Notes: Topography and Bathymetry
advertisement

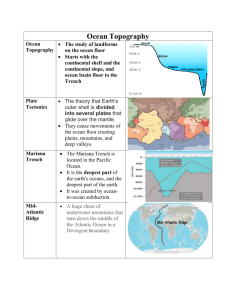
Notes: Topography and Bathymetry Topography The three dimensional shape of the_______________, including mountains and valleys Topography on Land Used to measure mountains, valleys, plains, changes in _________________ and building sites Measured using _____________________ techniques Topography at Sea Used to measure mountains, valleys, plains and changes in _______________ below sea level Also known as __________________________ bathy- depth meter- to measure Why map the seafloor? To learn more about the ____________________ of the ocean floor To identify areas of __________________ and deposition offshore (on the continental shelf) To locate geohazards (such as ______________________________) To locate pathways for movement of sediment and _______________________ Bathymetry First measured by sailors using long_______________ and _____________ Measuring Bathymetry Today SONAR- sends _________________ toward the sea floor and detects the _______________________of that sound back A sonar image- the ___________________ help identify features on the ocean floor Map based on a _______________________ Some Common Seafloor features Continental Shelf: An extension of the ___________________ that is covered by water Varies in ___________________ Very small in _________________ Continental slope: the ________________ of the ocean basin Connects the continental _______________ to the ocean floor Continental rise: A collection of __________________ (sand & mud) found near the edge of the basin Abyssal plain: The ______________________ of the ocean Can be up to _____________________ ft deep (6,000m) Diverse life forms, like this guy Mid ocean ridge: a chain of underwater _____________________ The ____________________ feature on Earth Seamount: an underwater __________________ mountain that has never reached the _____________________ Guyot: an underwater volcanic mountain that has a ___________ top. was once a ____________________ that was above water and had its top _____________________ away