability of the adrenal glands to secret reproductive hormones after menopause will have a dramatic effect on how a women experience menopausal symptoms related to diminishing sex hormone production by the ovaries Adrenal Cortex Hormone Pathways the guy with the bow tie 65 The Adrenal Stress Response • • • http://www.unm.edu/~lkravitz/Article%20folder/stresscortisol.html Alarm reaction – Initial response – Hyperfunctional – Increased cortisol with normal DHEA Resistance stage – Prolonged stress – “Prenenolone steal” – Increased cortisol with low DHEA Exhaustion Stage – Adrenal cannot adapt to stress—final stage – Normal cortisol with low DHEA, hyper or hypo with normal DHEA, when depleted, low cortisol and low DHEA, finally, low cortisol and normal DHEA Adrenal exhaustion progresses in three stages • Stage I is distinguished by an increase in output of ACTH by the anterior pituitary gland, increased adrenocortical stimulation, increased cortisol output and an increased probability of pregnenolone steal and decreased DHEA. Generally in Stage I cortisol increases and DHEA and its metabolites decrease or an imbalance occurs especially between testosterone and estrogen. • Stage II Adrenal Exhaustion is marked by the transition from increased to decreased cortisol output. This stage is characterized by continuing high levels of ACTH and thus: adrenocortical stimulation, normal total cortisol output, low or borderline low morning, noon or afternoon cortisol levels, normal nighttime cortisol level, and an increased probability of pregnenolone steal and a further decrease in DHEA. This is a transitional phase in which although ACTH stimulation remains high or even increases, the adrenal output of cortisol declines due to the adrenal fatigue associated with continued hyper stimulation. • Stage III Adrenal Exhaustion is an advanced stage of adrenal exhaustion characterized by decreased total cortisol output. This stage is characterized by continuing high levels of ACTH and thus adrenocortical stimulation, low total cortisol output, and increased probability of a low nighttime cortisol level and pregnenolone steal and even further decrease in DHEA. The adrenal glands are now exhausted to the point that even though there is ongoing hyperstimulation (high ACTH); they continue to lose their capacity and reserve to produce enough cortisol. The eventual result is a crash of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis (HPAA) in which essential neuroendocrine feedback loops are unable to return the system to homeostasis. During a high stress situation, levels of sIgA decrease. Secretory IgA protects the gut from pathogenic material. Chronic cortisol elevation may be associated with high antigliadin antibodies (gliadin is a protein component found in wheat) due to intestinal hyperpermeability. • • Cortisol Activity in Body • • • • • • • • • Increases glucose formation, and protein breakdown Increases glucose utilization by the CNS Increases "insulin resistance" in peripheral system Suppresses gastric emptying, slows digestion Inhibits sex hormone effects and production, alters reproduction Increases sodium retention — high blood pressure Suppresses immune function Alters thyroid function, production, and effectiveness Depletes the body of Magnesium, Zinc, Glutamine, Carnitine, etc Cortisol protects the cell from: http://charles_w.tripod.com/cortisol.htm Excess insulin Inflammatory reactions Electrolyte imbalance (Na, K) Cell dehydration Cell damage Auto-immune reactions Deficient blood glucose the guy with the bow tie 66 Adrenal fatigue/ Inadequate cortisol: • Potassium excess • Auto-immune reactions • Sodium loss • Deficient glucose • Electrolyte imbalance • Deficient energy production • Cell dehydration • Deficient enzyme production • Insulin excess • Decreased cellular repair • Increased cell damage http://www.drlam.com/A3R_brief_in_doc_format/adrenal_fatigue.cfm Adrenals – Known and as yet unknown • • • • Adrenal fatigue AKA Sub-clinical hypoadrenia, Hypoadrenia, Non-Addison’s hypoadrenia, Sub-clinical adrenal exhaustion, Neurasthenia, Hypocortisolism, Functional Hypoadrenia Total depletion of the adrenals is called Addison’s Disease and can be fatal but rare When the adrenals cannot keep pace with the demands placed upon them by the total amount of stress, it produces a condition called Adrenal Fatigue Adrenal fatigue first observed and recorded in 1898 in France by Emile Sargent as a sequelae to influenza Frequency of Adrenal Fatigue • “For the sake of credibility we have previously stated that about 16% of the population has some moderate to severe degree of hypocortisolism with hypoglycemia, but in actuality, the figure should read 67%, if all the arthritics, asthmatics, and hay fever sufferers, alcoholics and other elated groups were included.” J. Tintera, Hypocortisolism – Adrenal Metabolic Research Society of the Hypoglycemia Foundation, 1974 3/11/09 Adrenal fatigue incidence … hypocortisolism appears to be a frequent and widespread phenomenon C. Heim, Psychoneuroendocrinology, 2000 Jan; 25(1):1-35 80% of Americans are suffering from adrenal fatigue, and the other 20% are in denial! John Morganthaller, 2002 – author of Smart Drugs I&II Hypoadrenia Associated Conditions • • • • • • • • Fibromyalgia Chronic Fatigue Syndrome Rheumatoid Arthritis All autoimmune diseases (3,000) Cancer survival Asthma, Respiratory ailments Influenza Most diseases for which cortico-steroids are administered as treatments – If a condition responds to steroid tx, it is associated with adrenal fatigue Hypoadrenia and Clinical Conditions • • • • • • • • • • • • Immune down-regulation • Poor wound healing Cardiac myasthenia (inotrophic & chronotrophic) • Increased susceptibility to infection Loss of stamina/resilience • Alcoholism & Drug addiction Emotional paralysis • Burnout Jet lag • Hypoglycemia Altitude Sensitivity • Allergies Declining athletic performance • Environmental Sensitivities Post Traumatic Disorder Syndrome (PSTD) • Unresponsive hypothyroidism Sexual dysfunction, Libido loss Increased perimenopausal/menopausal condition Premenstrual tension, especially depression Depression – Loss of motivation, collapse after bad news, overwhelmed -ginseng increases cortisol output (used in chronic wasting/fatigue diseases) -getting frequent colds (coryza) is a form of adrenal fatigue -too much cortisol can shut down your thinking cortex the guy with the bow tie 67 Adrenal fatigue in PMS • Women who were significantly more depressed premenstrually showed significantly lower cortisol levels on the premenstrual day as compared to the postmenstrual day • Across the menstrual cycle, women who were significantly more depressed premenstrually also had lower evening cortisols in their premenstrual phase J. Odber at al, Psychosomatic Research, 1998 Dec; 45(6):557-68 The Heart of Cortisol – Cortisol concentration after out-of-hospital cardiac arrest are lower than those concentrations reported in other stress states – There is an association between cortisol concentrations and short-term survival after cardiac arrest. Survivors have significantly greater increase in serum cortisol concentrations than non-survivors during the first 24 hours – Lower than expected cortisol concentrations for the extreme stress of cardiac arrest may have pathologic significance in the hemodynamic instability seen after return of spontaneous circulation – The etiology of low cortisol concentrations may be primary adrenal dysfunction C H Schultz et al, Critical Care Medicine, 1993 Sep; 21(9): 1339-47 Adrenals & Survival • • • Adrenal dysfunction is common in high-risk ER patients. Overall it has a frequency of 19% among a homogenous population of hemodynamically unstable vasopressor-dependent patients -Emanuel Rivers et al, Academy of Emergency Medicine, 1999, Volume 6 (6), 626-630 These results indicate that adrenal dysfunction is common among a group of critically ill patients seen in this hospital ER. -SS Chang, Academy of Emergency Medicine, 2001 July; 8(7):761-4 The greater the adrenal fatigue, the less likely one will survive cardiac arrest or other life-threatening situations. -James Wilson, Adrenal Fatigue Hyperadrenia • • Elevated cortisol suppresses TSH, inhibits the conversion of T4 to T3, and increases the conversion of T4 to rT3 Cortisol reduces progesterone levels in primates, impairs endometrial secretions, increases estrogenic stimulation of endometrium • Cortisol interrupts testosterone, progesterone, DHEA, T3 and estradiol -too much estrogen can cause endometriosis, fibroid production, or uterine/ovarian cancer Cortisol Imbalance S&S • • • • • • • • Fatigue Headache with physical or mental stress Weak immune system Allergies Slow morning start Gastric ulcer Afternoon headache Weight gain • • • • • • Crave sweets, caffeine, nicotine Blurred vision, unstable behavior and mood Shaky and lightheaded if hungry Irritable before meals Eating