Lec: 1-2 Virology Definition Viruses are particles consisting of an
advertisement

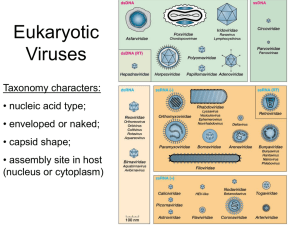
Lec: 1-2 Virology Definition Viruses are particles consisting of an RNA or DNA genome ,covered by protein coat called capsid . some viruses have outer lipoprotein membrane ,called envelope external to coat .They lack cellular structure(nucleus ,cytoplasm, mitochondria or ribosome) and independent metabolic processes. They replicate within living cells because they cannot generate energy or synthesis proteins ,so viruses are obligate intracellular parasites. Essential Characteristics of Viruses Size : Viral size very small ranges from 20 to 300 nm. 20nm (polio virus) to 300 nm ( small pox virus) Genome : DNA or RNA. Double-stranded or single-stranded nucleic acid, depending on the species. Structure : protein and nucleic acid; some viral species have envelope Reproduction: Only in living cells. Morphology and Structure A mature virus particle is also known as a virion. It consists of either two or three basic components: — A genome of virus is located internally and can be either DNA or RNA, double-stranded or single-stranded, linear or circular, and in some cases segmented. —Virus-coded proteins ONE protein ,The capsid ---enclosing the nucleic acid of the virus and determining its antigenicity; the capsid can have a cubic, helical or complex symmetry and is made up of subunits called capsomers . Each capsomer ,consisting of one or several proteins .Arrangement of capsomers gives virus structure of symmetry .there are three forms of symmetry in virus capsides 1- Icosahedral symmetry,in which capsomers are arranged in 20 triangles that forma symmetric (Icosahedron) with outline sphere. ex : polio virus. 2- Helical symmetry, in which capsomers are arranged in a hollow coil that appears rod. e x: influenza virus 1 Lec: 1-2 3- Complex symmetry, in which capsomers are arranged in more complicated structure . e x : small pox # SECOND protein are enzymes — In some cases an envelope that surrounds the capsid and is always derived from cellular membranes. Some viruses may have spikes to help attach to the host cell and depend on spikes ,Most viruses infect only SPECIFIC host cells. 2 Lec: 1-2 The capsid or envelope of viruses functions (1) to protect the nucleic acid genome from damage during the extracellular passage of the virus from one cell to another. (2) attach & entry into the cell. (3) in some cases to package enzymes essential for the early steps of the infection process. Types of Viruses Animal viruses: Rabies, Polio, Mumps, Small pox, and Influenza. Plant Viruses: Tobacco mosaic virus (TMV), Banana virus, Carrot virus. Bacterial Virus: Bacteriophages ( T1, T2, T3, and T4.) Atypical Virus like agent Two classes of infectious agents exist that are structurally simpler than viruses. Viroids are infectious circular RNA molecules that lack protein shells; they are responsible for a variety of plant diseases. Prions, are infectious agents composed only of protein, that appear to be responsible for some transmissible and inherited spongiform encephalopathies . 3 Lec: 1-2 comparison of viruses and cells Classification The taxonomic system used for viruses is based on the following morphological properties: — Genome: DNA or RNA genome as well as configuration of nucleic acid structure: single-stranded (ss) or double-stranded(ds). — Capsid symmetry: cubic, helical, or complex symmetry. — Presence or absence of an envelope. — Diameter of the virion. Viral Taxonomy Family names end in -viridae Genus names end in -virus Viral species: A group of viruses sharing the same genetic information and host. Common names are used for species Ex:---Herpesviridae -------Herpesvirus -------Human herpes virus 1, 2,3 4 Lec: 1-2 DNA VIRUSES NON ENVELOPE DOUBLE STRAND GENOME ENVELOPE SINGLE STRAND GENOME Adeno virus DOUBLE STRAND GENOME Parvo virus 5 Pox, Herpes viruses Lec: 1-2 6 Lec: 1-2 RNA VIRUSES ENVELOPE NON ENVELOPE DOUBLE STRAND GENOME SINGLE STRAND GENOME Reo viruses SINGLE STRAND GENOME Picorna, calici viruses 7 Orthomyxo , paramyxo ,corona, ,rhabdo viruses HIV Lec: 1-2 8