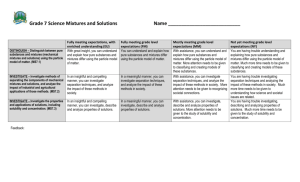
Science 7 Outcomes basic chart
advertisement
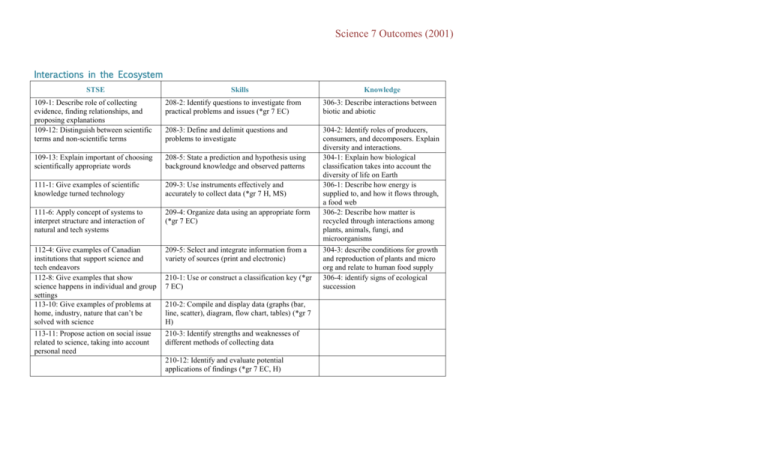
Science 7 Outcomes (2001) Interactions in the Ecosystem STSE Skills Knowledge 109-1: Describe role of collecting evidence, finding relationships, and proposing explanations 109-12: Distinguish between scientific terms and non-scientific terms 208-2: Identify questions to investigate from practical problems and issues (*gr 7 EC) 306-3: Describe interactions between biotic and abiotic 208-3: Define and delimit questions and problems to investigate 109-13: Explain important of choosing scientifically appropriate words 208-5: State a prediction and hypothesis using background knowledge and observed patterns 111-1: Give examples of scientific knowledge turned technology 209-3: Use instruments effectively and accurately to collect data (*gr 7 H, MS) 111-6: Apply concept of systems to interpret structure and interaction of natural and tech systems 209-4: Organize data using an appropriate form (*gr 7 EC) 304-2: Identify roles of producers, consumers, and decomposers. Explain diversity and interactions. 304-1: Explain how biological classification takes into account the diversity of life on Earth 306-1: Describe how energy is supplied to, and how it flows through, a food web 306-2: Describe how matter is recycled through interactions among plants, animals, fungi, and microorganisms 112-4: Give examples of Canadian institutions that support science and tech endeavors 112-8: Give examples that show science happens in individual and group settings 113-10: Give examples of problems at home, industry, nature that can’t be solved with science 209-5: Select and integrate information from a variety of sources (print and electronic) 113-11: Propose action on social issue related to science, taking into account personal need 210-3: Identify strengths and weaknesses of different methods of collecting data 210-1: Use or construct a classification key (*gr 7 EC) 210-2: Compile and display data (graphs (bar, line, scatter), diagram, flow chart, tables) (*gr 7 H) 210-12: Identify and evaluate potential applications of findings (*gr 7 EC, H) 304-3: describe conditions for growth and reproduction of plants and micro org and relate to human food supply 306-4: identify signs of ecological succession Science 7 Outcomes (2001) 211-5 Defend a position or issue on basis of findings Earth’s Crust STSE 109-7 Identify different approaches to answer questions, solve problems, and make decisions (*gr 7 MS) Skills 208-2: Identify questions to investigate from practical problems and issues (*gr 7 IE) Knowledge 311-4 examine some of the catastrophic events, such as earth quakes or volcanic eruptions that occur on or near the Earth’s surface 311-5 Analyse data on the geographical and chronological distribution of catastrophic events to determine patterns and trends 110-1 Give examples of ideas and theories used in the past to explain natural phenomena 209-1 Carry out procedures controlling major variables (*gr 7 H, MS) 110-4 Describe examples of how scientific knowledge has evolved in light of new evidence 209-4: Organize data using an appropriate form (*gr 7 IE) 111-2 Give examples of technologies used in scientific research 209-6 Use tools and apparatus safely (*gr 7 MS) 112-3 Explain how society’s needs can lead to development in science and technology 112-7 Give examples of how science and technology affects their lives and community (*gr 7 MS) 210-1: Use or construct a classification key (*gr 7 IE) 310-1 Describe the composition of the Earth’s crust 210-6 Interpret patterns and trends in data, and infer and explain relationships among variables 310-2a classify minerals based on their physical characteristics by using a dichotomous key 112-12 Give examples of Canadian contributions to science and technology 210-12: Identify and evaluate potential applications of findings (*gr 7 IE, H) 310-2b classify and describe rocks based on their method of transformation in the rock cycle 311-1 explain the processes of mountain formation and the folding and faulting of the Earth’s surface 311-6 Develop a chronological model or time scale of major events in the Earth’s history Science 7 Outcomes (2001) 113-1 Provide some positive and negative effects intended and unintended consequences of a particular science and technology development (*gr 7 MS) 113-7 Suggest solutions to problems from applications of science and technology, taking into account potential advantages and disadvantages 211-3 work