AKS 31 – Ancient India & Ancient China
advertisement
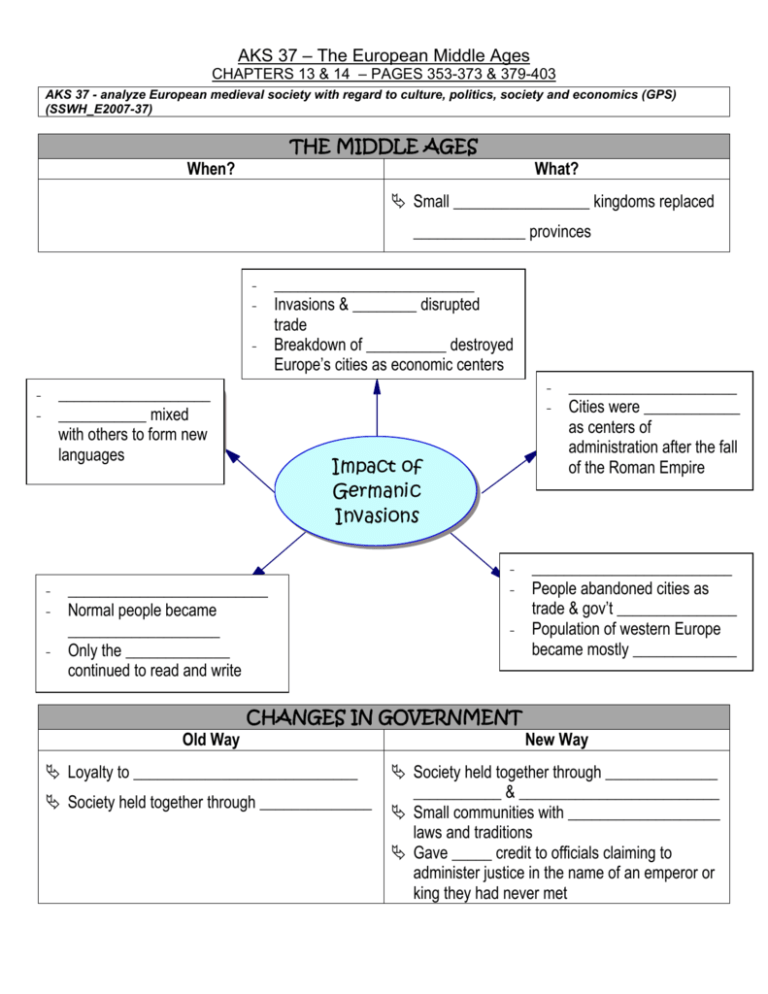
AKS 37 – The European Middle Ages CHAPTERS 13 & 14 – PAGES 353-373 & 379-403 AKS 37 - analyze European medieval society with regard to culture, politics, society and economics (GPS) (SSWH_E2007-37) THE MIDDLE AGES When? What? Small _________________ kingdoms replaced ______________ provinces - ___________________ - ___________ mixed with others to form new languages - _________________________ - Invasions & ________ disrupted trade - Breakdown of __________ destroyed Europe’s cities as economic centers - Impact of Germanic Invasions - _________________________ - Normal people became ___________________ - Only the _____________ continued to read and write - - _____________________ - Cities were ____________ as centers of administration after the fall of the Roman Empire - _________________________ - People abandoned cities as trade & gov’t _______________ - Population of western Europe became mostly _____________ CHANGES IN GOVERNMENT Old Way Loyalty to ____________________________ Society held together through ______________ New Way Society held together through ______________ ___________ & _________________________ Small communities with ___________________ laws and traditions Gave _____ credit to officials claiming to administer justice in the name of an emperor or king they had never met 37a - explain the manorial system and feudalism, to include the status of peasants and feudal monarchies and the importance of Charlemagne KINGDOM OF THE FRANKS Clovis Charles Martel Pepin the Short Charlemagne _____________________________________________________________ His wife wanted him to convert He was losing a battle and appealed to the Christian God – “For I have called on my gods, but I find they are far from my aid…Now I call on Thee. I long to believe in Thee. Only, please deliver me from my enemies.” He ended up winning, _________________, and he and 3,000 of his men were baptized. By 511, Clovis had _________________ the Franks into one kingdom The Church ____________________ him, marking the beginning of the partnership between two very powerful forces Gained political power when Clovis died because he was Mayor of the Palace ________________________________ was not king, but he led the armies and made policy, so in effect, he ruled the empire, but he was not king The _____________ (Muslims) attacked the Franks Charles Martel defeated Muslims at the _______________________ Charles Martel’s ________ He wanted to be the ___________ On behalf of the Church, Pepin fought the Lombards, who had invaded Italy and threatened Rome The _________ anointed Pepin “___________________________________” This began the __________________ Dynasty Ruled Franks from 751-987 Pepin the Short died in 768 Charles took over in 771 and ruled until 814 Became known as _____________________ (Charles the Great) Charlemagne _____________ Western Europe and spread ______________ throughout his lands Crowned “__________________________________” by the Pope **This was important because it was the first time a Pope had crowned a king and it signaled the joining of Germanic power, the Church, and the heritage of the Roman Empire _____________________________________________________ **Sent out ____________ to see that counts governed their counties justly **Regularly ______________ every part of his kingdom **Supervised the management of his huge estates ____________________________ **Invited English, German, Italian, and Spanish scholars to come to his empire to teach **Ordered all ____________ to be educated Charlemagne’s Death **Died in 814, left his son ___________________________ in charge – deeply religious, but ineffective ruler What Happened Next **Louis’ three sons fought for power, eventually split the kingdom into 3 parts **This resulted in Carolingian kings ____________ power & central authority ________________________ **Lack of strong rulers led to the rise of _______________________ FEUDALISM What led to it? What was it? The Feudal Pyramid Constant brutal fighting amongst _________________ Political system in which _______________ were granted the ____________ ___________ that legally belonged to the ______________ In return, nobles agreed to give their __________________ and _______________________________ to the king Developed not only in Europe, but in countries like Japan and China also Based on _____________ & _______________________ **In exchange for military & other services, a _________ (landowner) granted land (fief) to a ______________ (person receiving fief) FEUDAL SOCIAL CLASSES Those Who Fought Those Who Prayed Those Who Worked ____________________________________ ____________________________________ _________________ (most peasants were ___________) People who could not lawfully leave the place they were born They were bound to the land, but were not slaves because their lords could not buy or sell them. However, what their labor produced belonged to the lord. Manorial System Economic Arrangement Between Lord and Serf ______________ Self-contained communities that dotted