1 - OSU Chemistry
advertisement

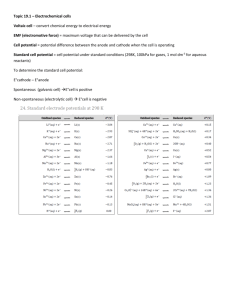
1. [7 points] Which substance is the reducing agent in the following reaction? Fe2S3 + 12HNO3 2Fe(NO3)3 + 3S + 6NO2 + 6H2O a. b. c. d. e. HNO3 S NO2 Fe2S3 H2O 2. [7 points] What is the oxidation number of manganese in potassium permanganate, KMnO4? (a) +1 (b) +2 (c) +5 (d) +4 (e) +7 3. [7 points] What is the coefficient of Fe3+, when the following redox equation is balanced in basic solution? a. b. c. d. e. 1 2 3 4 5 CN- + Fe3+ CNO- + Fe2+ 4. [7 points] What are the coefficients of H2S and H2O, when the following redox equation is balanced in acidic solution? a. b. c. d. e. 5, 8 5, 10 2, 4 2, 6 3, 8 MnO4- + H2S S + Mn2+ + H2O 5. [7 points] In a voltaic cell, electrons flow from ________________ . a. b. c. d. e. The salt bridge to the anode The anode to the salt bridge The cathode to the anode The salt bridge to the cathode The anode to the cathode 6. [7 points] Which one of the following substances would you expect to be the best oxidizing agent? a. b. c. d. e. H2 Na Cl2 Li Ca 7. [7 points] Which of the following reactions will occur spontaneously as written (standard reduction potentials are given on the back page)? a. Sn4+ (aq) + Fe3+ (aq) Sn2+ (aq) + Fe2+ (aq) b. 3Fe (s) + 2Cr3+ (aq) 2Cr (s) + 3Fe2+ (aq) c. Sn4+ (aq) + Fe2+ (aq) Sn2+ (aq) + Fe (s) d. 3Sn4+ (aq) + 2Cr (s) 2Cr3+ (aq) + 3Sn2+(aq) e. 3Fe2+ (aq) Fe (s) + 2Fe3+ (aq) 8. [7 points] Consider a voltaic cell where one half of the cell contains ZnCl2 (aq) in contact with a Zn electrode, while the other half of the cell contains FeCl2 (aq) in contact with a Fe electrode. Which electrode is the cathode and what is the standard cell potential, Eºcell ? a. Cathode = Zinc, Eºcell = +0.32 V b. Cathode = Iron, Eºcell = +0.32 V c. Cathode = Zinc, Eºcell = +1.20 V d. Cathode = Iron, Eºcell = +1.20 V e. Cathode = Zinc, Eºcell = -1.20 V 9. [7 points] In the above problem what would be the cell potential if the temperature were 298 K, the FeCl2 concentration was 0.50 M, and the ZnCl2 concentration was 0.0025 M? a. b. c. d. e. +0.39 V +0.25 V +0.46 V +1.27 V +1.34 V 10. [7 points] Consider a voltaic cell based on the following reactions: 2Fe (s) + O2 (g) + 4H+ (aq) 2Fe2+ (aq) + 2H2O (l) Which of the following actions would increase the measured cell potential? a. b. c. d. e. Increasing the size of the iron anode Adding FeCl2 to the anode compartment Adding NaOH to the cathode compartment (neutralization rxn) Adding NaOH to the anode compartment (precipitation rxn) None of the above actions will increase the cell potential 11. [7 points] The standard cell potential (Eºcell) of the reaction below is +0.126 V. What is the value of Gº for this reaction? Pb (s) + 2H+ (aq) Pb2+ (aq) + H2 (g) a. b. c. d. e. –24 kJ +24 kJ –12 kJ +12 kJ –50 kJ 12. [7 points] One of the differences between a voltaic cell and an electrolytic cell is that in an electrolytic cell _________ . a. b. c. d. e. an electric current is produced by a chemical reaction electrons flow toward the anode a non-spontaneous reaction is forced to occur O2 gas is produced at the cathode oxidation occurs at the cathode 13. [7 points] How many grams of copper (atomic weight = 63.55 g/mol) will be plated out by a current of 2.3 A applied for 25 minutes to a 0.50 M solution of copper (II) sulfate. a. b. c. d. e. 1.8 10-2 g 2.2 g 1.1 g 3.6 10-2 g 1.8 10-3 g 14. [7 points] Calculate the equilibrium constant at 25 ºC for the following reaction: Sn4+ (aq) + Sn (s) 2 Sn2+ (aq) a. b. c. d. e. 2.2 7.9 104 6.3 109 1.6 10-10 None of the above 15. [7 points] Construct a molecular orbital diagram for the peroxide ion, O22-. Based on this diagram what is the oxygen-oxygen bond order and the magnetic behavior of peroxide? a. b. c. d. e. Bond order = 2, magnetism = diamagnetic Bond order = 2, magnetism = paramagnetic Bond order = 1, magnetism = diamagnetic Bond order = 1, magnetism = paramagnetic Bond order = 1.5, magnetism = paramagnetic 16. [7 points] Which of the following statements is false? a. The number of molecular orbitals in a molecule is equal to the number of atomic orbitals in the constituent atoms b. A molecular orbital can hold 2 electrons, c. The splitting between bonding and antibonding molecular orbitals increases as the overlap increases d. Sigma bonds have a nodal plane intersecting the internuclear axis e. It’s not possible to form a pi bond through the overlap of two s atomic orbitals 17. [7 points] Which of the following MO’s is representative of an eg molecular orbital in a ML6 octahedral transition metal complex? (a) (b) (c) (d) 18. [7 points] Based on the electron configuration which one of the following complexes is most likely to be colorless? a. b. c. d. e. [Cu(NH3)4]2+ [Fe(H2O)6]3+ [CrCl6]3[Zn(OH)4]2[Ti(H2O)6]3+ 19. [7 points] Which complex ion is most likely to absorb light in the red region of the visible spectrum? a. b. c. d. [CuCl4]2[Cu(H2O)4]2+ [Cu(NH3)4]2+ [Cu(CN)4]2- 20. [7 points] What transition metal ion is responsible for the red color of a ruby? a. b. c. d. e. Mn2+ Cr6+ Fe2+ Ti3+ Cr3+ 21. [7 points] How many unpaired electrons are there on a [Co(CN)6]3- complex ion? a. b. c. d. e. 0 2 4 5 6 22. [7 points] What structure can be described as a hexagonal close packing of anions with 50% of the tetrahedral holes filled? a. b. c. d. e. Rock salt Nickel Arsenide Zinc Blende Wurtzite Cesium Chloride 23. [7 points] Nickel sulfide adopts the Nickel Arsenide structure type? What is the coordination environment of nickel and of sulfur. a. b. c. d. e. Ni octahedron, S octahedron Ni octahedron, S trigonal prism Ni tetrahedron, S tetrahedron Ni tetrahedron, S octahedron Ni octahedron, S tetrahedron 24. [7 points] The mineral oldhamite (CaS) adopts the rock salt structure type with a unit cell edge of 5.689 Å? What is the Ca-S bond distance? a. b. c. d. e. 2.84 Å 2.46 Å 4.39 Å 5.69 Å 2.56 Å 25. [7 points] The strongest peak in the X-ray diffraction pattern of cubic ZnS, which adopts the zinc blende structure type, is the (111) peak. If the diffraction pattern was collected with Cu K radiation (wavelength = 1.541 Å), and the 2-theta location of the (111) peak is 28.56º, what is the length of the unit cell edge, a ? a. b. c. d. e. 5.65 Å 3.12 Å 2.79 Å 5.41 Å None of the above Standard Reduction Potentials Half Reaction Eº (V) Cr3+ (aq) + 3e- Cr (s) -0.74 Ag+ (aq) + e- Ag (s) +0.80 Fe2+ (aq) + 2e- Fe (s) -0.44 Fe3+ (aq) + e- Fe2+ (s) +0.77 Cu2+ (aq) + 2e- Cu (s) +0.34 Zn2+ (aq) + 2e- Zn (s) -0.76 Pb2+ (aq) + 2e- Pb (s) -0.13 Sn4+ (aq) + 2e- Sn2+ (aq) +0.15 Sn2+ (aq) + 2e- Sn (s) -0.14 2H+ (aq) + 2e- H2 (g) +0.00 BiO+ (aq) + 2H+ (aq) + 3 e- Bi (s) + H2O +0.32 Spectrochemical Series Weak Field Ligands Cl- < F- < H2O < NH3 < NO2- < CN- Physical Constants & Conversion Factors h = 6.626 10-34 J-s c = 2.998 108 m/s R = 8.314 J/K-mol 1 Å = 10 pm = 1 10-10 m 1 eV = 1.602 10-19 J 1 F = 96,500 C/mol = 96,500 J/V-mol 1 A = 1 C/s 1 eV = 1.602 10-19 J Strong Field Ligands