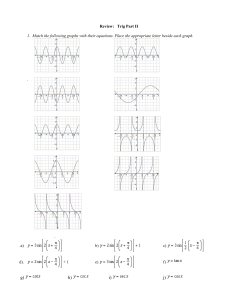
Equilibrium
advertisement

Equilibrium Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ 1. For the equilibrium system below, which of the following would result in an increase in the quantity of H2(g)? H2(g) + I2(g) <=====> 2HI(g) + 65 kJ a. removing some I2(g) d. both b and c b. removing some HI(g) e. both a and b c. decreasing temperature 2. 2.4 mol of PCl5(g) are injected into a 2.0 L container and the following equilibrium becomes established. PCl5(g) <=====> PCl3(g) + Cl2(g) If at equilibrium 1.0 mol of PCl5(g) is still in the container the Ke must be which of the following? a. 2.0 d. 0.98 b. 1.4 e. 1.02 c. 0.71 3. 10.0 mol of ammonia gas is injected into a 4.0 L container. At equilibrium 1.2 mol of nitrogen gas is found in the container. The number of moles of ammonia gas left in the container must be which of the following? N2(g) + 3H2(g) <=====> 2NH3(g) + 94 kJ a. 8.8 d. 6.4 b. 2.4 e. 9.2 c. 7.6 4. If the equilibrium shown below is heated at a constant pressure. H2(g) + I2(g) <=====> 2HI(g) + 65 kJ What is most likely to happen? a. Ke gets larger d. both a and c b. Ke gets smaller e. both b and c c. [H2] gets smaller 5. For this chemical system KOH(s) + HBr(aq) KBr(aq) + H2O(l) + 45 kJ which of the following is true? a. entropy has increased and enthalpy has decreased b. entropy has decreased and enthalpy has increased c. both entropy and enthalpy have decreased d. both entropy and enthalpy have increased e. heat of neutralization = 45 kJ/mol of HBr 6. If a solution of lithium phosphite has a [H1+] = 1.6 10-8, the pOH must be which of the following? a. 7.80 d. 7.0 b. 6.8 e. 6.20 c. 7.9 7. The Ksp expression for silver sulfate (Ag2SO4)is Ksp = a. [Ag][S] d. [Ag]2[SO42-] 2b. [Ag][SO4 ] e. none of the above 2- 2 c. [Ag][SO4 ] 8. When solid zinc hydroxide is in equilibrium with its ions, the ratio of zinc ion to hydroxide ion is which of the following? a. 1:2 d. 1:3 b. 2:1 e. 2:3 c. 1:1 ____ 9. In a saturated solution of silver sulfite (Ag2SO3), the concentration of silver ion is 3.6 10-4 mol/L. The Ksp of silver sulfite would be which of the following? a. 6.5 10-8 d. 7.6 10-19 -11 b. 2.3 10 e. none of the above c. 1.2 10-11 ____ 10. A precipitate of zinc hydroxide (Zn(OH)2)sits at the bottom of a test tube of distilled water. If the Ksp of this substance is 3.0 10-16 the [OH1-] in this solution in mol/L is which of the following? a. 8.4 10-6 d. 2.4 10-8 -6 b. 4.2 10 e. 7.5 10-17 -8 c. 1.2 10 Completion Complete each sentence or statement. 11. If solutions of barium chloride and sodium sulfate were mixed and a precipitate formed, the precipitate would be _________________________. Matching Look at the entropy and enthalpy changes below and match them to spontaneity choices below. a. S is positive, H is positive b. S is negative, H is positive c. S is positive, H is negative d. S is negative, H is negative ____ 12. spontaneity temperature dependent, spontaneous at high T ____ 13. nonspontaneous, proceeds only with continuous input of energy Here is a list of weak acids. Match to its conjugate base partner below. If no match exists indicate by writing none. a. H2O d. HPO422b. CO3 e. H2PO41c. H2CO3 f. OH1____ 14. PO43____ 15. HCO31Short Answer 16. Consider the equilibrium below: If 3.4 mol of HI was placed in a 2.0 L container and allowed to reach equilibrium, what would the equilibrium concentrations be for H2(g), I2(g) and HI(g) if the Ke = 49? H2(g) + I2(g) <=====> 2HI(g) (4 