the countryside throughout western Europe In exchange for ____________________________________________, serfs had to _______________________________________________ and pay several different kinds of _______________ Serfs The manor was practically _____________________, producing almost everything needed for daily life, so serfs rarely had to leave their manor for anything **Outside purchases included salt, iron, and a few unusual objects like millstones (used to grind flour) So why did they accept their economic hardship? **Acceptance was part of _________________________ **They believed that ________ decided people’s social position 37b - describe the political impact of Christianity to include Pope Gregory VII and King Henry IV 37c - explain the role of the church in medieval society AUTHORITY OF THE CHURCH When Charlemagne was crowned Roman Emperor, it was clear the Church sought to influence both ___________________ and ___________________ matters In Theory… In Reality… Church would hold authority in _____________ matters and the king would hold authority in _______________ matters The Church and King ____________________ for power In the Middle Ages, religion held people ________________ and _______________ them in a time of political turmoil and warfare Even though everyday life was hard, anybody could follow the ______________________ to salvation Church Structure Seven Sacraments _________________________ _________________________ _________________________ _________________________ _________________________ _________________________ What is it? Top _________________________ _________________________ _________________________ _________________________ _________________________ _________________________ (The continuation of Christ’s priesthood _________________________ Canon Law Punishments for Breaking Canon Law All medieval Christians, kings and peasants _____________________________ alike, were subject to canon law (____________ **Banishment from the Church and you were law) denied salvation (meaning you could not go to **Matters like marriage and religious practices Heaven) **Established courts to try people accused of _____________________________ breaking canon law **Sacraments & religious services could not be performed in the king’s lands Pope used __________________ and ________________ as political weapons **A disobedient king might get excommunicated **The king’s vassals would be freed from all their duties to him If king continued to disobey Pope, an interdict could be issued against him **Remember, sacraments & religious services could not be performed in the king’s lands **As Christians, the king’s subjects believed that without such sacraments they might be __________ ____________________, so the king _________ his authority Otto I Otto wanted to limit the power of the ____________ and form an alliance with the ___________, so he invaded __________ on the _________ behalf The __________ crowned Otto ______________ **This created a German-Italian empire called the Roman Empire of the German Nation – later came to be known as the ______________________ EMPEROR CLASHES WITH THE POPE Pope Gregory II King Henry IV Pope Gregory II Showdown at Canossa He resented the fact that kings, like Otto, had control over clergy He banned _________________________ in 1075 Ceremony in which kings and nobles appointed church officials Called a meeting of bishops and ordered Gregory to ___________________ ______________________ Pope Gregory ______________________ Henry Bishops & priests sided with the Pope Henry decided he wanted the Pope’s forgiveness January 1077 – Henry traveled to this town in the Alps and waited in the snow for three days, begging _______________________ Pope Gregory _________________________ Henry had been humiliated, but he felt triumphant and rushed home to punish rebellious nobles Concordat of Worms The issue of lay investiture remained _________________, despite all the (1122) stuff that happened between Henry & Gregory 1122 **Representatives of Church & emperor met in the German city of Worms **Compromise reached: ****The Church alone could _______________________, but the emperor could _________________________________ EMPEROR CLASHES WITH THE POPE Problems in the Church Benedictine Monastery Power of Pope Extended Cathedrals Some priests nearly ____________________ Some popes were men of _______________________________ Reformers Had Three Main Issues: Many village ___________________________________________ **This was against Church rulings Bishops sold positions in the church (__________________) Using __________________________, kings appointed church bishops **Reformers believed the Church alone should appoint bishops Reformers that founded it desired to return to the _____________________ ___________________ Church had its own court (_________________), tax system, and diplomats Church was _______________ Cathedrals represented the ___________________, so they were richly decorated and glorious buildings **Built in the ______________________ of architecture 37d - describe how increasing trade led to the growth of towns and