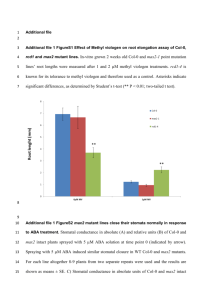
November 6
advertisement

Algorithms
input
output
definiteness
correctness
finiteness
generality
Pseudocode
Finding the largest element in a list
Best case
Worst case
Average Case
Analyzing Algorithms
function minmax(a1, a2, …, an)
// Find the largest and smallest elements of a list.
min a1
max a1
for i 2 to n do
if min > ai then min ai
if max < ai then max ai
return(max)
return(min)
What to count
Work done in the loop itself
Second example (Array initialization):
for i 1 to n
for j 1 to n do
A[i, j] 0
Definition again: f(x) = O(g(x))
Finding the largest and second largest list elements
1.
2.
Procedure big1(a1, a2, ...,an distinct integers)
max1 a1
for i 2 to n do
if ai > max1 then max1 ai
if max1 = a1 then max2 a2
else max2 a1
for i 2 to n do
if (ai > max2 and ai max1) then
max2 ai
return(max1, max2)
Procedure big2(a1, a2, ...,an distinct integers)
if a1 > a2 then {initialize max1 and max2}
max1 a1
max2 a2
else
max1 a2
max2 a1
for i 3 to n do
if ai > max1 then
max2 max1
max1 ai
else if ai > max2 then max2 ai
return(max1, max2)
Search Algorithms
Searching: Given a list of n numbers and some value x,
return the position of x in the list.
function linear search(x : int, a1, a2, ...,an: distinct int)
// return the location of x in the list, or 0 if x is not on list
i1
while (i n and x ai)
ii+1
if i n then location i
else location 0
Complexity:
Is there a more efficient searching algorithm?
The Binary Search Algorithm
function binary search( x: int, a1, a2, ...,an: increasing int)
i 1 // left endpoint of search interval
j n // right endpoint of search interval
while i < j
m (i+j)/2
if x > am then i m + 1
else j m
if x = ai then location i
else location 0
How the algorithm works:
Complexity of Binary Search
function binary search( x: int, a1, a2, ...,an: increasing int)
i 1 // left endpoint of search interval
j n // right endpoint of search interval
while i < j
m (i+j)/2
if x > am then i m + 1
else j m
if x = ai then location i
else location 0