Topic – Event - Concept - Lancaster Central School District
advertisement
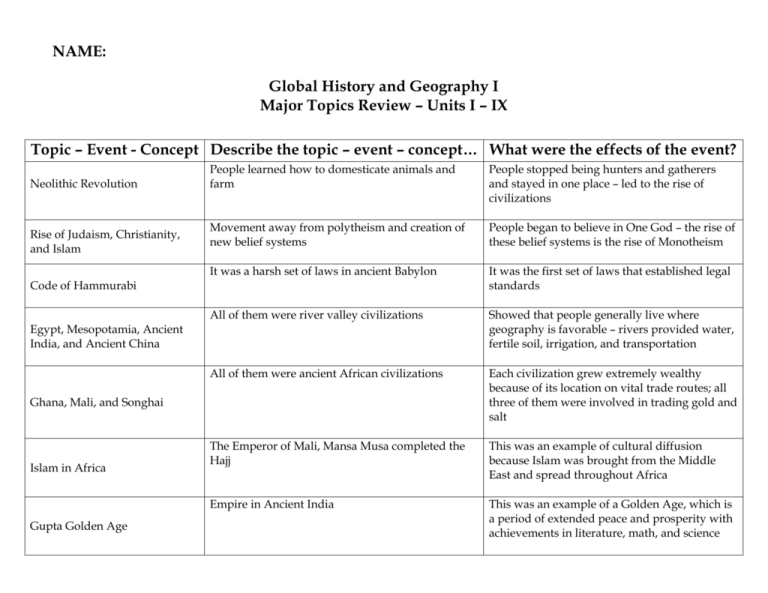
NAME: Global History and Geography I Major Topics Review – Units I – IX Topic – Event - Concept Describe the topic – event – concept… What were the effects of the event? Neolithic Revolution Rise of Judaism, Christianity, and Islam People learned how to domesticate animals and farm People stopped being hunters and gatherers and stayed in one place – led to the rise of civilizations Movement away from polytheism and creation of new belief systems People began to believe in One God – the rise of these belief systems is the rise of Monotheism It was a harsh set of laws in ancient Babylon It was the first set of laws that established legal standards All of them were river valley civilizations Showed that people generally live where geography is favorable – rivers provided water, fertile soil, irrigation, and transportation All of them were ancient African civilizations Each civilization grew extremely wealthy because of its location on vital trade routes; all three of them were involved in trading gold and salt The Emperor of Mali, Mansa Musa completed the Hajj This was an example of cultural diffusion because Islam was brought from the Middle East and spread throughout Africa Empire in Ancient India This was an example of a Golden Age, which is a period of extended peace and prosperity with achievements in literature, math, and science Code of Hammurabi Egypt, Mesopotamia, Ancient India, and Ancient China Ghana, Mali, and Songhai Islam in Africa Gupta Golden Age Topic – Event - Concept Describe the topic – event – concept… What were the effects of the event? A belief system that grew in Ancient India Followers of this belief system believed that Dharma and Karma would guide their cycle of reincarnation and their future location in the Caste System Peninsula located between China and Japan Served as a cultural bridge between China and Japan, which promoted cultural diffusion Civilization grows along the Yellow River in the Southeastern part of the country; isolated by mountains and deserts Civilization was isolated and the people developed a belief in ethnocentrism which was the belief that their civilization was the best Confucianism Most important belief system in Ancient China and used the Five Relationships and Filial Piety Provided a set of rules that when followed provided the Chinese with order and stability Growth of civilization in Ancient Japan Civilization develops despite geographic limitations, like mountains and a lack of natural resources Had to adapt to geographic features by developing terrace farming and taking or trading natural resources Feudalism in Europe and Japan during the Middle Ages Land was exchanged for loyalty and military service, and all people knew their role in a rigid social structure This system of government provided order and stability and was dominated by a military class that had its own code of conduct Belief System that developed in Ancient India and shared some beliefs with Hinduism Was brought to China through cultural diffusion; believed in Dharma, Karma, and reincarnation, but did not believe in the Caste System Shared a belief that all things in nature possessed a spirit Since these Belief Systems existed in traditional early civilizations, they reinforced polytheistic beliefs Rise of Hinduism Ancient Korea Growth of civilization in Ancient China Buddhism Animism and Shinto Topic – Event - Concept Describe the topic – event – concept… What were the effects of the event? Growth of civilization in Ancient Greece Alexander the Great and Hellenistic Culture The Roman Empire The Byzantine Empire The Manor System The Crusades The Black Plague English Monarchy Civilization grows in city-states that were separated by Greece’s geography He conquered most of what was known of the world at the time and spread Greek culture throughout his Empire Each city-state developed a unique culture because of being separated by geographic characteristics (Athens and Sparta) Promoted cultural diffusion because the ideas of Hellenistic Civilization were spread around the world Empire grows over time and develops long-lasting contributions in the area of law and government; experiences a Golden Age; and, its fall was a gradual process caused by many factors Formed the basis of the legal systems of many future civilizations and spreads its influence throughout Europe Eastern-Half of the Roman Empire that adopted many Roman customs; preserved Greek and Roman learning; its capital Constantinople was the center of Eastern Orthodox Church and an important trading center Saved Christianity and Greek and Roman learning while Europe was in the Dark Ages; long-lasting contributions in the area of law (Justinian’s Code); influenced early Russia through cultural diffusion Most serfs worked in the fields on a medieval manor growing crops for their feudal lord; went along with the Feudal System of government The manor was self-sufficient and most serfs never left throughout the entirety of their lives Christians wanted to regain control of the Holy Land from the Muslims Were a successful failure; trade between Europe and the Middle East increased; and, feudalism was weakened in Europe Epidemic that began in Asia and was spread around Europe through trade The European economy was devastated because of the massive depopulation of the continent The Magna Carta, Parliament, and Common Law all limited the power of the Monarchy This was the first time that the power of a Monarch was limited, and more power was put in the hands of the people Topic – Event - Concept Describe the topic – event – concept… What were the effects of the event? Renaissance Protestant Reformation Scientific Revolution European Exploration It was the rebirth