cities CHANGES IN MEDIEVAL SOCIETY _________________________________ _________________________ **Horses gradually replaced oxen for plowing and for pulling wagons **Farmers began growing crops on 2/3 of their land each year (rather than ½) **Farmers began using a new type of harness that fit across a horse’s chest **Food production, including sources of vegetable protein, increased **This led to an increase in population __________________ **Organized and changed the way business was done **Trained young people in a skilled job, regulated the quality of goods sold, and were major forces in community life ________________________________ **Expansion of trade and business **More goods were available **New trade routes opened Towns became trade centers **Banking became an important business Urban Life Revival of Learning As trade blossomed and farming methods improved, the population of western Europe ____________________ **Rose from 30 million to 42 million between 1000 and 1150 As people left life on the manor for life in towns, they challenged the __________________ ways of feudal society in which everyone had a place **People were pursuing the economic and social opportunities the towns offered _____________________ = everyday language **Writers brought literature to many people, since most people could not read or understand Latin Growing trade & growing cities brought a new interest in learning **____________________ (groups of scholars and students) arose in western Europe Expanded ___________________ **Christian scholars from Europe visited Muslim libraries in Spain, and Jewish scholars translated Arabic copies of Greek writings into Latin **Europeans acquired a whole new body of knowledge in this way Medieval Philosophy **___________________________ **Argued that the most basic religious truths could be proved by __________ __________________ **Scholastics, like Aquinas, debated Aristotle and issues of the time **Teachings on law & gov’t influenced thinking of western Europeans (especially French and English) **Thus began the development of democratic institutions & traditions OTHER NOTABLE EVENTS OF THE TIME PERIOD: ENGLAND 1066 Battle of Hastings 1154 Henry II becomes ruler of England Normans, under __________________________, defeated Harold Godwinson, Anglo-Saxon king **English lords lost their land William granted fiefs to Norman lords **They swore loyalty to him personally **Laid the foundation for ____________________ Became ruler of England in 1154 Strengthened England’s ____________________ Sent royal judges to parts of England to collect taxes, settle lawsuits, & punish crimes Introduced the use of the ______ in English courts Laid foundation for English __________________ 1215 1295 1204 1226 Estates-General Magna Carta signed by King Signed by King John of England in 1215 John Justinian’s Code was very similar to the Magna Carta Guaranteed what are now seen as ____________ ____________________________ in both England and the US Included: **No taxation without ______________________ **Trial by __________ **Protection of the law Meeting of Model Parliament Met in 1295 under the reign of Edward I Considered a major step toward ______________ ________________ because: It was a legislative group composed of __________________ – burgesses from every borough and knights from every county ** Under Edward I, Parliament was a royal tool that weakened the great lords, but as time went on, it became strong enough to provide a check on royal power FRANCE Philip II regains Normandy Strengthened __________________________ in France Increased land under his control and became more powerful than any of his vassals Established royal officials called bailiffs who presided over his courts and collected his taxes throughout Europe Louis IX becomes king Becomes king in 1226 Strengthened ________________, weakened ____________________ by: **Created an _____________________________ **This court could overturn decisions of local courts 1st Estate: __________________________ 2nd Estate: __________________________ 3rd Estate Added by Philip: __________________________________________ that Philip invited to participate in the council THE END OF MEDIEVAL SOCIETY FACTOR 1: THE GREAT SCHISM When & How Began When & How Resolved Effect on Medieval Life _____________ _____________ French pope moved papacy Council of Constance elected from ____________ to a ________________ to _______________ replace the 3 popes FACTOR 2: THE BUBONIC PLAGUE Where & How Spread Began in ______________ Spread through ___________ Economic Effects Caused severe decline in ___________________ and This event _______________ ___________________ the Church Effect on Church Church _________________ ________________________ ____________ ______________ prices Decline in _______________ system FACTOR 3: THE HUNDRED YEARS’ WAR Reason Outcome Effect on Medieval Society French eventually _________ Age of Chivalry ___________ ________________________ English ___________ France ________________________ England’s Edward II ________________________ when Philip IV of France died replaced feudal loyalties









