Podium Presentation Skills: Quick Reference Guide
advertisement

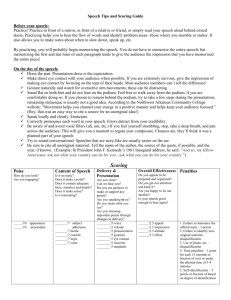
Podium Presentation Skills Quick Reference Guide Techniques to Overcome Anxiety Technique Pointers Notes Adequately Prepare Prepare speech Edit speech into short phrases Rehearse at location before Devise a speech that follows your natural speaking delivery Edit your content to fit your time allowance Test any equipment needed before you present Anticipate questions and prepare answers Learn to Relax Normal to be nervous Visualize success Use relaxation techniques Avoid caffeine Use deep breathing exercises to relax you Step through your speech in your mind and visualize a positive reaction from your audience Get acquainted with your location and audience Be early Familiarize yourself with the podium Meet audience before hand Walk the route from your chair to the podium before the audience arrives Take the opportunity to talk with audience members before the meeting starts Make eye contact with some of the audience members you talked with before the meeting Focus on Key Points Concentrate on the message Speak with energy in your voice Use pauses to emphasize Stay focused on the main point of the message Use voice tone and inflection to emphasize your main points Practice Practice in front of a mirror Ask a friend to listen and give feedback More experience in presentations leads to more confidence Practice before ever delivering a presentation Visualize the expected audience as you practice Podium Avoid leaning on the podium Determine distance when speaking into the microphone Use good posture when standing at the podium Confirm ahead of time how close your mouth needs to be to the microphone Avoid rocking behind the podium and distracting your audience Verbal and Non-Verbal Skills Description Type of Verbal Skills Voice Projection Pitch Rate Pronunciation Fillers Voice projection is vital in front of a large audience. Get someone to stand at the back of the room and practice projecting your voice. Vary the pitch of your voice to keep your audience interest. A high-pitched voice tends to convey nervousness to an audience, so try to lower your pitch to express confidence. The rate at which you speak can affect your audience understanding. Slow down when talking about complex concepts. Pronunciation relates to how you articulate or string words together. Avoid using contractions such as “gonna” instead of “going to,” as it may come across as too casual. Avoid using fillers such as “you know’ and “like” to fill silence. Use a pause of silence to emphasize your point and allow the audience to process the message. Description Type of NonVerbal Skills Stance Eye Contact Facial Expression Movement Gestures Stance relates to how you hold your body. Stand tall and keep weight evenly distributed between both feet. Making eye contact with your audience is a sign of respect, as it shows that you’re trying to engage them. When making eye contact, do so for no more than five seconds at a time. Your facial expression is often interpreted as a reflection of what you’re truly feeling. Smiling can reassure your audience and make you look confident. Movement is used to convey excitement or to build rapport with audience members. When using a podium don’t get stuck in one spot. Gestures help emphasize important points, and should relate to what you’re presenting. Avoid pointing at audience members, and reduce any distracting habits such as fidgeting with pens, keys, hair, or glasses. Audience Profile o o o o o o o o Who is the decision maker or decision makers? How much does the decision maker(s) know about the situation? How does the decision maker(s) view the situation? How will the decision maker(s) react to the proposal? Who else will attend the presentation? What are their views of the presentation or proposal? Who else will be affected by this presentation? What's the next step? Preparing Your Introduction Your introduction should: Grab their attention State your purpose Show specific benefits Other ways to begin your presentations: A statement of your qualifications Present facts and figures Use Quotes that prove your point Use an Analogy to clarify Remember: An audience will remember best what you say first and what you say last.