YEAR 8- ASSESSMENT CHEMICAL MODELS
advertisement

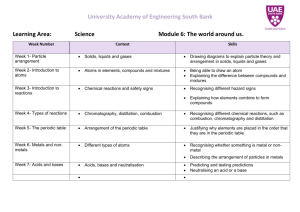
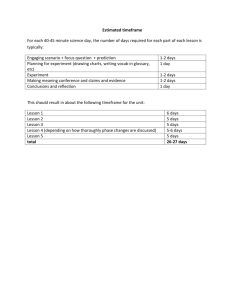
Group Names…………………………………….Group No……….. YEAR 8- ASSESSMENT CHEMICAL MODELS 2 Assessment AreasKnowledge and Understanding Communicating Information Planning & Conducting Investigations Equipment (per group) 1-2 Sheets of A3 paper. Glue or glue sticks or masking tape Paint (assorted colours) Paint brushes- 2 Polystyrene balls (bean bag balls)-plastic beaker full Photocopies from Science Now Book 3-Chap. 2 and Science Now Book 4-Chapter3 Instructions for Students Time Allowed - 1 Period for Part A Part A-Model Construction- Group work-ALL members to contribute Hint 1: Useful information about the substances listed below can be found in the photocopied sheets from the textbooks. It would be a good idea to carry out some research first eg. check whether the substance is an element, or a compound or a mixture. Is it a solid, a liquid or a gas? Answers to these questions will help you decide how the “atoms” will be glued in your different models. Step 1: Fill in your answers in the table in the planning space below. Ask your teacher to check this table before you proceed to making your models. Substance 1.tin 2.copper 3.pure water 4.bronze 5.carbon dioxide 6.air Teacher Mark Element, compound or mixture? element Solid, liquid or gas? solid /5 Step 2: What you have to do next: Based on your understanding of elements, compounds and mixtures make accurate models of the substances 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 & 6 listed below. You will use painted polystyrene balls to represent atoms in your model. Stick these onto your A3 sheet(s) in a way that best shows the arrangement of atoms in each substance. Substances to Model 1.tin 2.copper 3.pure water 4.bronze 5.carbon dioxide 6.air Hint 2: It is probably better to glue the balls on your models first and then place a dab of paint of appropriate colour on them after the glue has dried a bit. Science Unit Curriculum K–12 Directorate NSW Department of Education and Training Oxley High School Year 8 assessment task page 1 of 7 Clean up your work area and return equipment when you have completed your models. Name……………………………………………Group No……….. Part B –These questions are to be done individually Use the table below and the photo of the models to answer the following questions Model number 1 2 3 4 5 6 Substance Element, compound or mixture? Solid, liquid or gas ? tin copper pure water bronze carbon dioxide air element element compound mixture compound mixture solid solid liquid solid gas gas 1. Why should you use different coloured paint in models 1 and 2? Marks(1) ………………………………………………………………………………………….. 2. Choose one of the element models. Model………How does this model show that this substance is an element? ……………………………………………………………………………………… (2) 4. Choose one element model. Model…. Choose one compound model. Model…. a) Use these two models to describe the difference between elements and compounds. (1) ………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………… b) Use these two models to describe what is similar about elements and compounds. (2) ………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………… 5. Choose a compound model. Model…. Choose a mixture model. Model… (1) a) Use these two models to describe the difference between compounds and mixtures. (2) ……………………………………………………………………………………………. …………………………………………………………………………………………. b) Use these two models to describe what is similar about compounds and mixtures. (2) ……………………………………………………………………………………………. ………………………………………………………………………………………… (2) 6. No model is perfect but models are still of use in Science. State one benefit of using the models you have made in class. ………………………………………………………………………………………… State one feature of atoms your models fail to show. Science Unit Curriculum K–12 Directorate NSW Department of Education and Training (1) Oxley High School Year 8 assessment task page 2 of 7 ………………………………………………………………………………………… (1) YEAR 8- ASSESSMENT CHEMICAL MODELS Outcomes and content in which progress can be assessed PFA 4.2 uses examples to illustrate how models, theories and laws contribute to an understanding of phenomena 4.2 d) clarify with examples the benefits and limitations of using models DOMAIN 4.7.2 properties of solids, liquids and gases a) relate properties of solids, liquids and gases to the particle theory of matter 4.7.5 mixtures b) identify some common mixtures 4.7.6 compounds and reactions a) distinguish between elements and compounds c) distinguish between compounds and mixtures SKILLS 4.13 clarifies the purpose of an investigation and, with guidance, produces a plan for a first-hand investigation 4/5.13.1 identifying data sources f) use data sources to develop an understanding of the problem/question/hypothesis to be tested 4/5.14 performing first-hand investigations a)use a planned procedure when performing an investigation e)make modifications to procedures as problems arise in practical situations 4.15 gathers, processes, analyses and presents relevant information 4/5.15.2 gathering information from secondary sources f)organise data using a variety of methods including diagrams, tables, spreadsheets and databases 4/5.17.1 working individually e)evaluate the effectiveness of their performance in completing tasks 4/5.17.2 working in teams c)accept specific roles in a team while planning and conducting investigations, communicating information and understanding and solving problems f) evaluate the process used by the team and effectiveness of the team in completing the task Instructions for teachers-Prior to students doing the task Before attempting this task you should have