relieves fatigue Cannot stay asleep or fall asleep Epinephrine Function • • • • • • Epinephrine causes transient hyperglycemia by activating enzymes whose actions promote gluconeogenesis and glycogenolysis in the liver while inhibiting glucose breakdown. Epinephrine decreases glucose uptake in the muscle and other organs and decreases insulin release from the pancreas. The decrease in insulin release prevents glucose from being taken up by the peripheral tissue and thus preserves it for the CNS. Epinephrine mobilizes free fatty acids and cholesterol by stimulating lipolysis, freeing triglycerides and fatty acids from fat stores, and inhibiting the degradation of circulating cholesterol to bile acids. Epinephrine increases oxygen supply, bronchodilation and increased ventilation. Epinephrine decreases protein synthesis -adaptogens help to balance the hypo/hyper adrenal function -deep breathing tells your brain that you are not stressed the guy with the bow tie 68 Norepinephrine Norepinephrine rarely if any reaches distal tissue and principally is involved in the regulation of blood pressure. • It is the primary constrictor of smooth muscle in all blood vessels. • During stress, norepinephrine raises blood pressure by constricting peripheral vessel, inhibits gastrointestinal activity and dilates the pupils of the eyes. Catecholamine Activity in the Body • • • • • • • Increases HR, return of blood to heart, cardiac output, and blood pressure Dilates blood vessels of skeletal muscle Increases blood sugar — promotes glucose formation Decreases Insulin release from the pancreas Prevents glucose uptake from peripheral tissues Increases FFA's and cholesterol in bloodstream Overall effect is to conserve energy for the Central Nervous System, and skeletal system for proper body function in relation to a stressful situation. Catecholamine Imbalance S&S • • • • • • Dizziness from recumbent position to standing Transient spells of dizziness Asthma Hemorrhoids associated with hepatic portal congestion and poor Venous return Varicose veins Ragland Test Aldosterone Imbalance S&S • • • • • • • Rough sandpaper tongue=dehydrated Excessive urination, up to 15-20 times per day (may also be a thiamine deficiency or a hypertrophic prostate) Excessive perspiration or perspire with little or no activity, night sweat Paradoxyl pupillary light reaction Non-pitting edema of the extremities Crave salt Tinnitus Adrenal Stress Syndrome Impact on Physiology • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • Elevated cortisol will down-regulates insulin receptors and induces insulin resistance – Hyperinsulinemia and CVD Decreased cortisol will un-stabilize blood sugar levels—hypoglycemia cannot be corrected unless the adrenal are normalized Adversely impacts HPA axis, binding of thyroid hormones, peripheral thyroid hormone conversion and thyroid detox pathways Elevated cortisol suppresses the enzyme 5’diiodinase, prevents the conversion of T4 to T3 Lower thyroid function Elevated cortisol or increased steroid hormones suppresses the HPA axis TSH below 2.0 Reduced or absent sex drive Increase ability to eat sugars without symptoms Abnormal thirst Amenorrhea Weight gain around the hips and waist Blunted ACTH response Elevated cortisol suppress the bodies detoxification system Cortisol overloaded the detox pathways: – Skin blanching with pressure – Acne or acne worse at menses – Constipation – Bloating – Sensitivity to medication, supplements – Unresponsive to endocrine support the guy with the bow tie 69 Adrenal Stress Syndrome Impact on Physiology cont… • Elevated cortisol suppresses SIgA in the GI tract • Delays mucosal cell regeneration • Promotes GI inflammation • Contributes to leaky gut and dysbiosis • Chronic yeast infection • Suppresses the immune system • Gastric ulcer and duodenal ulcers • Inhibits bone production—osteoporosis • • • Insomnia due to blood sugar imbalance or elevated cortisol just before bedtime Reduce RAM sleep “Elevated evening cortisol levels in late life probably reflect an impairment of the negative feedback control of the HPA axis in aging” JAMA Aug. 2000 • • Elevated cortisol has been associated with neurodegenerative disorders “The degree of HPA axis hyperactivity is related significantly to the clinical course of MS.” –Neurobiology 1999;53:772-777 Hippocampal cell destruction due to excitotoxicity of cortisol sensitive hippocampal cells Induce glial cells to produce inflammatory cytokines and neurotoxic agents (NO, free radicals), damage neurons and cause apoptosis—gliosis • • • Increase CVD – Stress increase blood pressure (catecholamines) – Alters mineralcorticoid metabolism – Suppresses DHEA synthesis – Vasoconstriction – Sodium retention – Loss of potassium – Insulin resistance – Hypertriglyceridema – Obesity the guy with the bow tie 70 the guy with the bow tie 71 Find the root causes • • • • • • • Rule out Gastrointestinal Infections Rule out Gluten Intolerance Rule out Toxic Heavy Metals Rule out Toxic Chemicals Rule out Viruses Rule out Molds and Mycotoxins Rule out Oral Infections Nutritional Management of Adrenal Stress Syndrome • Adaptagenic herbs: – Panex ginseng – Siberian ginseng – Ashwagandha – Holybasil leaf – Rhodiola – Licorice root – Boerhaavia Diffusa Adaptagenic Herbs • • Herbs that normalize impact on the HPA axis under stress, defined by Russian pharmacologist, I.I.Berkman in 1957: 1. Must be harmless and cause minimal problems in physiology 2. Non-specific in function to increase resistance to negative influences by a wide range of stressors— chemical, physical, emotional 3. Normalizes irrespective of the direction of the pathological state Useful in both adrenal hyper- and hypo- functions Adaptagenic Herbs • • • • • • • Panax Ginseng—Korean ginseng, enhances fatty acid oxidation during exercise, conserve glycogen, increase O2 supply to working muscles, improve stemina, energy and physical work, reduces immune suppression caused by cortisol Siberian ginseng—enhances athletic and mental performance during stress situations Ashwagandha—Indian ginseng in Aryredic medicine, similar activity to panax ginseng Holybasil leaf Extract—prevents hypercortisolemia caused by stress, antagonized histamine, normalizes blood sugar and HPA axis activity, immune system and gastric mucosal protective Rhodiola rocea—enhances CNS, antidepressant, anticarcinogenic, cardioprotective, physical endurance, improve cognitive and mental functions Boerhavvia diffusa—support both hyper and hypo- adrenal function, buffer the elevations of serum cortisol and prevent immunosuppression, enhance cortisol levels with end stage adrenal exhaustion. Licorice root—glycerrhizin, restores exhausted adrenal function, prevent cortisol breakdown by down-regulate 11beta-hydroxylase, increase the half-life of cortisol in serum, support the immune system, anti-allergic and antiinflammatory Boerhaavie Diffusa: Useful Parts: Root, leaves and seeds. Medicinal Uses: According to Ayurveda, Punarnava is bitter, cooling, astringent to bowels, useful in biliousness, blood impurities, leucorrhoea, anaemia, inflammations, heart diseases, asthma, alternatives etc. The leaves are useful in dyspepsia, tumours, spleen enlargement, abdominal pains. According to Unani system of medicine, the leaves are appetizer, alexiteric, useful in opthalmia, in joint pains. Seeds are tonic expectorant, carminative, useful in lumbago, scabies. The seeds are considered as promising blood purifier. Nutritional Management of Adrenal Stress Syndrome • Nutritional factors – Pantethine—B-complex, lowers and raises cortisol as needed – Phosphatidylserine (PS)—endogenous phospholipid, synthesis depends on commonly deficient nutrients (B12, folic acid, S-adensylmethionine [SAMe], EFA), enhance cellular communication and metabolism, anti-oxidant, decrease anxiety, antidepressant, memory and cognition, lowers cortisol, neuroprotective, trans-dermal delivery may be better than oral delivery bypassing the GI mucosa – MVM – Essential fatty acids the guy with the bow tie 72 Lifestyle Changes Adrenal Stress • • Improve digestion Stabilize blood glucose – Do not skip breakfast – Eat a high quality protein based breakfast – Snack on low glycemic foods—proteins – Avoid concentrated sugars—refined sugars, fruits and carrot juices – Avoid adrenal stimulants – Eat well balanced meals—whole food, vegetables, meats and whole grains – Eat frequent small meals • Exercise in aerobic heart range – Low impact aerobic – Yoga – Weight lifting – Walking – Swimming – Cycling – Taichi – If you still feel tired after 24 hours, you overdid it. • Avoid adrenal stimulants – Refined sugars – Caffeine – Nicotine – Alcohol – Allergic foods – Trans fat – Artificial sweeteners (excitotoxins) – pollutions – Overtraining – Inadequate sleep • Stress management • Wholesome diet • Relaxation techniques • Body work • Adequate sleep, 8 or more hours • Chiropractic adjustment • Acupuncture • Emotional energy techniques www.emofree.com the guy with the bow tie 73 Nutr2 - Exam 3 (Final) 3/17/09 Endocrine Disorders (part 2 – Insulin Resistance) Increased obesity in the USA • • • • • • 58 million overweight 40 million obese 3 million morbidly obese 80% people over 25 are overweight 78% don’t meet basic recommended activity level 25% are completely sedentary Increased Diabetes • • • • • 76% increase in type II in 30-40 yrs old since 1990 90% diabetes is linked to high carb consumption Diabetes alone represents 11% of US health care expenditure Cost $98 billion in 1997(health care and lost wages) In 2002, total cost went up to $132 bil. Increased Nutrient Deficiencies • • • Consumption of refined sugars causes severe deficiencies in nutrients that regulate blood sugars e.g. Bs and Mg, K Excess sugar consumptions puts tremendous stress on the organs of blood sugar regulation: pancreas, liver, adrenals One serving of sugar has been shown to decrease the immune response of certain white blood cells by 50% for over 8 hours Sugar and CVD • • When 20 lbs. of sugar is consumed per year, there are 60 deaths per 100,000 due to CVD When 150 lbs of sugar is consumed pre year, there are 300 deaths per 100,000 due to CVD Increased dysfunctions associated with blood sugar dysregulation • • • • • Hypoglycemia CVD Strokes Diabetes Oxidative stress • • • • • Metabolic syndrome Insulin resistance Adrenal dysfunction Pancreas dysfunction Liver detox dysfunction Insulin Resistance (IR) • A state in which insulin receptors become unresponsive to the stimulation of insulin – Defects in ligand/receptor binding – Signal transduction – Intercellular communication – Polymorphism – Found in 25-35% of population in westernized nations – Major contributing factor to diabetes, CVD, sleep apnea, hormonal imbalance, obesity and certain kinds of cancer http://www.biblelife.org/rosedale.htm Insulin Resistance • Symptoms of Insulin Resistance – Fatigue – Cravings for sugar – Unable to lose weight – Constant hunger – Fatigue after meals – Migrating aches and pains the guy with the bow tie 74 Insulin Resistance • Signs of IR: – Elevated fasting or post-prandial glucose – Elevated fasting or post-prandial insulin – Elevated triglycerides – Triglyceride : Cholesterol ratio > 1 – Low HDL – Elevated uric acid – Increased waist to hip ratio – High blood pressure – Central obesity Insulin Resistance and CVD • • • • • • Blood pressure affected by the plasma levels of insulin in positive direct relationship. Hyperinsulinemia may alter coagulation proteins involved in fibrinolysis Plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 is elevated in hyperinsulinema Insulin up-regulate HMG-CoA reductase Impacts cholesterol ester transfer protein(CETP), lowers HDL levels Increased BP, blood clot and cholesterol, lowers HDL Am J Hypertens 1989;2:164-170 Metabolism 1993;42:945-949 Diabetes Metab Res 1991;7:139-153 Diabetes Care 1992;15:1258-1263 Circulation 1996;94(9):2057-2063 CETP = Cholesterol ester transfer protein Insulin and Hormone Metabolism Disorders in Women • • • Alters female hormone metabolism towards androgen dominance and estrogen dominance 4-10% women of reproductive age suffers from PCOS—leading cause of infertility Symptoms of PCOS: hyperandrogenism, insulin resistance, chronic anovulation, irregular periods, infertility, unexplained weight gain, fluid retention, fatigue, mood swings, acne, hair loss, unwanted hair growth, estrogen proliferative cancers, acanthosis nigricans, increased risk of CVD and dyslipidemia 0best Gynecol Surv 2000;55:321-328 Contemporary Endocrinology: Insulin Resistance. Totowa NJ:Humana Press;1999:347-365 Fertil Steril 1992;85:3520-3525 J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2000;85:3520-3525 Am J Med 1995;98:27S-32S IR and Androgen Dominance • • IR androgen excess IR – Elevated testosterone, estrogen, – Decreased sex-hormone binding globulin(SHBG) – Increased androstenedione – Increased DHEA, 17-hydroxy-progesterone and LH Decreased SHBG causes overexposure of hormone to tissues Euro J Endorinol 2000;143:383-388 J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1991;72:83-89 the guy with the bow tie 75 IR and Sex Hormones • • • • • IR leads to increase testosterone Increase T blunt estrogen effect lead to anovulation Anovulation reduces progesterone production Reduced P lead to estrogen dominance ED increases IR IR and Cortisol • • IR leads to increase cortisol and epinephrine Cortisol suppresses insulin receptor 3/18/09 IR, PCOS and Hyperinsulinemia • • • Defects in the hypothalamus-pituitary feedback loop that sets up a pattern of elevated LH, anovulation and menstrual irregularities (oligomenorrhea, anemorrhea, menorhagia) The root of the problem is insulin resistance and adrenal disorder Hormonal imbalance is only a symptom -MSG stimulates appetite center, encouraging you to eat more Conventional Treatments for Female Hormone Imbalance • • • • Oral contraceptives (OC) to suppress the pituitary feedback loop Suppresses the production of ovarian androgen Usually make worse the estrogen dominance problem by these synthetic estrogen Chronic OC use may cause prolonged inhibition of the hypothalamus-pituitary-ovarian feedback loop—post-birth control syndrome (inability to regain normal menstrual cycles) Conventional Treatments • • • • • GnRH analogue drugs (Lupron) to completely suppress all ovarian hormone production Causing symptoms of hormone deficiency such as hot flashes, low libido, vaginal dryness Exogenous synthetic hormone therapy is then Rx to treat deficiency symptoms Glucocorticoid, prednisone, dexamethasone to suppress adrenal function Increases risks and side effects From Website: http://www.drugs.com/sfx/lupron-side-effects.html Lupron All medicines may cause side effects, but many people have no, or minor, side effects. Check with your doctor if any of these most COMMON side effects persist or become bothersome when using Lupron: Breast tenderness; constipation; decreased sex drive; difficulty sleeping; hot flashes/sweating; impotence; infection (fever, chills, sore throat); nausea or vomiting; pain; swelling; urination problems. Seek medical attention right away if any of these SEVERE side effects occur when using Lupron: Severe allergic reactions (rash; hives; difficulty breathing; tightness in the chest; swelling of the mouth, face, lips, or tongue); blood in urine; chest pain; dizziness or lightheadedness; fast or irregular heartbeat; increase in bone pain; severe drowsiness; severe headache; swelling of the lungs; unusual or one-sided weakness; vision changes. Conventional Treatments • • • Androgen antagonists: ketoconazole, finasteride (side effects include cortisol production suppression, severe liver toxicity) Insulin sensitizing drug: metformen (lactic acidosis, malabsoption, B12 deficiency) These should be the last resort instead of the first line therapy Insulin and Hormone Metabolism Disorders in Men • • • • • Hyperinsulinemia induces hypercortisolemia Shifts progesterone conversion to cortisol Progesterone protects the prostate – Impacts nervous system function – and has a role in osteoblast activity Increases androstenedione and lowers DHEA—decrease vitality, weight gain and lowers testosterone level Androstenedione has high affinity to testosterone receptors and acts as a testosterone antagonist at high levels J Card Pharm 1997;30:523-527 FASEB 1992;9:1073-3074 the guy with the bow tie 76 -this man is addicted to heroin Insulin and Hormone Metabolism Disorders in Men • • • IR increases body fat and aromatase activity Aromatase converts testosterone into estrogen Any patients that demonstrates aromatase upregulation need to be checked for adrenal and insulin resistance problems IR and Obesity • • • Obesity due to impaired glucose transport, increase lipogenesis (fatigue and wt gain) IR hypercortosolemia leptin resistance lead to lost of appetite control and inability to burn fat Patient complaints of low energy, fatigue, hungry all the time, fat gain and not able to lose wt with exercise. the guy with the bow tie 77 IR And Liver Detox • • • IR suppresses glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) decrease hexose monophosphate shunt (HMS) decrease NADPH NADPH is required for glutathione (GSH) production Decreased GSH levels will compromise liver’s phase 1 and phase 2 detox pathways IR And Cancer • IR is associated with colorectal cancer and breast cancer – J Natl Cancer Inst 1997;89:660-661 – Nutr Cancer 1997;27:316-320 IR And Essential Fatty Acid • • • • Low cellular insulin response inhibits the activity of the rate-limiting enzyme, delta-6-desaturase (D6D) Lowers the conversion of linoleic and linolenic acid into GLA, EPA and DHA Lowers D6D activity can alter the production of prostaglandins, eicosanoids and leukotrienes thus impact intercellular communication Decrease D6D will increase D5D activity and lead to increase arachidonic