Actual midterm []
advertisement
![Actual midterm []](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/007320928_1-19ffd5f4751f34bab503d71d40ff27c2-768x994.png)
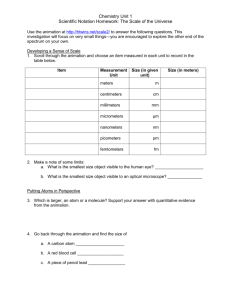
Name: ________________________________ Student ID: ______________________ 1) List compounds that (0.5 pts each, max 3 pts) a) are able to cross biological membranes on their own: b) are NOT able to cross biological membranes on their own: 2) Draw a schematic of a small unilamellar vesicle (SUV) with an integral membrane protein (label the various entities). (2 pt) 1 Name: ________________________________ Student ID: ______________________ 3) Draw the chemical structure of a phosphatidyl ethanolamine diacyl lipid (including formal charges) and label the various moieties. (0.5 pts each, 3 pts max). What is the net charge of this molecule at pH 7 (1 pt)? 4) Draw a diagram of the major components of a typical plasma membrane (“fluid mosaic” model) and label them. (0.5 pts each, max 4 pts) 2 Name: ________________________________ Student ID: ______________________ 5) Briefly, describe the role of detergents in membrane protein structural & functional studies. Why do different membrane proteins require different detergents? (2 pts) 6) Where in the cell and under what circumstances does a eukaryotic membrane protein first come into contact with a lipid bilayer? Be specific, you can use a diagram with labels. (3 pts max) 3 Name: ________________________________ Student ID: ______________________ 7) Name the general classes integral membrane proteins along with their respective functions. (0.5 pts, 4 pts max) 8) Why are high-resolution three-dimensional structures of integral membrane proteins generally more difficult to obtain than those of soluble proteins? Give at least three reasons. (3 pts) 4 Name: ________________________________ Student ID: ______________________ 9) Approximately, what is the percentage of membrane proteins (relative to the total number of proteins) in the human genome? What is the approximate total number of membrane proteins in the human genome? (2 pts) 10) Draw a schematic with labels showing how the short 15-mer gramicidin, composed of a mixture of D- and L-amino acids, can form selective channels across a bilayer. (3 pts) 5 Name: ________________________________ Student ID: ______________________ 11) Draw a simple membrane topology plot for a membrane protein with five transmembrane helices and place labels. Will the N- and C-termini be on the same or on opposite sides of the membrane? (3 pts) What is the approximate thickness of the bilayer? (1 pt) 12) Please answer the following questions based on the excerpt of a PDB file below (see also next page): a) What is the primary sequence of the section for which 3-dimensional coordinates are shown (you can use one- or three-letter code)? (1 pt) b) Find and list the Z coordinate [Å] and the B factor [Å2] of the main chain alpha carbon of residue valine 31 (Val31). (2 pts) z = ______________ Å, HEADER TITLE TITLE COMPND COMPND COMPND COMPND SOURCE SOURCE SOURCE SOURCE SOURCE KEYWDS KEYWDS B = ____________ Å2 MEMBRANE PROTEIN / HYDROLASE 05-OCT-07 2RH1 HIGH RESOLUTION CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF HUMAN B2-ADRENERGIC G 2 PROTEIN-COUPLED RECEPTOR 2 MOLECULE: BETA-2-ADRENERGIC RECEPTOR/T4-LYSOZYME CHIMERA; 3 CHAIN: A; 4 SYNONYM: BETA-2 ADRENERGIC RECEPTOR, BETA-2 ADRENOCEPTOR, 5 BETA-2 ADRENORECEPTOR / LYSIS PROTEIN, MURAMIDASE, MOL_ID: 1; 2 ORGANISM_SCIENTIFIC: HOMO SAPIENS, BACTERIOPHAGE T4; 5 EXPRESSION_SYSTEM: SPODOPTERA FRUGIPERDA; 9 OTHER_DETAILS: THE CONSTRUCT HAS BEEN OBTAINED BY 10 OVERLAPPING EXTENSION PCR GPCR, 7TM, ADRENERGIC, FUSION, LIPIDIC CUBIC PHASE, LIPIDIC, 2 MESOPHASE, CHOLESTEROL, MEMBRANE PROTEIN, MEMBRANE PROTEIN 6 Name: ________________________________ Student ID: ______________________ KEYWDS EXPDTA AUTHOR AUTHOR AUTHOR HELIX HELIX ATOM ATOM ATOM ATOM ATOM ATOM ATOM ATOM ATOM ATOM ATOM ATOM ATOM ATOM ATOM ATOM ATOM ATOM ATOM ATOM ATOM ATOM ATOM ATOM ATOM ATOM ATOM ATOM ATOM ATOM ATOM ATOM ATOM ATOM ATOM ATOM ATOM ATOM ATOM 3 / HYDROLASE COMPLEX X-RAY DIFFRACTION V.CHEREZOV,D.M.ROSENBAUM,M.A.HANSON,S.G.F.RASMUSSEN, 2 F.S.THIAN,T.S.KOBILKA,H.J.CHOI,P.KUHN,W.I.WEIS,B.K.KOBILKA, 3 R.C.STEVENS 1 1 ASP A 29 LYS A 60 1 2 2 VAL A 67 MET A 96 1 1 N ASP A 29 -52.822 -1.611 23.137 1.00 98.48 2 CA ASP A 29 -51.922 -2.262 22.148 1.00 98.06 3 C ASP A 29 -52.178 -1.713 20.742 1.00 97.74 4 O ASP A 29 -51.291 -1.100 20.143 1.00 96.54 5 CB ASP A 29 -52.106 -3.786 22.184 1.00 97.64 6 N GLU A 30 -53.394 -1.944 20.236 1.00 98.37 7 CA GLU A 30 -53.821 -1.515 18.887 1.00 98.17 8 C GLU A 30 -54.424 -0.104 18.879 1.00 98.57 9 O GLU A 30 -54.197 0.649 17.943 1.00 99.79 10 CB GLU A 30 -54.840 -2.498 18.305 1.00 99.00 11 CG GLU A 30 -54.377 -3.969 18.286 1.00 99.46 12 CD GLU A 30 -55.432 -4.928 17.733 1.00 98.77 13 OE1 GLU A 30 -56.228 -4.527 16.853 1.00 97.60 14 OE2 GLU A 30 -55.463 -6.092 18.185 1.00 99.75 15 N VAL A 31 -55.190 0.248 19.918 1.00 97.89 16 CA VAL A 31 -55.757 1.618 20.079 1.00 96.48 17 C VAL A 31 -54.643 2.678 20.185 1.00 95.12 18 O VAL A 31 -54.838 3.837 19.803 1.00 93.37 19 CB VAL A 31 -56.729 1.697 21.306 1.00 96.71 20 CG1 VAL A 31 -57.185 3.135 21.580 1.00 96.80 21 CG2 VAL A 31 -57.948 0.806 21.077 1.00 96.80 22 N TRP A 32 -53.486 2.259 20.709 1.00 95.21 23 CA TRP A 32 -52.267 3.063 20.735 1.00 94.60 24 C TRP A 32 -51.837 3.491 19.319 1.00 93.60 25 O TRP A 32 -51.335 4.603 19.140 1.00 91.48 26 CB TRP A 32 -51.129 2.273 21.427 1.00 96.93 27 CG TRP A 32 -49.770 2.899 21.304 1.00 98.27 28 CD1 TRP A 32 -49.169 3.734 22.197 1.00100.48 29 CD2 TRP A 32 -48.844 2.737 20.216 1.00100.89 30 NE1 TRP A 32 -47.924 4.105 21.737 1.00101.70 31 CE2 TRP A 32 -47.700 3.507 20.523 1.00102.25 32 CE3 TRP A 32 -48.874 2.013 19.010 1.00100.84 33 CZ2 TRP A 32 -46.587 3.578 19.667 1.00101.34 34 CZ3 TRP A 32 -47.771 2.082 18.158 1.00100.68 35 CH2 TRP A 32 -46.640 2.860 18.493 1.00101.20 36 N VAL A 33 -52.036 2.600 18.332 1.00 92.39 37 CA VAL A 33 -51.667 2.852 16.922 1.00 91.10 38 C VAL A 33 -52.435 4.017 16.332 1.00 89.89 39 O VAL A 33 -51.827 4.918 15.748 1.00 88.01 7 32 30 N C C O C N C C O C C C O O N C C O C C C N C C O C C C C N C C C C C N C C O