Linear Relations: Partial Variation Worksheet
advertisement
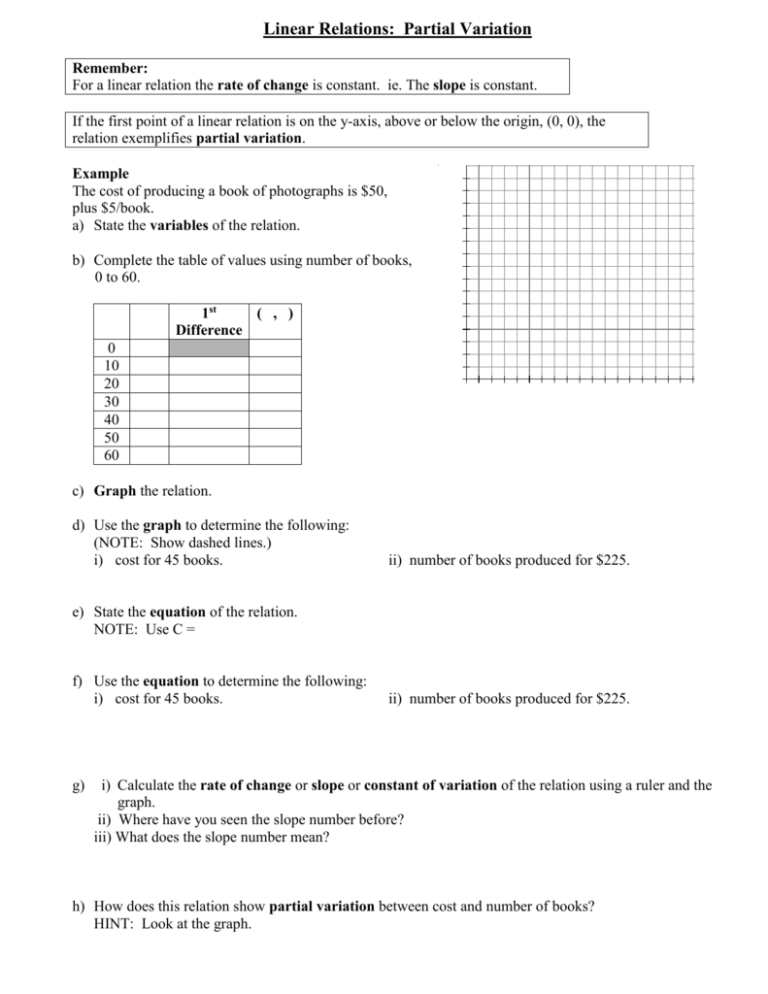
Linear Relations: Partial Variation Remember: For a linear relation the rate of change is constant. ie. The slope is constant. If the first point of a linear relation is on the y-axis, above or below the origin, (0, 0), the relation exemplifies partial variation. Example The cost of producing a book of photographs is $50, plus $5/book. a) State the variables of the relation. b) Complete the table of values using number of books, 0 to 60. 1st ( , ) Difference 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 c) Graph the relation. d) Use the graph to determine the following: (NOTE: Show dashed lines.) i) cost for 45 books. ii) number of books produced for $225. e) State the equation of the relation. NOTE: Use C = f) Use the equation to determine the following: i) cost for 45 books. g) ii) number of books produced for $225. i) Calculate the rate of change or slope or constant of variation of the relation using a ruler and the graph. ii) Where have you seen the slope number before? iii) What does the slope number mean? h) How does this relation show partial variation between cost and number of books? HINT: Look at the graph. Assignment Yoga costs $20 for registration, plus $8 per class. a) State the variables of the relation. b) Complete the table of values using number of classes, 0 to 6. 1st ( , ) Difference 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 c) Graph the relation. d) Use the graph to determine the following: (NOTE: Show dashed lines.) i) cost for 4 classes. ii) number of classes that can be attended for $44. e) State the equation of the relation. NOTE: Use C = f) Use the equation to determine the following: i) cost for 4 classes. g) ii) number of classes that can be attended for $44. i) Calculate the rate of change or slope or constant of variation of the relation using a ruler and the graph. ii) Where have you seen the slope number before? iii) What does the slope number mean? h) How does this relation show partial variation between cost and number of classes? HINT: Look at the graph.