acid production and enhanced inflammatory response Prostaglandin Leukot Essent Fatty Acids 1997;57(4-5):379-385 Prog Lipid Res 1982;20:41-48 IR and Energy Metabolism Decreases cellular uptake of glucose decreased citric acid cycle pathway Shift cells metabolism into an energy requiring lipogensis pathway Produces an inflammatory state which will further short circuit the CAC and uncouple oxidative phosphorylation pathways lead to lowered ATP production • Alters EFA metabolism which inhibits lipolysis and beta-oxidation http://www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/300/5622/1140 • • • Conditions Associated with Hyperinsulinemia • • • • • • • • • • • Acne Addictions Asthma Cancer Sweet cravings Delay puberty Mood disorders Eating disorders Weight gain Heart burn and GI problems Heart disease • • • • • • • • • • Hypercholesterolemia High triglyceride Infertility Insomnia Fatigue Type II diabetes Low estrogen Estrogen dominance Migraine headache osteoporosis Functions of Insulin and Glucagon Insulin Glucagon Lowers elevated blood sugar Raise low blood sugar + anabolism and energy storage + catabolism and release energy Converts glucose and protein to fat Concerts protein and fat to glucose Store dietary fat Converts dietary fat to ketone to use for energy Remove blood fat into adipose tissue Release fat from adipose for energy Increase cholesterol production Decrease cholesterol production Stimulate the use of glucose as energy Stimulate the use of fat for energy Dr. Bernstein’s Diabetes Solution (considered the Bible for diabetes tx) the guy with the bow tie 78 Effects of Foods on Insulin and Glucagon Food Group Insulin Glucagon Carbohydrate +++++ No change Protein ++ ++ Fat No change No change Carb + fat ++++ No change Protein + fat ++ ++ Hi Prot Lo Carb ++ + Hi Carb Lo Prot +++++++++++ + The Functional Approaches for MetS and Diabetes • • • • • • • Improve insulin sensitivity Reverse insulin resistance Regulate liver gluconeogensis and glycogenolysis Reduce postprandial hyperglycemia Prevent systemic complications Decrease or eliminate insulin use in T2DM Decrease of eliminate oral hypoglycemic medications Four Strategies 1. 2. 3. 4. Dietary modification Supplementation with nutritional and botanical agents Exercise Lifestyle modification Dietary Modifications For IR • • • • • • • • • Reduce or eliminate all forms of simple and refined sugar from the diet Eat whole and minimally processed foods Eat plenty of organic produced protein as the main focus of the meal Eat healthy fat liberally (traditional fats) Eat only low glycemic carbohydrate, vegetables Eat complex, unrefined carbohydrate Eat mainly non-starchy vegetables. Use only natural stevia as sweetener Leptin diet Nutritional Support for IR • • • • • • • • • • Vitamin E—men with lowest plasma levels of vitamin E had almost a 4 times greater incidences of getting T2DM. Improve insulin sensitivity, lowers triglycerides and LDL, antioxidant that prevents oxidative complications associated with diabetes, reduces CRP, glucose transport and anti-imflammatory. 400-1200IU mix tocopherol with at least 200 IU gamma tocopherol Vitamin C— Found to be low in T2DM Glucose and ascorbic acid compete for the same transport pathway Vitamin C lowers serum glucose and CRP, inhibits glycation, prevents accumulation of sorbitol in retina, protects against oxidative stress 1000-3000 mg daily Gymnema sylvestre—reduces IR, decrease fasting blood glucose, enhance insulin action, may regenerate beta-cells • Used for type I diabetes Chromium—depleted in refined carbohydrate diet, common deficient in US diet, co-factor in glucose tolerance factor which is important for insulin on receptor site and improve cellular glucose uptake, normalize post-prandial glucose and insulin levels, glycated Hgb, serum cholesterol Vanadium—insulin-like impact on receptor sites, improves function of glucose transport, improves intercellular transduction reactions, reduces IR the guy with the bow tie 79 Nutritional Support for IR (cont) • • • • • • • • • Alpha-Lipoic Acid—a sulfur-containing substance, improves insulin function by activating glucose transporters (GLUT1 and 4) which enhance glucose disposal and reset signaling response to insulin, powerful antioxidant, improves ATP production Magnesium—deficient in IR patients, optimizes insulin secretion, activate glucose transporter, improves insulin intercellular transcriptional response, 500 mg/day Evening Primrose oil —hyperinsulinemia blocks D6D and reduce production of PgE1, EPO protect the insulin receptors and reduce CRP, 900 mg/day Biotin—improves insulin response to GTT, lowers post-prandial glucose levels, upregulate glucokinase (first step in liver glucose utilization) Zinc—protect beta-cells, increase insulin sensitivity, insulin metabolism, diabetics excrete zn Inositol—ability to re-establish normal myoinositol levels in deficient neurons, helpful in diabetic neuropathy Niacin—a component of GTF, potential to prevent the onset of type 1 diabetes, inhibits macrophage and interleukin-1 mediated beta-cell damage, inhibits nitric oxide, has antioxidant function L-Carnitine—enhance whole-body glucose uptake and increase gluconeogenesis, improves peripheral nerves and vascular function, improves serum dyslipidemia in diabetics Fiber supplement • glucomannan (from Konjac root), slows sugar absorption for improve serum glucose control, 500-700 mg/100 calories in diet • Fenugreek seeds, soluble fiber, 15 grams/meal reduces postprandial rise in blood sugar Exercise • Anaerobic strength training – increases insulin receptor sensitivity Liftstyle Modification • • • • Stress reduction Diet modification (reduce refined carbs) Exercise Reduces chemical exposure (including alcohol) 3/20/09 Functional Endocrinology and Nutrition Part 3 - Detox, Thyroid “Until you cleanse your organs, your vitamins and herbs will be useless and you won’t cure your illnesses” -Dr. Richard Schulze (Medical Herbalist) "Toxicology textbooks list the first symptoms of chronic poisoning as low energy, fatigue, muscle weakness, inability to concentrate and intestinal complaints. These symptoms are virtually identical to those experienced by the chronically ill." - Jeffrey Bland, Ph.D. Toxins Interference • • • • • Metabolism is the sum of catabolism and anabolism The balance of metabolism is homeostasis which is health The endocrine system directs metabolism Every steps of the endocrine hormonal communication is vulnerable to toxins interference Toxins: chemical, heavy metals, minerals imbalance, nutritional deficiency, metabolic wastes, emotional stress Symptoms of Toxicity • • • • • • • • • Furry coating on the tongue Drowsiness after meals Weight gain Constipation - sticky stool Tiredness upon waking in the morning Halitosis (Bad breath) Poor concentration Mood changes Acne / Boils • • • • • • • • • Failing memory Tiredness after minimal exertion Joint pain and muscle ache Poor appetite Frequents colds and influenza Low back pain - not traumatic Depression Candida infections Irritable bowel -if patient is fatigued, then don’t do a detox (need energy to detox) the guy with the bow tie 80 Gulf War Syndrome • Recent government study finally admitted that chemical exposure are responsible for the multiple symptoms that the veterans and their family are experiencing. -http://www.gulfweb.org Toxins, Toxins, Toxins • • • • • It has been estimated that more than 36 million pounds of pesticide active ingredients are used annually in Nebraska. Risk = Toxicity × Exposure Toxicity is accumulative. That means they stored in the body over times. Increased exposure=increased risk. