Month by Month Mapping Standards Septemer
advertisement
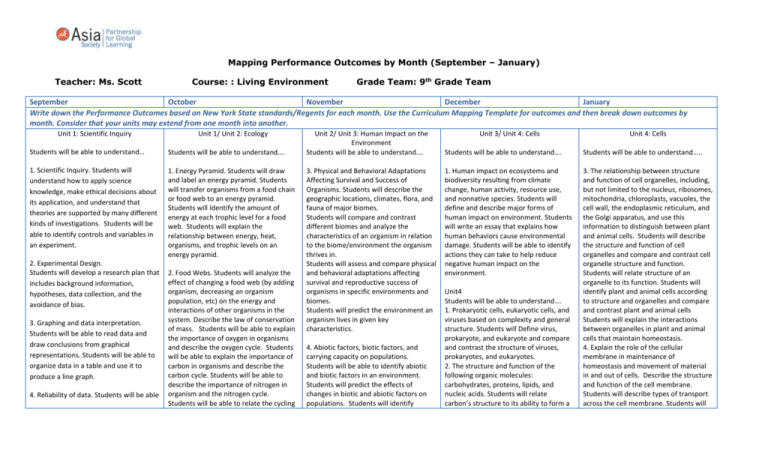
Mapping Performance Outcomes by Month (September – January) Teacher: Ms. Scott Course: : Living Environment Grade Team: 9th Grade Team September October November December January Write down the Performance Outcomes based on New York State standards/Regents for each month. Use the Curriculum Mapping Template for outcomes and then break down outcomes by month. Consider that your units may extend from one month into another. Unit 1: Scientific Inquiry Unit 1/ Unit 2: Ecology Students will be able to understand… Students will be able to understand…. 1. Scientific Inquiry. Students will understand how to apply science knowledge, make ethical decisions about its application, and understand that theories are supported by many different kinds of investigations. Students will be able to identify controls and variables in an experiment. 1. Energy Pyramid. Students will draw and label an energy pyramid. Students will transfer organisms from a food chain or food web to an energy pyramid. Students will Identify the amount of energy at each trophic level for a food web. Students will explain the relationship between energy, heat, organisms, and trophic levels on an energy pyramid. 2. Experimental Design. Students will develop a research plan that includes background information, hypotheses, data collection, and the avoidance of bias. 3. Graphing and data interpretation. Students will be able to read data and draw conclusions from graphical representations. Students will be able to organize data in a table and use it to produce a line graph. 4. Reliability of data. Students will be able 2. Food Webs. Students will analyze the effect of changing a food web (by adding organism, decreasing an organism population, etc) on the energy and interactions of other organisms in the system. Describe the law of conservation of mass. Students will be able to explain the importance of oxygen in organisms and describe the oxygen cycle. Students will be able to explain the importance of carbon in organisms and describe the carbon cycle. Students will be able to describe the importance of nitrogen in organism and the nitrogen cycle. Students will be able to relate the cycling Unit 2/ Unit 3: Human Impact on the Environment Students will be able to understand…. 3. Physical and Behavioral Adaptations Affecting Survival and Success of Organisms. Students will describe the geographic locations, climates, flora, and fauna of major biomes. Students will compare and contrast different biomes and analyze the characteristics of an organism in relation to the biome/environment the organism thrives in. Students will assess and compare physical and behavioral adaptations affecting survival and reproductive success of organisms in specific environments and biomes. Students will predict the environment an organism lives in given key characteristics. 4. Abiotic factors, biotic factors, and carrying capacity on populations. Students will be able to identify abiotic and biotic factors in an environment. Students will predict the effects of changes in biotic and abiotic factors on populations. Students will identify Unit 3/ Unit 4: Cells Unit 4: Cells Students will be able to understand…. Students will be able to understand..... 1. Human impact on ecosystems and biodiversity resulting from climate change, human activity, resource use, and nonnative species. Students will define and describe major forms of human impact on environment. Students will write an essay that explains how human behaviors cause environmental damage. Students will be able to identify actions they can take to help reduce negative human impact on the environment. 3. The relationship between structure and function of cell organelles, including, but not limited to the nucleus, ribosomes, mitochondria, chloroplasts, vacuoles, the cell wall, the endoplasmic reticulum, and the Golgi apparatus, and use this information to distinguish between plant and animal cells. Students will describe the structure and function of cell organelles and compare and contrast cell organelle structure and function. Students will relate structure of an organelle to its function. Students will identify plant and animal cells according to structure and organelles and compare and contrast plant and animal cells Students will explain the interactions between organelles in plant and animal cells that maintain homeostasis. 4. Explain the role of the cellular membrane in maintenance of homeostasis and movement of material in and out of cells. Describe the structure and function of the cell membrane. Students will describe types of transport across the cell membrane. Students will Unit4 Students will be able to understand…. 1. Prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells, and viruses based on complexity and general structure. Students will Define virus, prokaryote, and eukaryote and compare and contrast the structure of viruses, prokaryotes, and eukaryotes. 2. The structure and function of the following organic molecules: carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids. Students will relate carbon’s structure to its ability to form a Mapping Performance Outcomes by Month (September – January) to identify factual claims and make decisions based on evidence, bias, sample size, repeated trials, and objective data collection. of nutrients to food webs and energy pyramids. Students will be able to compare and contrast the cycling of energy and matter. population growth given a scenario or a graph as exponential or logistical and identify carrying capacity in the event of logistical growth. wide variety of organic compounds. Students will define and describe the structure and function of carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids. Students will compare and contrast the structure and function of carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids. relate solute properties to the type of transport used across the cell membrane and identify relative concentrations of water and solutes in intra and extracellular fluid. Students will relate the movement of water and solutes across the cell membrane to maintain homeostasis. 5. Students will define and describe the purpose of mitosis and describe the steps of mitosis. Assessments Weekly quiz (vocab, regents based questions) End of unit assessment (Regents style) Homework Assessments Assessments Assessments Assessments Weekly quiz (vocab, regents based questions) End of unit assessment Critical Thinking Questions Weekly quiz (vocab, regents based questions) Critical Thinking Questions Poster board Project Exit Slips Weekly quiz (vocab, reading) Critical Thinking Questions Foldable Project Unit Test Exit Slips Weekly quiz (vocab, regents based questions) Unit Test Venn Diagrams Exit Slips Resources Resources Resources Resources Resources Biology Textbook Lab Materials Brainpop.com Power points Biology Textbook Lab Materials Brainpop.com Power points Holt Biology Additional Resources Biology Textbook Lab Materials Brainpop.com Power points Holt Biology Additional Resources Biology Textbook Lab Materials Brainpop.com Power points Biology Textbook Lab Materials Brainpop.com Power points Important Dates/Trips Important Dates/Trips1st Marking Pd ends 10/23 Parent/Teacher conf. 10/29 Important Dates/Trips Important Dates/Trips Marking Pd ends 12/11 Holidays begin 12/23 Important Dates/Trips Marking Pd ends 1/22 Regents begin 1/26/10 Source: New York State Standards, New York States Regents, Interim Assessment Data








