Migrainous Headaches
advertisement

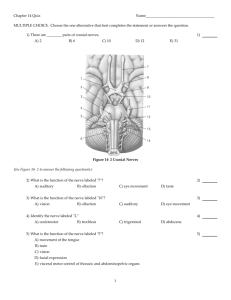
Migrainous Headaches Theory of mechanical irritation of peripheral potentially hyperexcited, peripheral sensory nerves o Migraine headache is postulated to be caused by dilatation of large vessels innervated by the trigeminal nerve. o Vasodilatation is the consequence of release of calcitonin gene–related peptide, substance P, and neurokinin A, found in the cell bodies of trigeminal neurons o Irritation of the peripheral branches of the trigeminal nerve results in release of substance P and neurokinins which travel along the nerve and produce a localized meningitis Guyuron (PRS 2000) reported 80% of patients had relief of migraine symptoms after corrugator resection Guyuron (PRS 2002 prospective) 95.5% experienced some degree of improvement in headache frequency and/or intensity Nerves involved: 1. frontal region - both supratrochlear (main trunk) and supraorbital (branches) nerves pierce the corrugator supercilii muscle. 2. temporal region – zygomaticotemporal Constricted by temporalis muscle 3. occipital region - greater occipital nerve (medial branch of the C2 dorsal root) Constriction by semispinalis capitis muscle as nerve passes through it This occurs 3 cm below the occipital protuberance and 1.5 cm lateral to the midline 4. Septonasal trigger sites Elimination of friction between a deviated septum and an enlarged turbinate Irritation of intranasal branches of trigeminal Botox injection useful for confirming the diagnosis 1. may cause temporary temporal hollowing – improves with cessation of injection Surgical Treatment (Guyuron PRS Jan 2005) 1. Frontal - glabellar muscle group including the corrugator supercilii, depressor supercilii, and procerus muscles removed through a palpebral incision to relieve compression of the supraorbital and supratrochlear nerves, which traverse these muscles. 2. Temporal - endoscopic removal of 3 cm of the zygomaticotemporal branch of the trigeminal nerve to prevent its compression by the temporalis muscle. commonly transected during craniofacial or aesthetic forehead surgery, with no reported consequence. 3. Occipital – Removal of a small portion of semispinatus capitus around the greater occipital nerve 4. Intranasal - septoplasty and inferior and/or middle turbinectomies based on intranasal abnormality. Complications