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) currently recognizes more than four million chemical compounds. More than 60,000 of these are produced commercially, with three new compounds introduced each day. These are all chemicals not in existence 100 years ago. Bioaccumulation • • An EPA biopsy study showed that 100% of people studied had dioxins, PCBs, dichlorobenzene, and xylene stored in their bodies — some of the most potent causes of cancer known to us. These inescapable everyday chemicals permeate every aspect of our lives. A minute among over time and we cannot detoxify all of the many chemicals we inhale and digest every day, they bioaccumulate in our tissues. – Detox or Die, Sherry Rogers Toxins Cause All Diseases • Environmental toxins causing all diseases. Dr. Sherry Rogers describes the major health-destroying chemicals and heavy metals, their sources, EPA studies, and how ubiquitous these substances are in our everyday environment. Studies are cited showing that 95% of cancer, for instance, is caused by diet and environment. Toxins in Cancer • When cancerous breast tissue is compared with non-cancerous tissue from elsewhere in the same woman's body, the concentration of toxic chemicals such as DDT and PCBs was "much increased in the malignant tissue compared to the normal breast and adjacent adipose tissue.” • Jerome B. Westin and Elihu Richter, "The Israeli Breast-Cancer Anomaly," in Devra Lee Davis and David Hoel, editors, TRENDS IN CANCER MORTALITY IN INDUSTRIAL COUNTRIES (New York: New York Academy of Sciences, 1990), pgs. 269-279. Following public outcry, Israel banned these chemicals from being used on feed for dairy cows and cattle. Over the next ten years, the rate of breast cancer deaths in Israel declined sharply, with a 30% drop in mortality for women under 44 years of age, and an 8% overall decline. At the same time, all other known cancer risks--alcohol consumption, fat intake, lack of fruits and vegetables in the diet--increased significantly. During this period, worldwide death rates from cancer increased by 4%. The only answer scientists could find to explain this was the reduced level of environmental toxins. It All Goes to Your Head The most common organ affected by chemical exposure is the brain, leading to drowsiness, fatigue, exhaustion, sluggish thinking, or a host of other symptoms -Tired or Toxic, Sherry Rogers • Detoxification is regarded highly in all traditional healing arts Bowel Cleansing Program • • • • Before attempting a liver cleans, the bowel must be free of obstructions. Constipation allows time for toxins to reabsorbed into the body Pre-package bowel cleansing programs Increase dietary fibers and water Hepatic Detoxification • • • • Especially important for the chronically ill Liver detox imbalance will make any endocrine problem patterns more difficult to evaluate and unresponsive to treatment Many times hormonal imbalance occurs as a result of compromised detox function Patients usually presents with contradicting symptoms, history of toxin overload and drugs exposure (HRT) the guy with the bow tie 81 Hepatic Detoxification • Symptoms of a compromised liver detox system: – Neurological disorders – Chemical sensitivity – Adverse drug reactions – Autoimmune problems – Hormonal imbalance – Blood sugar imbalance – Fatigue Hepatic Detoxification • • Defects in hormone detox can lead to many problems: Partially breakdown hormones can compete with non-metabolized active hormones at the receptor site and blocks their active functions • Patient may present with symptoms of hormone imbalance but not supported by lab results, making recommendations for treatment difficult for the less experienced practitioners • Phase 1 and phase 2 detoxification pathways • Phase 1—oxidative/reduction reactions involves the cytochrome P-450 enzymes pathway • Uses oxygen and NADH to add a reactive group such as a hydroxyl radical • Either complete neutralize the compound or renders it more reactive to bind with the phase 2 conjugation moiety • Intermediates of phase 1 detox is more reactive and much more toxic—free radicals • Pathological Detoxifier • Patients with very active phase 1 detox and very slow or inactive phase 2 detox enzymes • Most chronically ill patients have this problem • Increase glutathione is imperative, NAC • Glutathione also involved with phase 2 detox • Phase 2—conjugation of phase 1 intermediates • Neutralized toxins or make them more water soluble in order to be excreted via urine, sweat or bile • 6 main pathways: glutathione conjugation, glycine conjugation, methylation, sulfation, acetylation and glucuronidation -beet root is a good methyl donor -sulfur-containing compounds (like carnitine, taurine, methionine, N-acetyl-cystine) can increase production of glutathione Liver Detox Profile • Great Smokies Diagnostic Lab’s Comprehensive Detoxification Profile that include both phase 1 and phase 2 liver detoxification functions. Phase 1 test: Mainly a saliva sample, collected after the ingestion of a measured amount of caffeine for phase 1I system For phase 2: urine or blood sample is collected after the ingestion of aspirin and acetaminophen depends on the profile selected. The report include caffeine clearance (phase 1), conjugates of 4 phase 2 pathways. Ratio of phase 1 and phase 2 and other information can be obtained depending on which profile tests selected. 3/24/09 Dietary And Lifestyle Support for Liver Detoxification • • • • • • • • • Increase fruits and vegetable, cholesterol, whey protein (sulfur containing foods) Exercises Sauna—sweating and circulation Skin brushing Epsom salt bath Colonic Coffee enema Liver and gallbladder flush Fasting the guy with the bow tie 82 the guy with the bow tie 83 Nutritional and herbal Support For Detox Function • • • • • • • • Dandelion—improves liver and gallbladder function, promote bile production and secretion to the GB, contraction of GB Milk Thistle—increase bile solubility, reduces bile concentration, potent antioxidant protects against phase 1 free radical damages to the liver, prevent glutathione depletion, anti-inflammatory, inhibits PGE2 and leukotriene, promote liver cells regeneration Ginger—increase bile production (cholagogue), reduces hepatic cholesterol Lipotropic agents—Beet root and leaves (betaine HCl), taurine, vitamin C, lecithin (phosphatidylcholine) Centella Asiatica (gotu kola)—improves histological findings of liver cirrhosis, venous insufficiency, venous hypertension Panax Ginseng—improves liver function, reverse fatty liver in animal models, anti-hepatotoxic properties, promotes Kupffer cells, increases nRNA, rRNA and mRNA synthesis Multiple vitamins and minerals to insure nutritional co-enzymes and co-factors sufficiency B-complex, Mg, Zn, Mo, Se, K Liver/Gallbladder Flush • • • • • The purpose of this procedure is to assist your body in its efforts to maintain free-flowing bile and to help keep the gall bladder free of debris. First, natural forms of natural acids are used to “cut” the sludge or hardened bile to allow for it to be expelled from the gall bladder, through the bile duct, into the colon and out the body. Second, adequate amounts of magnesium are ingested which allows for relaxation of the smooth musculature, including relaxation and contraction of the bile duct. Third, a natural oil, e.g.., olive oil, or heavy cream is ingested to cause the gallbladder to contract, forcing the expulsion of the bile sludge out of the gall bladder into the bile duct. Finally, green tea and/or coffee enema may be used to stimulate the release of waste from the liver into the bile duct, which also increases the rate of bile released from the liver. Liver/Gallbladder Flush DAYS 1-5: • Eat a normal breakfast (supplements) • Ingest as much apple juice as you feel comfortable. Use organic apple juice (free of preservatives). Fresh is always best, then frozen, and lastly cooked, bottled apple juice. • Add a total of 90 drops of ortho-phosphoric acid (Phosfood by Standard Process) to the apple juice each day. This is taken at once (or 45 drops twice or 30 drops three times a day) • Alternative, pure apple cider vinegar may be used instead of the ortho-phosphoric acid DAY 6 • Eat a normal breakfast (supplements) • 2 hrs. after breakfast, dissolve 2 TBSP Epsom salt in 3 ounces of warm, pure water and drink it. Chase with a little citrus juice. • If gall stones are present, take a coffee enema with ¼ cup Epsom salts dissolved in it. • 5 hrs. after breakfast, dissolve 1 TBSP Epsom salt in 3 ounces of warm water, and drink it. Chase with citrus juice. • 6-7 hrs. after breakfast, you have a choice: - Fast, or - Fruit and whipped cream salad (variety of fresh or frozen fruit of your choice and whipped cream). Eat as much as desired • At dinner time, drink one-half cup of extra virgin olive oil (unrefined) or other oil. If necessary, you may blend the oil with an equal amount of fresh squeezed orange, grapefruit or diluted lemon juice. Or alternate swallowing oil with juice. Should nausea be felt, it is due to the contraction of the gall bladder. Lay on your right side for at least 20 minutes. • In the morning, drink 3 ounces of water with 1 TBSP Epsom salt dissolved in it, also if stones are present, take another coffee enema with ¼ cup of Epsom salt dissolved in it. Resume your normal diet. • Can repeat flush in 2 weeks, if needed. -if patient has gallstones, then take a lot of betaine HCl (and/or apples) before doing a gallbladder flush the guy with the bow tie 84 Liver/Gallbladder Flush Contraindications/cautions • Stones are calcified and very large • During pregnancy • If liver disease is present • The gallbladder in non-functional • If patient is very obese Fasting • • • • • An integral part of many religions—Buddhism, Islam, Judaism and Christianity When the glucose store in body is depleted fat and carbohydrate stores are used for energy When protein stores begin to be depleted for energy (resulting in loss of muscle mass)—starving. Autolysis—breaking down of fat stores in the body in order to produce energy Ketosis—depleted glycogen lead to the breaking down of stored fats and creates these ketone bodies Fasting Benefits • • • • • • Detoxification--normal