Activity9.2
advertisement

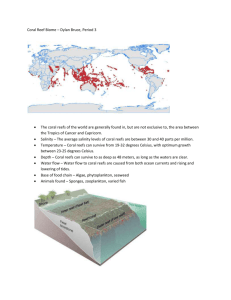
Activity 9.2: Extreme Algae I. Meet the Algae The single-celled algae that reside in coral reefs and sea ice provide excellent examples of the adaptability and evolutionary diversity of these amazing organisms. But before we can understand the role these organisms play in their respective environments, we need to know who they are. Using the web sites below, write a brief description of each of the following types of coral reef or sea ice algae. Include the following in your description: the phyla or division to which the alga belongs (common names are acceptable) where it lives (be as specific as possible) some general traits or characteristics (such as shape and size, light and nutrient preferences, major pigments, unique biochemistry, etc) Coral Reef Algae Symbiodinium (coral zooxanthellae) Coralline algae Red algae Green algae Brown algae Sea Ice Microalgae Diatoms Phytoflagellates II. Extreme Photosynthesis One of the most fascinating aspects of coral reef zooxanthellae and ice algae is how they capture light and obtain the necessary mineral nutrients for survival. The closeassociation of corals with their zooxanthellae and the close association of ice algae with bacteria and microflagellates are subjects of intense study by researchers interested in algal symbioses. Explore the web sites below and gather information on the photosynthetic processes of zooxanthellae and ice algae. In particular, pay attention to the relationship of zooxanthellae to their coral hosts and focus on the relationship of ice algae to bacteria and microflagellates. You will find good illustrations of these relationships. Pick one or two and complete the following: illustrate the light and nutrient pathways (carbon, nitrogen) of corals and their symbiotic zooxanthellae illustrate the light and nutrient pathways (carbon, nitrogen) of sea-ice algae, bacteria and microflagellates compare and contrast the photosynthetic environment (i.e., the availability of light and nutrients) of zooxanthellae and ice algae III. The Effects of Global Warming The warming of the oceans in recent decades has had a profound effect on coral reef and ice-edge ecosystems. High water temperatures may be one cause of coral bleaching while the melting and shrinking of polar sea ice is reducing plankton and benthic productivity. Study the web sites below and prepare a one-page statement on the negative consequences of global warming on coral reefs or polar ecosystems. Defend your statements by illustrating the effects of global warming on algae living in these environments and the consequences for the food webs that they support. Formulate your statement as if you were addressing the United Nations or a public forum. Recommended web sites: Getting Up to Date on Zooxanthellae http://www.aquarium.net/0998/0998_4.shtml Marine Biology – Coral Reefs (Outline) http://www.oaerre.napier.ac.uk/users/p.tett/MB/MBcoral.html An Introduction to Coral Reefs http://www.uvi.edu/coral.reefer/ Coral-Algal Symbiosis http://ww2.mcgill.ca/biology/undergrad/c442b/lect19/3.htm Hawaiian Reef Algae http://www.botany.hawaii.edu/ReefAlgae/default.htm About Reef Algae http://www.reef.crc.org.au/aboutreef/coral/algaeabout.html Algae in the Coral Reef Environment http://www.com.univ-mrs.fr/IRD/atollpol/ecorecat/ukalgrec.htm Coral reef Ecology: The Trophic Structure of Hawaiian Reefs http://krupp.wcc.hawaii.edu/BIOL200/powerpnt/trophic/ Arctic Sea Ice: Channels of Life http://oceanexplorer.noaa.gov/explorations/02arctic/background/sea_ice/sea_ice.ht ml Major Food Reserve Discovered Under Antarctic Ice http://unisci.com/stories/20021/0308022.htm Organisms Which Thrive in Arctic Sea Ice http://www.arctic.noaa.gov/essay_krembsdeming.html Studies on the Ecology of Polar Microalgae http://www.uni-kiel.de/ipoe/Websitealt/resgroup/phytopl.html Sea Ice Working Group http://www.uni-kiel.de/ipoe/Websitealt/resgroup/seaice.html Biomass, production and horizontal patchiness of sea ice algae in a high Arctic fjord http://www.int-res.com/abstracts/meps/v223/p15-26.html Coral Mortality and African Dust http://coastal.er.usgs.gov/african_dust/ Arctic Ecosystems (pdf file) http://envirosphere.ca/pdf/arctic.pdf Ecological States and Resilience of Coral Reefs http://www.consecol.org/vol6/iss2/art18/main.html Eutrophication and Water Quality in Coral Reefs http://globalcoral.org/Eutrophication%20and%20Water%20quality.html Water Quality Characterization and the Health of Coral Reefs http://www.epa.gov/owow/oceans/coral/symposium/szmant.html Climate Change Harms Ocean Life http://www.twnside.org.sg/title/1953-cn.htm Antarctic Krill Populations Crash in Response to Warming http://www.mlml.calstate.edu/news/loebpr.htm