and Golden Age of arts, literature, and education in Europe where Humanism developed and people questioned traditional teachings; it began in Italy due to its geographic location A tremendous amount of new art, literature, and music were created; and, traditional institutions like the RCC began to lose a great deal of power Martin Luther sets out to reform the RCC with his 95 Theses that exposed the RCC’s corrupt practices, especially the sale of indulgences; Luther is excommunicated for questioning the RCC Religious Unity shattered in Europe as new Christian denominations emerged; many Kings and Queens gained power as the RCC lost it; forces the RCC to look at its practices during the Counter-Reformation Thinkers began to ask questions and examine the natural laws governing the universe; new theories were developed using the Scientific Method People began to rely on human reason instead of traditional teachings; the Scientific Method used experimentation and observation to prove/disprove hypotheses; the RCC lost power Europeans are motivated by “Gold, God, and Glory;” they wanted to make money and spread Christianity throughout the world Signals the beginning of European Imperialism and the domination of native peoples by superior European technology The exchange of goods between the Americas and Europe, Africa, and Asia Introduction of European diseases depopulated many Native American cultures and Europeans were introduced to new foods from the Americas Europeans began to bring Native Africans to their colonies in the Americas to work on their plantations because European diseases had devastated the Native American Population Large-scale destruction of African cultures and the creation of a system of forced labor that was inhumane and was based on African heritage Columbian Exchange Trans-Atlantic Slave Trade Topic – Event - Concept Describe the topic – event – concept… What were the effects of the event? The Mesoamerican Civilizations Spanish Colonial System Mercantilism European Imperialism Peter the Great and Catherine the Great Absolute Monarchy Mayas, Incas, and Aztecs were located in Central and South America; all three civilizations were advanced long before European Colonization. The Aztecs developed an advanced city at Tenochtitlan and the Incas used terrace farming in the Andes Mountains All were examples of advanced civilizations; and, all of them were destroyed because the Europeans had better weapons and technology and transferred diseases to the natives for which they had no immunity The colonists set up plantations in the New World to make money. They used native and slave labor to work the plantations, and set up a rigid social structure to maintain control over their colonies The cultures of the Native Americans and the imported African slaves were destroyed and the colonists made their colonies ship natural resources to Europe and made them entirely dependent on Europe for everything Raw materials are shipped from a colony to a mother country where they are turned into a finished good and sold back to the colony at a higher price; colonies were not allowed to trade with anyone except for the mother country Colonies became economically dependent on the European mother countries because they only shipped cash crops and were not allowed to produce their own goods Europeans began taking on colonies to make money, spread Christianity, gain land and increase their feelings of Nationalism Native cultures were destroyed by Europeans and colonies become dependent on Europe, while European countries gained power Both were Absolute leaders of Russia that westernized and modernized Russia – she also gained warm-water ports Increased power of Czar/Czarina and brought in Western European ideas while increasing the amount of territory held by Russia King or Queen claims the Divine Right to Rule and holds complete power in governing his/country; similar to Mandate of Heaven in China Monarchs like Peter the Great of Russia and Louis XIV of France centralize power and rule their nations with unlimited power Topic – Event - Concept Describe the topic – event – concept… What were the effects of the event? Limited Monarchy Enlightenment Thinkers French Revolution Napoleon Bonaparte England is the best example because The Magna Carta, Parliament, and Common Law all limited the power of the Monarchy John Locke, Montesquieu, and Rousseau all questioned the source of power for Kings and Queens, and they wanted to apply human reasoning to matters of government The power of a Monarch was limited, and more power was put in the hands of the people The people were dissatisfied with the Absolute Monarch not meeting their needs, being taxed too much, and were inspired by the thinkers of the Enlightenment and the success of the American Revolution to overthrow the King – the Third Estate leads it The Monarch is overthrown and it goes through many different stages – it was the first time that this happened to an Absolute Monarch – while democracy is established, it does not last. At the end Napoleon gains power because he provided stability for the people Provides order and stability in France after the Revolution by establishing schools, setting up the Napoleonic Code of Law, fixing the economy, and creating a strong military; then, he began his conquests of Europe He took over much of Europe during his conquests; many places adopted the Napoleonic Code; also, his conquests fostered nationalism in many European countries because they wanted to be independent; finally, he fell from power when his invasion of Russia failed due to Russia’s cold climate Kings and Queens began to lose power because of the questioning spirit of the thinkers; also, they inspired the American and French Revolutions and provided the basis for modern democratic government