body process of eliminating or neutralizing toxins through the colon, liver, kidneys, lungs, lymph glands, and skin Enhance immunity--during a fast, energy is diverted away from the digestive system towards the metabolism and immune system Growth hormones are also released during fasting A slower metabolic rate, more efficient protein production, an improved immune system, and the increased production of hormones contributes to this long-term benefit of fasting Rejuvenation and extended life expectancy The only reliable evidence to extend the lifespan of a mammal is caloric restriction without malnutrition Homotoxicology • “The theory of disease developed by Dr. Hans-Heinrich Reckeweg (1905-1985), understands illness as the human body’s defense against toxic substances (homotoxins) that threaten to overwhelm the intercellular matrix. According to this therapeutic model, the type and severity of an illness are determined by the duration and intensity of toxin loading in relationship to the body’s inherent capacity for detoxification. «Clogging» of the matrix obstructs the movement of nutrients from blood vessels into cells, disrupting the body’s steady state and hindering important biological processes. The resulting disturbances, which eventually manifest as illness, are the body’s attempt to restore a state of biochemical balance. For Reckeweg, restoring this balance was the ultimate goal of all medical treatment.” • http://www.heel.com/homotox/ The Six Phase Table • • Subdivided into three blocks Each block has two phases Humoral phases: • Excretion • Inflammation Matrix phases: • Deposition • Impregnation Cellular phases: • Degeneration • Dedifferentiatio n 3/25/09 Fasting • • • • • • • Juice Fast—3-7 days or more Water fast—3 day max, but natural hygienists promote prolong water fast as a way to heal serious illnesses. No food nor water—24 hours Brown rice fast—3-7 days Master Cleans (Water/lemon/lime/maple syrup/cayenne pepper)—3-21 days Raw food—7-21 days Fasting/detox programs—combining raw food or caloric restricting diet with herbal and nutritional supplements (721 days) the guy with the bow tie 85 Fasting Precaution • • • • • • Wasting states Pregnancy and nursing Infants and children Medication Gallstone Physical activities—depends on the type of fasts – None for water or abstinence of food (avoid physical activity with water fast) – Light exercise for juice, lemon/lime/maple syrup fast – 30-45 minutes moderate, raw food, weight loss fast What to Expect During a Fast? • • • • • Tired the first day or two Increase energy when ketosis established Increase urination Bowel movement will increase or decrease depends on types of fasts May experience euphoria on the third day onward How to break a fast? • • • • Short fast, just resume normal eating Longer than three days, start with something light for dinner, gradually add back normal foods 21 days fast, normal raw veggies and fruits, add light protein for dinner, the first day, add more the next day to lunch, resume normal the third day at breakfast Continue on with a healthy dietary style Thyroid Disorders Most patients with functional thyroid problems do not have primary thyroid imbalances -insulin can inhibit proper conversion of T4 to T3 -gut flora can convert T4 to T3 Low Thyroid S&S • • • • • • • • • • Fatigue Increase wt gain with low cal diet Morning headache wears off as day progresses Depression Constipation Hypersensitivity to cold weather Poor circulation and numbness in extremities Muscle cramps while at rest Chronic infections Loss of lateral third of eyebrow • • • • • • • • • Slow healing wounds Required more sleep to function Chronic digestive problems Hypochlorhydria Itchy dry skin Dry brittle hair Hair loss Lower axillary temperature Edema (myxedema) the guy with the bow tie 86 Serum Thyroid Panel • • • • TSH—lab reference range: 0.5-5.5, functional range: 1.5-3.5 – Hypothyroid—above 3.5 – Hyperthyroid—below 1.5 Free T4—can be altered by many drugs Free T3—active thyroid hormone, impacted by drugs Thyroid antibodies—auto-antibodies indicates autoimmune attack of thyroid Malnutrition or Hypothyroid • • • Symptoms are similar Insulin resistance is a major factor – IR impair cellular utilization of macronutrients – IR cause weight gain lead to the mistaken action of eating low fat and low protein diet – Leads to malnutrition – IR also cause under conversion of T4 to T3, a protective mechanism to slow down the effects of malnutrition Hypothyroidism is a malnutrition problem Tyrosine and Iodine for Thyroid? • • • • • • Caution should be exercise when using tyrosine and iodine Use improperly can cause suppression of thyroid hormone production The relationships of tyrosine and iodine metabolism is more complicated then simply supplementing them without thorough understanding of the whole symptoms picture Tyrosine may be indicated for vegans Increase iodine can be used for hyperthyroidism Always support the adrenals first with thyroid problems, don’t treat the thyroid and ignore the adrenal which is usually the underlying cause of thyroid problems. Nutrition And Herbs For the thyroid • • • • • • • • • Procine thyroid glandular—Armour Thyroid, a prescription thyroid HRT, Apex Energetics and American Biologic produce desiccated thyroid glandular Withania (Ashwangandha)—stim both T3 and T4 production, support hepatic function, reduces oxidative stress, adaptogen activity that modulate cortisol release Vitamin A—influence thyroid hormone nuclear receptors transcription activation Vitamin D—immune modulation, suppresses autoimmune thyroiditis (Hashimoto) Selenium—co-factor for 5’deiodinase which convert T4 to T3 and degrades rT3 Zinc—improves thyroid fxn, co-factor for 5’deiodinase, reduces thyroid antibodies Commiphora (Gugulipid)—stim. T3 production, reduce LDL, cholesterol and lipid peroxides Antiperoxidative compounds—lipid peroxidative and antioxidant enzymes systems play a profound role on the peripheral thyroid hormone conversion. Substances (alpha lipoic acid, N-acetyl cysteine, protein, B-complex) that support the synthesis of glutathione and decrease free-radical and oxidative stress (antioxidants, bioflavonoids, polyphenol, OPC) will improve thyroid hormone conversion and thyroid function Omega-3 EFA—imbalance of eicosanoids is linked to inflammatory reactions and thyroid disorders -Iodoral supplement (~12mg iodine) -excess iodine (10x the RDA) is not toxic for the body) the guy with the bow tie 87 Thyroid HRT • • • • • • • • • • • Desiccated Thyorid—generic or brand name desiccated pig thyroid (Armour Thyroid, Westroid, Naturethroid, Proloid) Cytomel—brand name for synthetic T3 Levothroid—brand name for synthetic T4 Levothyroxine—generic T4 Levoxyl—brand name T4 Synthroid—brand name synthetic T4 (most Rx drug in the US) Thyrolar—brand name fixed-ratio mix of synthetic T3 and T4 Patients may respond well to natural thyroid replacement or synthetic ones If synthetic not working well, suggest to patient to consult with their MD to switch to natural replacement which may work better and vise versa. Synthetic usually to be taken on empty stomach, in the morning, avoid taking calcium along Natural thyroid med better be taken in 2 divided doses, after breakfast and dinner for optimal function according to Joseph Mercola, DO (www.mercola.com) What happens when you give thyroid hormones to a malnourished without re-feeding? • • • • • • Initially feels better Unravels the protective mechanism against rapid tissue breakdown Thyroid meds are stimulants Increases IR and accelerates muscles and protein reserves breakdown Health deteriorates rapidly Hormone replacement must be used with caution the guy with the bow tie 88 Functional Endocrinology and Nutrition (on Final exam) Part 4 - Female Hormonal Problems “Because the family of glands is closely interrelated, it is difficult to hurt one member without injuring others.” -Endocrine Handbook by Harrower Female Hormonal Imbalance: Estrogen Dominance The Female Cycle • • The female menstrual cycle is a complex interactions and orchestration of many hormonal messengers. Endocrine disruptors are especially damaging to the female cycles because most of these chemicals are also estrogen mimics. Estrogen • • • • • • • Estrogen's functions are primarily the growth and development of sex organs and other tissues related to reproduction Water retention Fat storage Maturation of the female adolescents Stimulate endometrial growth during the first half of menstrual cycle. Promote target cell proliferation Develops progesterone receptors the guy with the bow tie 89 Estrogen (cont) • • • • • Inhibits osteoclast activity and retard bone resorption Over thirty different forms of estrogen have been described. Produce by the ovaries in females Can be converted from testosterone by aromatase in adipose tissues The most common are: • Estrone (E1)—10% • Estradiol (E2)—10% • Estriol (E3)—80% Progesterone • • • • Progesterone is the other primary female hormone. Balance the activities of estrogen. Produced in the ovaries and the adrenal gland. Precursor for both estrogen and testosterone, as well as cortisol. Functions of Progesterone • • • • • • • • • Target cell differentiation and maturation (to grow up and be ) Maintain the endometrium in pregnancy New bone formation (stimulate osteoblasts) Blood pressure regulation Fat conversion and energy production Sugar metabolism Maintaining myelin Regulating estrogen production Increasing estrogen receptors sensitivity Estrogen and Progesterone • • • Estrogen has to be in balance with progesterone to function well in the body. The excess or deficiency of either hormones will cause symptoms and disruption of the normal working of the endocrine system. Insulin, thyroid hormones and adrenal hormones (the major endocrine hormones) all exert influence. Estrogen Dominance • • • • • • • • • • • • • Anxiety, irritability, anger and agitation, mood swings Cramps, heavy and prolong bleeding, clots Breast tenderness Water retention and weight gain Fibrocystic breast Sweet cravings Foggy thinking Allergies Cervical dysplasia Increased risk of cancers Increased risk of autoimmune diseases Back pain Acne • • • • • • • • • • Uterine fibroids Endometriosis Irregular periods Insulin resistance and unstable blood sugar Lost of sex drive, infertility Gall bladder problems Insomnia Osteoporosis PCOS Fat gain in hip and thigh areas Causes of Estrogen Dominance • • • • • • • • • Nutritional deficiency Insulin resistance Adrenal Stress--hypercortisolemia Chronic inflammation Excess of estrogen in comparison to Progesterone. Estrogen disruptors or xenoestrogen—HRT and Oral Contraceptives Other endocrine disruptors—thyroid disruptors Digestive issues Hepatic detoxification issues the guy with the bow tie 90 Endrogen Dominance • Increased androgens (testosterone and DHEA) produce metabolic disorders in women – Insulin resistance – Central obesity – T2DM – CVD – PCOS – Poor glycemic control and poor health Insulin Resistance • • • • Hyperinsulinemia upregulates 17,20-lyase, an anzyme produced in the theca cells 17,20-lyase increases androgen production by shifting away from estrogen production Increased androgens in women promotes insulin resistance and the vicious cycle goes on and on… Androgen dominance, estrogen dominance and insulin resistance promotes reproductive organs cancers in women Xenostrogens • • • • • • • • • • DDT DES Dioxin Drug version of HRT Plastics Pesticides Cosmetic and skin care products Perfume Laundry products Phytoestrogens WHI Findings on HRT • • • • • • Findings from the Women's Health Initiative (WHI) studies showed that women using estrogen with or without progestin may increase their chances of strokes and blood clots. Using estrogen with progestin also increased a woman's chance of getting breast cancer and heart attacks, but using estrogen alone did not. For women with a uterus on hormone therapy, a combination of estrogen plus progestin is prescribed. For women who have had a hysterectomy, hormone therapy consists of estrogen alone. Using estrogen with or without progestin may increase the risk of dementia in women age 65 years or older. Estrogen, with or without progestin, may decreased women's chances of developing osteoporosis. Estrogen with progestin decreased the risk of colorectal cancer in women. – FDA Press Release P04-94, September 29, 2004. Risks and Benefit of HRT • • For some women, menopausal hormone therapy may increase their chances of getting blood clots, heart attacks, strokes, breast cancer, and gall bladder disease. For a woman with a uterus, estrogen alone slightly increases her chance of getting endometrial cancer (cancer of the uterine lining). benefits of using hormones for menopause, HRT is the most effective FDA approved medicine for relief of hot flashes, night sweats, and vaginal dryness. It may also reduce the chances of getting weak bones, a condition called osteoporosis. • FDA Press Release P04-94, September 29, 2004. HRT and Heart Disease • • Women with or at high risk of coronary heart disease should not start HRT Women without coronary heart disease might experience even greater net harm from HRT. • Archives of Internal Medicine October 23, 2000;160:2897-2900 the guy with the bow tie 91 HRT and Stroke • • • An analysis of some 40,000 women involved in 28 clinical trials has discovered: Women who use HRT increase their risk of stroke by 29 PERCENT and the likelihood of a fatal or disabling stroke by 56 PERCENT. The effect is seen in ischaemic strokes, caused by blockages of blood flow to the brain, not in the less common form of hemorrhagic stroke. The University of Nottingham research team recommended patients with a high risk of stroke should stop taking HRT unless there is a strong medical reason not to do so. • BMJ, January 7, 2005 Three Major Problems 1. 2. 3. Soy Trans Fatty acids Refined Carbohydrate Soy Alert • “Deleterious effects include endocrine disruption, thyroid suppression, immune system suppression, suppression of sperm production, DNA breakage and increased incidence of leukemia, breast cancer, colon cancer, infertility, growth problems and subtle changes in sexually dimorphic behaviors.” • http://www.westonaprice.org/soy/dangersisoflavones.html Soy Isoflavone China (1990 survey) 3 mg/day Japan (1996 survey) 10 mg/day Japan (1998 survey) 25 mg/day Japan (2000 survey) 28 mg/day In Japanese subjects receiving adequate iodine, causing thyroid suppression after 3months 35 mg/day In American women, causing hormonal changes after 1 month 45 mg/day=0.75 mg/kg* In American women, causing changes presaging breast cancer after 14 days 45 mg/day FDA recommended amount 24 mg/day AdvantaSoyTMClearTM 30-50 mg/ 100 g serving In children on soy formula 38 mg/day=6.25 mg/kg* *assumed 60 kg for adult, 6 kg for infants Source: www.westonaprice.org Trans Fatty Acid • • • • • Unnatural Disrupt cell membrane Disrupt cell receptors Disrupt essential fatty acid metabolism Disrupt hormone productions Refined Carbohydrate • • • • • • Carbohydrate intake increases insulin Insulin encourages fat gain Fat tissues increase estrogen Estrogen also promote fat gain Estrogen also induces insulin resistance Insulin resistance cause carbohydrate cravings the guy with the bow tie 92 2 / 4 /16 Estrogen Metabolites the guy with the bow tie 93 To understand all the complex interactions involved is nearly impossible! But we can rely on the body to clear it all up once we find the causes and solutions are available. Tests and Evaluation • • • • • Hair Analysis Saliva hormone tests History Lifestyle assessment Questionnaires: endocrine assessment, metabolic typing, emotional, behaviors, symptoms survey the guy with the bow tie 94 Solutions • • • • • • • • • Clean up the environment Clean up the diet, rely on whole foods Clean up the body, detoxify liver, GI tract Exercise and dietary modification Hormone modulating herbs and supplements Bio-identical hormones (must be tested first and monitor regularly) Stress management Balance blood sugar Agricultural and food processing reform Hormone Modulating Herbs • • • • • • • Black cohosh Blue cohosh Licorice Chaste tree Wild yam Dong Qui Red clover • • • • • • Raspberry leaves Ginseng Tribulus Gymnema White peony Shepherd’s Purse Hormone Modulating Herbs • • • • Black Cohosh—modulates estrogen effects in the body, improves estrogen deficiency symptoms, decreases hot flashes, increase pelvic blood flow, reduce spasms, reduce depression Dong Quai—has “selective estrogen receptor modulator” properties, 1/400th the activity of true estrogen on cells, useful in both estrogen deficiency and excess conditions, hemotonic, analgesic, anti-inflammatory, anti-allergenic, cardiocprotective, mild laxative, increase vaginal secretion Chaste Berry (Vitex Angus-Castus)—optimizing impact in luteal phase function, increases progesterone levels and LH, decreases FSH, modulates prolectin associated with hyperprolactinemia induced by corpus luteum insufficiency, reduces PMS symptoms, improve fertility and optimizing luteal phase funcition Sheperd’s Purse (Capsella busa-pastoris)—increase uterine tone, hemostatic properties, helpful in dysmenorrhea associated with progesterone deficiency, help shedding of uterine lining (excessively thickened due to estrogen dominance), also helpful in treating hemorrhoids and diarrhea Chem Pharm Bull 1992;40(4):954-946 Chinese Herbal Medicine Materia Medica, Bensky D, et al The complete Botanical Prescriber, Sherman JA. Acta Pahrmacol et Toxical 1983;52:246-253 Nutrients For Hormone Balance • • • • • • Calcium Magnesium Zinc Vitamine E Vitamin B complex – B6 – Pentothenic acid Vitamin C • • • • • • Vitamin D Cod liver oil Evening primrose oil Gamma linolenic acid Wheat germ oil Glandular extracts Nutrients For Hormone Balance • • • • • Pyridoxal-5-phosphate—reduces tissue