Vocabulary Teaching Techniques
advertisement

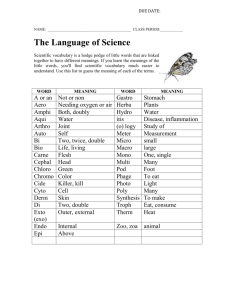
Vocabulary Teaching Techniques Paul Nation LALS, Victoria University of Wellington, New Zealand Where does vocabulary teaching fit in a course? The four strands Activities and techniques Meaning focused input Reading graded readers, Listening to stories, Communication activities Language focused learning Direct teaching of vocabulary, Direct learning, Intensive reading, Training in vocabulary strategies Meaning focused output Communication activities with written input, Prepared writing, Linked skills Fluency development Reading easy graded readers, Repeated reading, Speed reading, Listening to easy input, 4/3/2, Rehearsed tasks, 10 minute writing, Linked skills What are the features of a good vocabulary teaching technique? Psychological processes Does it involve normal language use? Does each activity set up useful conditions for vocabulary learning? Does the activity motivate the learners to pay attention? Does the activity involve retrieval? Receptive or productive? Recognition or recall? Does the activity involve generative use? Receptive or productive? What degree of generation? Does the activity involve imaging or instantiation? Does the activity involve a useful focus of effort? Does the activity result in new learning? Does the activity avoid interference? Involvement load Involvement load involves three factors, each of which may be absent (-), present with moderate strength (+), or with full-strength (+ +). Need is a motivational factor. Is the unknown word needed to complete the task? Search -- does the learner need to search for or retrieve the meaning or form of a particular word? Evaluation -- does the task involve having to compare the form or meaning with other possible words or meanings to choose the most suitable one for the context? The sum of the strengths of these three factors represents the involvement load of the task. The greater the involvement load, the better the learning. Researching teaching techniques There are three major ways of researching vocabulary teaching techniques - (1) by doing technique analysis such as looking at involvement load (need, search, evaluation) (Laufer and Hulstijn, 2001), or by analysing the goals, learning conditions, signs, and design features of techniques (Nation, 2001), (2) by getting the learners to think aloud during or after they have done a vocabulary learning activity (Hosenfeld, 1976), or (3) by doing experimental comparisons of vocabulary learning activities (Hulstijn and Laufer, 2001). spoken form written form form word parts form-meaning connection concept and reference meaning associations grammar use collocates constraints on use Pronounce the words Read aloud Word and sentence dictation Finding spelling rules Filling word part tables Cutting up complex words Building complex words (Word-making & word-taking) Choosing a correct form Matching words and definitions Find the words in the text Discussing the meanings of phrases Drawing and labelling pictures Peer teaching Comprehension questions, True/False Discussion Dictionary use* Guessing from context Using word cards* Riddles Finding common core meanings Choosing the right meaning Semantic feature analysis Answering questions Word detectives* Finding examples Finding substitutes Explaining connections Making word maps Classifying words Finding opposites Suggesting causes or effects Suggesting associations Odd-one-out Matching sentence halves Reword the sentences Fill the blanks Analysing concordances* Putting words in order to make sentences Write a sentence Matching collocates Finding collocates Identifying constraints Classifying constraints * involves several aspects Hosenfeld, C. (1976) Learning about learning: Discovering our students= strategies. Foreign Language Annals, 9(2), 117-129. Hulstijn, J., & Laufer, B., (2001). Some empirical evidence for the involvement load hypothesis in vocabulary acquisition. Language Learning, 51(3), 539-558. Laufer, B., & Hulstijn, J., (2001) Incidental vocabulary acquisition in a second language: the construct of task-induced involvement. Applied Linguistics, 22(1), 1-26. Nation, I.S.P. (2001) Learning Vocabulary in Another Language. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.