NutritionalFactorsinPerformanceandHealthpt1
advertisement

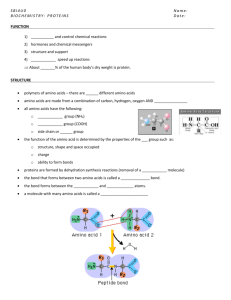
Nutritional Factors in Performance and Health What is eaten, how it is eaten and when it is eaten may have marked effects on health and performance. Poor nutrition contributes to a host of health concerns as well as limitations to athletic performance Sports nutrition is one of the most studied areas of nutrition, and many long-held concepts of good nutrition, particularly those relevant to athletes, are being challenged. FOOD is the carrier of nutrients To get the nutrients we need, we require the right food exposure Six Classes of Nutrients There are 6 classes of nutrients, which include: 1. Water 2. Vitamins 3. Minerals 4. Proteins 5. Fats 6. Carbohydrates Energy(fuel) is derived from foods that contain three different compounds in combination or as separate: Proteins, Fats, and Carbohydrates Vitamins and Minerals do NOT provide energy although they have many very important functions Water is a nutrient that literally ties everything together It helps circulate nutrients to tissues, allows for metabolism to take place, regulates body functions etc. Each nutrient is equally essential, no class of nutrient can be eliminated in order to maintain a general level of health Protein Proteins are relatively complex molecules that have enzymatic and structural functions and are important in a variety of biosynthetic and bioenergetic reactions related to body growth, maintenance and repair, and energy production Proteins may also be used as an energy source because energy requirements take priority over anabolic functions If carbohydrate and fat are inadequate protein will be converted to usable energy source The amount of protein in muscle is determined by the balance between protein anabolism and catabolism If dietary protein is above requirement it can be oxidized for energy or converted to fat Thus eating an excessive amount of protein can increase body fat deposition. Composition of Proteins The basic units of protein structure are AMINO ACIDS All amino acids contain nitrogen Nitrogen is necessary for the formation of peptide bonds Proteins are essentially long chains of amino acids linked together by peptide bonds Protein requirements are related to the requirement for amino acids Synthesis of proteins in humans requires approximately 22 distinct amino acids 9 of these amino acids are ESSENTIAL AMINO ACIDS Essential Amino Acids: amino acids that CANNOT be synthesized by the body and must be obtained from plant or animal proteins ingested in the diet The remaining 13 amino acids are termed NONESSENTIAL AMINO ACIDS Nonessential Amino Acids can be obtained from diet but can also be synthesized from other substances present in the body as long as there is an adequate source of Nitrogen Dietary proteins that contain low amounts of one or more of the essential amino acids are known as INCOMPLETE PROTEINS Incomplete proteins are generally of plant origin- nuts, grains, legumes and seeds Dietary proteins that contain all the amino acids essential and nonessential are known as COMPLETE PROTEINS Complete proteins are generally found in animal sources and products: meat, dairy products, eggs and fish