hypersensitivity to estrogen, modulate hormone receptor complex and the binding of this complex to DNA, deficiency of B6 lead to exaggerated symptoms of estrogen excess with normal or slightly increased estrogen levels Magnesium—essential for hepatic Phase II detoxification of estrogens, co-factor for Catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT) which converts estrogen metabolites from phase I into water-soluble metabolites, up-regulates glucuronyl transferase which helps detoxify estrogens Vitamin B12—essential support for phase II, methylation pathway Indole-3-Carbinal(I3C)—natural compound found in cruciferous vegetables, shifts the 2/16 ratio in favor of 2-OH estrone which is not carcinogenic. Diindolylmethane(DIM)—More active then I3C, but less stable the guy with the bow tie 95 Principles for Health 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. Optimize GI fxn: digestion and absorption Support liver detoxification Support lymphatic function—skin brushing, rebounding, walking, dancing Proper breathing to increase blood O2 Promote adrenal health by managing stress and reducing adrenal stimulants Maintain normal glycemic control Whole, real, organic, locally-grown food diet Pure drinking water Proper exercises—aerobic and anaerobic Avoid fake fats Avoid all artificial sweeteners the guy with the bow tie 96 Functional Endocrinology and Nutrition Part 5 - Male Hormonal Problems Male Hormonal Disorders Andropause—decline in testosterone production in males Andropause • • • • • • • • • • • • A gradual decline in men’s ability to maintain an androgen dominant state Production of testosterone decline Emerging health problem in developed nations Due to increased exposure of xenoestrogens, exotoxins in the environment, stress, EFA and nutritional deficiencies, and impaired hepatic detox function A product of chemical, physical and environment factors—industrialization Primary, secondary and functional Functional is the most common cause The ratios between testosterone and other hormones changed, the most common between testosterone and estrogen Normal T:E should be 50:1 Estrogen dominant syndrome in men Can be found in men of all ages from late 20’s to the aged Typically presents a middle-age man with gradual decline in sex drive, strength, energy and enthusiasm for life, inactive, physical and mental fatigue for no apparent reason, depressed, pessimistic, difficult to get along, deteriorating family and social relationships, erectile dysfunction http://www.andropause.com/ http://health.discovery.com/centers/mens/articles/andropause.html S/S of Andropause • • • • • • • • • • • Typically identified with low testosterone levels Obesity Increased waist-to-hip ratio Insulin resistance Hyperglyceridemia Hyperlipidemia and hypercholesterolemia Low HDL Low LDL Increased fibrinogen levels Increased lipoprotein B Venous congestion • • • • • Mental fatigue and poor concentration Depression Lost of initiative Myalgia Decrease in • morning erection • Fullness in erection • Libido • Physical stamina • Visual acuity Testosterone Functions • • • • • • Cardiovascular—heart has more testosterone receptors than any other muscles in the human body, statin lowers cholesterol has been shown to reduce testosterone Energy and hemopoesis—as T decline, so does RBC count, reduced O2 leads to lowered ATP production Bone density—testosterone and progesterone stimulates osteoblasts activity Prostate health—testosterone is not responsible for prostate hyperplasia, both DHT and estrogen induce prostate hypertrophy Sex drive—testosterone promotes libido in both sexes Moods—testosterone promotes a man’s sense of well-being and mood the guy with the bow tie 97 Causes of Male Hormone Imbalance Problems • • • • • • • • Andropause—overall reduction of T Adrenal stress disorders—increased cortisol and estrogen dominance Prostate hypertrophy—lowered progesterone Gastrointestinal disorders Hepatic detoxification problems—most common reason for low DHT Nutritional deficiency—EFA, vitamins and minerals Statin drugs and corticosteriods Insulin resistance Insulin Resistance • • • As levels of T wane in men, glycemic control goes out of control Reduced T and increases in cortisol lead to insulin resistance, central obesity and metabolic disorders Declining T may be the primary driving factor for IR, MetS and CVD in men Diabetes 1996;45:1605-160 Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia • • • Voiding problems such as decreased caliber of urine stream, hesitancy, intermittency, staining, incomplete emptying and urine retention Storage problems such as urgency, frequency, nocturia, dysuria, urge incontinence These may also relate to bladder tone, especially in older men • The Lancet 2003;361(9366):1359-1367 BPH Pathogenesis Two theories: 1. Mechanical components or the hormone dependent hyperplasia • Androgen hypothesis • Estrogen hypothesis 2. Dynamic component or alpha-adrenergic tone • Modern Phytotherapist 2003;7(2):22-28 Androgen Hypothesis • • • Prostate function and growth are androgen dependent In the prostate, T is converted to DHT by 5-alpha reductase DHT is the active intracellular androgen which binds with the nuclear androgen receptor. This complex then bind to a specific DNA sequence, initiating mRNA production, protein synthesis, cell growth • Modern Phytotherapist 2003;7(2):22-28 the guy with the bow tie 98 Estrogen Hypothesis • • • • • • • Estrogen originate from T and androstenedione via the action of aromatase Observation from experiment showed that administration of estrogen could induce BPH As men age, endocrine environment becomes more estrogen dominant with a dramatic increase in estrogen compare to T It has been shown that estrogen, mediated by sex hormone binding globulin (SHBG), participates with androgen in setting the pace of prostate growth SHBG has been shown to increases with age and can act like an additional androgen receptor It is suggested that E binds to SHBG in the cell membrane, IGF-1 is synthesized leading to proliferation of prostate epithelial cells Further addition to the proliferating stimulation by androgens • Modern Phytotherapist 2003;7(2):22-28 Dynamic Component • • • • • Urethral obstruction—prostatism Alpha-adrenergic (sympathetic) fibers innervate the smooth muscle of the prostatic urethra and bladder neck Contraction of this smooth muscle can lead to BPH symptoms Alpha-adrenergic blocker such as prozosin hydrochloride are usually prescribed to alleviate prostatism symptoms Sympathetic dominance caused by stress may contribute to neurogenic inflammation and BPH symptoms • Modern Phytotherapist 2003;7(2):22-28 Herbal Support for Andropause • • • • • • • • Tribulus terrestris—supports sexual dysfunction for both sexes, improves spermatogensis, increase sertoli cells LH and T in males Lepidium meyenii (Maca)—enhances fertility in both sexes, increase spermatogensis, and hormones, aphrodisiac, adaptogenic Chrysin—passion fruit flower extract, inhibits aromatase activity, thus prevents the conversion of T into Estrogens, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-histamine, anti-viral, anti-cancer Panax Ginseng—increases T production, promotes spermatogensis, libido Saw Palmetto (Seronoa repens)—reduce 5-alpha reductase activity and lowered DHT which stimulates prostate cell to proliferate, reduce symptoms of BPH • Cautions: overdoes can reduce T production Pygeum Africanum—reduced benign prostate hypertrophy (BPH) similar to Saw palmetto Cerniltion—inhibits growth of prostate cells, reduces BPH and related symptoms: urinary urgency, dysuria, nocturia, incomplete voiding and dribbling Stinging Nettle (urtica dioca)—intercepts DHT and receptor binding, reduces BPH Nutritional Support for Male Hormone Disorders • • Zinc—improves male fertility and T concentration, down-regulates 5-alpha reductase and reduces DHT, inhibits prolactin levels Amino Acids (glycine, glutamic acid, alanine)—influences neurotransmitters activity of the bladder and relieve BPH symptoms Summary of Functional Endocrinology • • • • • • • • Complex interactions of endocrine glands to each other, to the environment, internal and external stressors Interactions of major hormones: cortisol, insulin, thyroxin, and adrenalin Interactions of major hormones with minor hormones: estrogens, progesterone, testosterone, Look for the root cause of problems Support whole body health by addressing the 3Ts: Trauma, toxins and thoughts Don’t miss digestive, liver detox and adrenal stress issues Focus on using dietary and lifestyle changes, wholesome foods, whole food based supplements (priority), individual nutrients for short term corrective action, essential fatty acids, anti-oxidants, botanicals Chiropractic care and nutritional counseling form a solid foundation for a wellness care program Resources • Seminar: Dr. Datis Kharrazian—Functional endocrinology, Functional Blood Chemistry the guy with the bow tie