FIELD VALIDATION OF MOLECULAR SANDWICH HYBRIDIZATION
advertisement

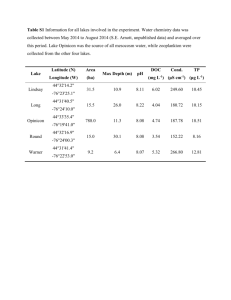
FIELD VALIDATION OF MOLECULAR SANDWICH HYBRIDIZATION ASSAYS TO DETECT Karenia brevis IN SOUTH-WEST FLORIDA COASTAL WATERS Allison J. Haywood1, Christopher A. Scholin1, Roman Marin III1, Kim Petrik2, Ryan Pigg2, Karen A. Steidinger2,3, and Cynthia Heil2. 1 Monterey Bay Aquarium Research Institute, Moss Landing, CA. 2 Florida Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission, Fish and Wildlife Research Institute, St. Petersburg, FL. 3 Florida Institute of Oceanography, 830 1st St South, St. Petersburg, FL. Sandwich hybridization assays (SHAs) for Karenia brevis, K. mikimotoi, K. selliformis and K. papilionacea were concurrently tested with the same whole, seawater samples collected offshore and inshore during the 5-year Monitoring and Event Response for Harmful Algal Blooms (MERHAB) Gulf of Mexico Sentinel Program and the local red tide monitoring program respectively. Results from testing ~900 samples (~700 from ship surveys, ~200 local samples) for the principal bloom-forming species in the region, Karenia brevis, were converted into cells.L-1 equivalents using an average standard curve (Charlotte A3 strain) to allow comparison with cell counts from microscopy. The 96-well plate version of the K. brevis SHA accommodates two different sensitivities. The lower limit of detection approximates near background cell concentrations (~1000 cells.L-1) and the upper detection limit extends to ~400,000 cells.L-1 given a fixed sample volume of 250 mL, although the range can be varied by altering sample and lysis buffer volumes. Cell equivalents were binned into the same categories currently used for reporting K. brevis cell concentrations and the associated risk assessment to the public, spanning 4 orders of magnitude from 1x103 to >1 x 106 cells.L-1. Additionally, natural and cultured samples were processed using the SHA in both the 96-well plate and printed probe array format for six different gymnodinioids including the above four species of Karenia using the Environmental Sample Processor (ESP). Preliminary results with matched sample lysates showed that that a similarly wide dynamic detection range to >1 x 106 cells.L-1 is also possible using the ESP, to allow remote, in situ categorical reporting of cells.L-1 equivalents. Both the 96-well plate and ESP array SHA techniques offer the ability to screen for multiple harmful algae including concurrently present Karenia species. For example, the SHA allowed the discrimination of overlapping populations of K. brevis and K. mikimotoi present during a 2005 marine mortality event, even though cells were misshapen in the hypoxic to anoxic conditions encountered.