revised differences in the packing arrangement of atoms in solids, liquids and gases. At the beginning of the unit students should have made some models like those described in the task (include some of the listed ones). They should be familiar with the components (atoms and molecules) making up common elements, compounds and mixtures eg. the components of copper, oxygen, carbon dioxide, water ,air and common alloys such as stainless steel. You will need 10 copies of the photocopied sheets from Science Now Books 3 and 4. It is best to do this assessment activity towards the end of the unit so it won’t be just a basic recall of work done a couple of periods before. Instructions to be Given on the Day Each student group (2-3people) is to construct models for each of the substances listed. Tell students that it is important that all members of the group contribute in some way towards completion of the task. Each person’s performance will be assessed. Students work in a group in Part A. Allow 10minutes for the groups to organize & then research .Do a teacher check or class swap and mark the table. Collect this sheet from each group. Write the correct entries for this table on the board. In addition write the formulae for carbon dioxide and water as well as giving a hint that air is a mixture of 3 main gases while bronze is a mixture of two metals. Allow 5-10 minutes to clean up afterwards. Science Unit Curriculum K–12 Directorate NSW Department of Education and Training Oxley High School Year 8 assessment task page 3 of 7 Do Part B in the following lesson (the next day preferably). Students attempt these questions individually. It is best that they refer to 6 accurate models eg. a videotape or a colour photo. Marking Criteria For Models-Part A Student Names- Rating Criteria Marks a) consistent use of colour used for atoms in all (4)models ie the same colour used for oxygen atoms in models 3,5 and 6 etc. b) correct use of colour for the atoms in most (5-6) models Marks Each 3 c)correctly depicts molecules in all 3 models( 3, 5, 6 ) A d)shows correct packing arrangement for atoms in most ( 5-6) models e)shows the correct proportions of atoms/molecules in bronze & air f) uses a key and labels each model B a) same colour used for the same atoms in 3 models b) correct use of colour for the atoms in some (3-4) models c)correctly depicts molecules in 2 models Marks Each 2 C d) shows correct packing arrangement for atoms in some(3-4) models e)shows correct relative amounts of atoms or molecules in bronze & air f) labels each model D a) same colour used for the same atoms in 2 models b) correct use of colour for the atoms in a couple 2 models c)correctly depicts molecules in 1 model E Marks Each 1 d) shows correct packing arrangement for atoms in some(1-2) models e) shows correct relative amounts of atoms/molecules in bronze OR air f) identifies eg. numbers or labels some models US Ratings: A:16-18 marks B:13-15 marks C: 10-12 marks D: 7-9 marks E: 1-6 marks US:0 marks .................cut along here and hand this bottom section to your Teacher …………………………… Student Evaluation for Group No……..Student Name………………………………… Make a comment on how well you and your group went on this task- your successes, problems and suggestions for improvement next time. ……………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………… Give a rating for the work done by each member of your team including yourself. Write names in the appropriate box in the table below (more than one name can go in each box) Science Unit Curriculum K–12 Directorate NSW Department of Education and Training Oxley High School Year 8 assessment task page 4 of 7 Did all of the work Did most of the work Shared in the work Science Unit Curriculum K–12 Directorate NSW Department of Education and Training Did a bit of work Did no work Oxley High School Year 8 assessment task page 5 of 7 Marking Criteria –Part B Student name- Rating Criteria Marks a) explains the purpose of different colours in models b) correctly matches models for elements, compounds and mixtures in most(4-5) cases A c) correctly uses models to describe similarities and differences between elements and compounds Marks Each 3 d) correctly uses models to describe the diffences and the similarities between compounds and mixtures e) correctly states a benefit and a limitation of using models B a) describes the use of colour in models b) correctly matches models for some( 2- 3) elements, compounds or mixtures in the situations described C c) correctly uses models to describe similarities OR differences between elements and compounds Marks Each 2 d) correctly uses models to describe the similarities OR differences between compounds and mixtures e) correctly states a benefit OR a limitation in the use of models D a) tries to relate the use of different colours in models b) successfully matches a model with an element, compound or mixture E c) attempts to describe the similarities or the differences between elements and compounds Marks Each 1 d) attempts to describe the similarities or the differences between mixtures and compounds e) attempts to relate a benefit or a limitation of using models US Suggested mark ranges for grading purposes. A 13 - 15 B 10 - 12 C 6 - 9 D 3 - 5 E 1 - 2 To gain a more representative measure you should also look at the overall distribution of grading obtained by highlighting student achievement in the relevant areas in the table above. Science Unit Curriculum K–12 Directorate NSW Department of Education and Training Oxley High School Year 8 assessment task page 6 of 7 Science Unit Curriculum K–12 Directorate NSW Department of Education and Training Oxley High School Year 8 assessment task page 7 of 7