marks) 17. Write the equilibrium expression and the Kb expression for the anion of potassium nitrite (KNO2) reacting with water. Show how this anion acts like a base in water. Make sure to identify the two pairs of conjugate acid - base partners. (4 marks) Problem - Inquiry (17 marks) 18. If the concentration of Zn2+ is found to be 1.7 10-5 mol/L in a saturated solution of this salt, what is the Ksp of Zn(OH)2? (4 marks) 19. What is the molar solubility of CaF2 in a 0.65 mol/L solution of NaF. (Ksp of CaF2 is 4.9 10-11) (4 marks) 20. What is the pH and [OH1-]of a 1.47 mol/L solution of HCN(aq) if its Ka = 3.5 10-11? (5 marks) 21. What is the inital concentration of a weak acid if its Ka = 3.7 10-7 and its pH = 3.38? (4 marks) Essay - Application (5 marks) 22. Shown below is the Haber process for the commercial production of ammonia. N2(g) + 3H2(g) <=====> 2NH3(g) + 92 kJ Discuss the problem Fritz Haber had in determining the temperature to make the ammonia (the rate vs. equilibrium perspectives). Identify the goal Haber had to achieve and the two main uses Germany had for the ammonia production. (5 marks) Equilibrium Answer Section MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: A D C B A E D A B A REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: I I I I K/U I I K/U I I OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: OBJ: 7.3 7.5 7.5 7.2 7.7 8.2 7.6 7.1 7.6 7.6 LOC: LOC: LOC: LOC: LOC: LOC: LOC: LOC: LOC: LOC: CS1.03 CS2.06 CS2.06 CS2.06 CS1.05 CS2.06 CS1.07 CS1.06 CS2.06 CS1.02 COMPLETION 11. ANS: barium sulfate REF: K/U OBJ: 7.6 LOC: CS1.06 12. ANS: A 13. ANS: B REF: K/U REF: K/U OBJ: 7.7 OBJ: 7.7 LOC: CS1.05 LOC: CS1.05 14. ANS: D 15. ANS: C REF: K/U REF: K/U OBJ: 8.1 OBJ: 8.1 LOC: CS2.01 LOC: CS2.01 MATCHING SHORT ANSWER 16. ANS: mol/L H2(g) + I2(g) <=====> 2HI(g) initial 1.7 shift –2 @E 1.7 2 Ke = (1.7 2)2 / (2) = 49 (take the square root of both sides) 1.7 2 / = 7 7 = 1.7 –2 9 = 1.7 = 0.019 mol/L = [H2] = [I2]; [HI] = 1.7 2(0.019) = 1.3 mol/L REF: I 17. ANS: OBJ: 7.5 LOC: CS2.06 NO31- + H2O(aq) base-1 acid-2 <=====> HNO3(aq) + OH1-(aq) acid-1 base-2 Kb = HNO3 OH NO2 REF: K/U OBJ: 8.1 LOC: CS1.08 PROBLEM 18. ANS: Zn(OH)2(s) <====> @E Zn2+(aq) 1.7 10-5 2OH1-(aq) 2 1.7 10-5 + Ksp = 1.7 10-5 ( 2 1.7 10-5 )2 = 2.0 10-14 REF: I OBJ: 7.6 LOC: CS2.06 19. ANS: CaF2(s) <=====> Ca2+(aq) + 2F1-(aq) initial 0.65 @E 0.65 + 2 (negligible) 0.652 = 4.9 10-11 solubility = 1.2 10-10 mol/L REF: I 20. ANS: initial shift @E OBJ: 7.6 LOC: CS2.04 HCN(aq) <====> H1+(aq) + CN1-(aq) 1.47 -x x x x x 1.47 x x2 / 1.47 = 3.5 10-11 x = (3.5 10-11 1.47)0.5 pH = – log x pH = 4.56 pH = 5.14 REF: I OBJ: 8.2 21. ANS: HX(aq) <=====> H1+(aq) + X1-(aq) x 10-pH 10-pH [H1+] = 10-pH = 10-3.38 [H1+] = 4.17 10-4 mol/L (4.17 10-7)2 / = 3.7 10-7 LOC: CS2.06 x = 0.47 mol/L REF: I OBJ: 8.2 LOC: CS2.06 ESSAY 22. ANS: High temperatures do not favour the production of ammonia even though it speeds up the reaction rates. High pressures favour the production of ammonia by forcing the equilibrium to the side with fewer molecules. He discovered the introduction of a catalyst, iron oxide, increased the production of ammonia without the use of extreme temperatures. Ammonia dissolves in water in the soil forming ammonium ion that is converted into nitrates in the soil, which is assimilated by plants into amino acids and ultimately protein. This greatly enhances mans ability to provide relatively cheap food for a growing population. REF: C OBJ: 7.4 LOC: CS1.03