notes chapter5practical phase modulator
advertisement

Practical Phase Modulator
VDD
RFC2
Carrier signal
from oscillator
C1
C2
Output
RFC1
Q1
Modulating
signal input
R1
R2
C3
Explaination:
Carrier signal applied directly to output through C1 and C2.
Also to the gate of FET through C1.
Series of capacitance C1 and C2 and resistance of FET source to drain produce a
leading phase shift of current in FET; leading voltage at output.
Carrier signal that is applied to gate FET varies the FET current. The leading
voltage across R1 also controls the FET current. These two signals that controls,
result in a phasor sum of current.
Modulating signal is applied to the gate of FET-it also controls the current in
FET. Changes the amplitude relationship of the two controlling inputs before,
thus producing a phase shit that is directly proportional to the amplitude of
modulating signal.
Thus, the carrier output varies in phase and amplitude.
From output, passed through a class C amplifier or frequency multiplier to
remove the amplitude variations but preserves the phase and frequency variations.
Problems:
Only capable of producing small amont of phase shift(20%). Thus limited
frequency shift.
Using a Tuned Circuit for PM
RF Amplifier
C1
Carrier input
PM Output
L
C2
+V
R1
C4
R3
Modulating
signal
C5
C3
RFC
R4
D1
R2
Operation:
Modulating signal is passed through low pass network (R3 – C5){provide
amplitude compensation necessary to produce FM}
Modulating signal appears across R4 (potentiometer).Potentiometer acts as
deviation control
higher modulating voltage, higher the frequency deviation.
Modulating signal applied to D1 through C4.
RFC has high impedance at carrier frequency to minimize the loading of tuned
circuit, which will reduce the Q.
When modulating signal=0, capacitance of D1 and C2, and L1 will set the
resonant frequency of tuned circuit.
When modulating signal goes negative, capacitance increases, reactance
decreases, thus circuit become capacitive, it produce a leading phase shift. The
tuned circuit looks like a capacitor to the RF amplifier’s output; output lags input.
When modulating signal goes positive, capacitance decreases, reactance
increases, circuit becomes inductive, the tuned circuit looks like inductor to RF
amplifier’s output, and so, output leads input.
This result in a wide phase shift, thus linear frequency deviation.
Advantage:easy implementation
Disadvantages: 1) amount of phase shift, thus frequency deviation is relatively low
2) All the PM cct produced amplitude variations, thus need other means to remove them.
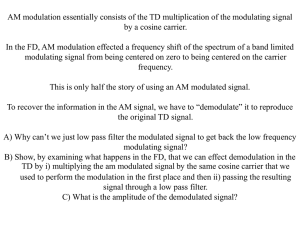
Frequency Demodulator
Foster Seeley Discriminator(the oldest and the best)
Ratio Detector(a variation of Foster Seeley)
Pulse Averaging Discriminator
Quadrature Detector
Differential Peak Detector(in IC form that uses differential amplifiers)
Phase Lock Loop Demodulator
Foster Seeley Discriminator




![( ) ( ) ] ( )t - Electrical and Computer Engineering at UNC Charlotte!](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/008111395_1-93714dad75fd37a24d3ca03a1e986ddf-300x300.png)

![Sample_hold[1]](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/005360237_1-66a09447be9ffd6ace4f3f67c2fef5c7-300x300.png)