cooperatively with team members to develop and carry out a plan, and trouble shoot problems as they arise 311-2 explain various ways rocks can be weathered 211-4 Evaluate individual and group processes used in planning, problem solving, decision making, and completing a task 310-3 classify various types of soil according to characteristics, and investigate ways to enrich soils 311-3 relate various meteorological, geological, and biological process to the formation of soils Science 7 Outcomes: Heat STSE 109-4 Give examples technologies used in past were developed trial and error 110-7 Give examples technologies used in past to meet human Skills of how the through of the needs 111-5 Describe the science underlying particular technologies designed to explore natural phenomena, extend human capabilities, or Knowledge 208-8 Select appropriate methods and tools for collecting data and for solving problems 209-1 Carry out procedures controlling the major variables (*gr 7 IE, MS) 308-1 Compare various instruments used to measure temperature 209-3: Use instruments effectively and accurately to collect data (*gr 7 IE, MS) 308-4 Explain changes of state using particle model of matter 308-3 Explain how each state of matter reacts to changes in temperature Science 7 Outcomes (2001) solve problems (*gr 7 MS) 112-1 Describe how an individuals needs can lead to developments in science and technology 112-9 Identify science and technology based careers in their community 113-4 Analyze the design technology and the way it functions on the basis of its impact on their daily lives 210-2: Compile and display data (graphs (bar, line, scatter), diagram, flow chart, tables) (*gr 7 IE) 210-10 Identify potential sources and determine the amount of error in measurement 210-11 State a conclusion, based on experimental data, and explain how evidence gathered supports or refutes an initial idea 210-12: Identify and evaluate potential applications of findings (*gr 7 IE, EC) 210-13 Test the design of a constructed device or system 211-2 Communicate questions, ideas, intentions, using lists, notes in point form, sentences, data tables, graphs, drawings, oral language, and other means 308-2 Explain temperature, using the concept of kinetic energy and the particle model of matter 308-5 Compare transmission of heat by conduction, convection, and radiation 308-7 Explain, using the particle model of matter, differences among heating capacities of some common materials 308-6 Describe how various surfaces absorb radiant heat Science 7 Outcomes (2001) Science 7 Outcomes (2001) Science 7 Outcomes: Mixtures and Solutions STSE Skills 109-4 Give examples of how technologies used in the past were developed though trial and error 109-7 Identify different approaches to answer questions, solve problems, and make decisions (*gr 7 EC) 109-10 Relate personal activities in formal and informal settings to specific science disciplines 109-14 Explain the importance of using precise language in science and technology 111-5 Describe the science underlying particular technologies designed to explore natural phenomena, extend human capabilities, or solve problems (*gr 7 MS) 208-1 Rephrase questions in a testable form and clearly define practical problems 208-6 Design an experiment and identify major variables 209-1 Carry out procedures controlling the major variables (*gr 7 IE, EC) 209-3: Use instruments effectively and accurately to collect data (*gr 7 IE, H) 209-6 Use tools and apparatus safely (*gr 7 EC) Knowledge 307-1 Distinguish between pure substances and mixtures, using the particle model of matter 307-2 Identify and separate the components of mixtures 307-3 Describe the characteristics of solutions, using the particle model of matter 307-4 Describe qualitatively and quantitatively the concentration of solutions 307-5 Describe qualitatively the factors that affect solubility Science 7 Outcomes (2001) 112-7 Give examples of how science and technology affects their lives and community (*gr 7 EC) 113-1 Provide some positive and negative effects intended and unintended consequences of a particular science and technology development (*gr 7 EC) 209-7 Demonstrate a knowledge of WHMIS standards by using proper techniques for handling and disposing of lab materials 210-4 Predict the value of a variable by interpolating or extrapolating from graphical data 210-7 Identify, and suggest explanations for, discrepancies in data 210-9 Calculate theoretical values of a variable 210-16 Identify new questions and problems that arise for what was learned