3 Sociological Perspectives
advertisement
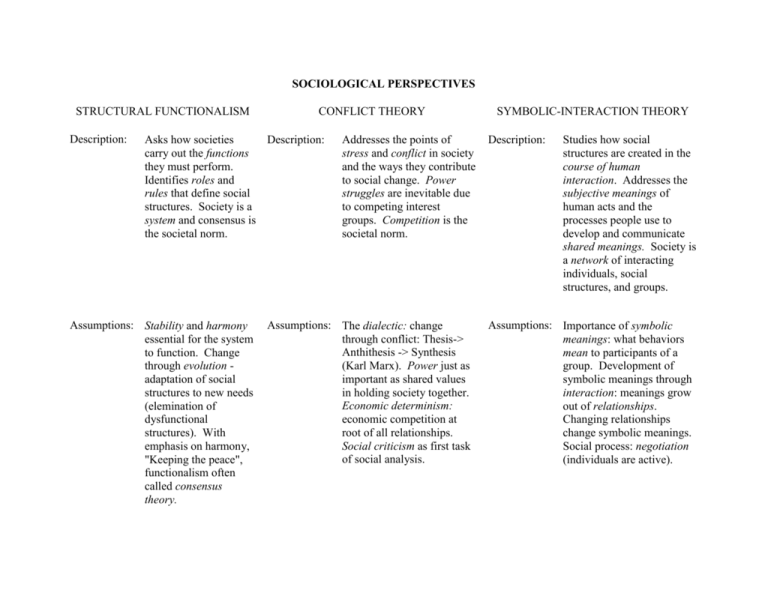
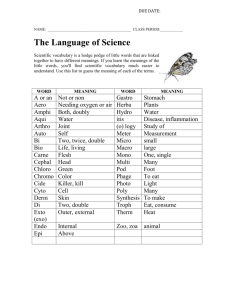
SOCIOLOGICAL PERSPECTIVES STRUCTURAL FUNCTIONALISM Description: CONFLICT THEORY Asks how societies Description: carry out the functions they must perform. Identifies roles and rules that define social structures. Society is a system and consensus is the societal norm. Assumptions: Stability and harmony essential for the system to function. Change through evolution adaptation of social structures to new needs (elemination of dysfunctional structures). With emphasis on harmony, "Keeping the peace", functionalism often called consensus theory. Addresses the points of stress and conflict in society and the ways they contribute to social change. Power struggles are inevitable due to competing interest groups. Competition is the societal norm. Assumptions: The dialectic: change through conflict: Thesis-> Anthithesis -> Synthesis (Karl Marx). Power just as important as shared values in holding society together. Economic determinism: economic competition at root of all relationships. Social criticism as first task of social analysis. SYMBOLIC-INTERACTION THEORY Description: Studies how social structures are created in the course of human interaction. Addresses the subjective meanings of human acts and the processes people use to develop and communicate shared meanings. Society is a network of interacting individuals, social structures, and groups. Assumptions: Importance of symbolic meanings: what behaviors mean to participants of a group. Development of symbolic meanings through interaction: meanings grow out of relationships. Changing relationships change symbolic meanings. Social process: negotiation (individuals are active). Who benefits from the exercise of power and who loses? Is inequality built into the social structures of society? What tensions are inevitable? How does power affect the distribution of scarce resources? Who are the "haves" and the "have-nots"? Questions Raised: How do people behave in intimate groups? What are the symbols that give value to the social order? How are social roles "constructed" and changed through interaction? How does individual behavior affect social situations? Questions Raised: Do parts of the system work in harmony? How do social structures contribute to the maintence of society? (What is their function in society?) What are the shared values of a society? Questions Raised: Application: Study of formal organizations. Development of social policies. Application: Study of policies, social movements, corporate power structures, and hierarchies of power. Application: Educational practice, courtroom procedure, therapy. Evaluation: Focus on conflict alone ignores issues related to societal stability, a critical view of society can overlook positive consequences of order. Evaluation: Has limitations for study of large social organizations.