Lab Takehome Test 2013 b
advertisement

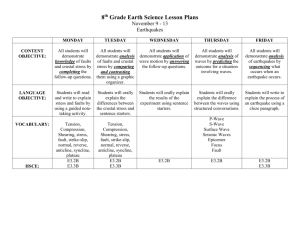
Lab Final Part 2 Take-home portion, Open Notes, Open Book Print out, fill out, turn in. Due Thursday, December 12th, 2013 Name: ___________________ I pledge my honor that I have neither given nor received assistance during the course of this examination. Signature: ______________________ Answer All Questions 1) This rock is granite. The pink mineral in this rock has a pearly luster, and is a 3-D Framework silicate. It has two planes of cleavage at about 90o. It is a type of: (a) (b) (c) (d) Quartz Feldspar Biotite mica Hornblende (an amphibole) 2) The clear gray mineral has a hardness of 7 and no cleavage. The gray mineral is (a) Quartz (b) Feldspar (c) Biotite mica (d) Hornblende (an amphibole) 3) Granite has course, visible crystals. It forms: (a) at the earth's surface (b) deep in the earth's interior (c) neither of the above 4) Limestone is mostly made of the mineral _____________. Hint: When weak acid is dropped on limestone, it fizzes. 5) If a rock has fossils, it is almost certainly (choose one: igneous/metamorphic/sedimentary). 6) The circled fossil is a (choose: Trilobite / Coral / Brachiopod) 7) Write down the smallest and largest particle diameters for sand: smallest ________ mm largest ___________ mm 8) Sedimentary rocks made of sand-sized particles are called: (choose one: sandstone/conglomerate/breccia) 9) This photograph, taken by Kean University student Andrew Stockum, shows Mt. Vesuvius, near Pompeii and Herculaneum, and east of Naples, Italy. It sits above a subduction zone. Its lavas and tephra are most likely: a. Basaltic b. Andesitic c. Rhyolitic 10) Suppose you are in a mine, and a fault passes through the area where you are standing. The hanging wall is: a. above your head b. below your feet c. both of the above d. neither of the above 11) If A and B mark the same key bed, we know the fault is a: a. b. c. d. Reverse Fault, typical of divergent margins Normal Fault, typical of convergent margins Normal Fault, typical of divergent margins Reverse Fault, typical of transform margins 12) This is a type of (choose one: dip-slip/strike-slip/rotational) fault 13) Lines of equal longitude measure angular position East or West of Greenwich, England. True or False? 14) The picture below shows a Precambrian Limestone over Cretaceous Shale. Both are right-side-up. This reverse fault has a very shallow dip, less than 10 degrees. Such a reverse fault is: a. called a thrust fault, typical of collisions b. called a normal fault, typical of collisions c. called a transform fault, typical of subduction 15) Shales are typical of (choose: fast moving water / still water) 16) On a topographic map, contours mark lines of equal elevation. True or False? 17) Here is a geologic map from small region in western Nepal. There are both Precambrian (symbol pC_ ) and Tertiary (symbol T__) rocks. The Question is below, under the map. C' North C Now look at the Strike and Dip symbols on the map. North is up. Question: On this map, the Tertiary Rocks Tsm Tsu and Tsl, shown in yellow, are all dipping approximately (choose one: northeast / southwest). 18) Here are some elevations measured in your Wyoming field area. The topo map does not have enough resolution, so you will have to make your own. Draw the 280 meter contour in the white area provided. 19) These sedimentary structures are called ________________. Geologists use them, along with graded bedding, to tell if rocks are _____________________________________. 1 20) This fossil is a: (a) brachiopod (b) crinoid (c) rugose coral (d) trilobite 21) Fossil 2 is a: (a) brachiopod (b) crinoid (c) rugose coral (d) trilobite 2 22) Fossil 3 is a: (a) brachiopod (b) crinoid (c) rugose coral (d) trilobite 23) Fossil 4 is a: (a) brachiopod (b) crinoid (c) rugose coral (d) trilobite 3 4 24) If you found the above fossils in one layer of sediment, you would be certain the sediments were (a) Cenozoic (b) Mesozoic (c) Paleozoic (d) Precambrian 25) ___________ is an olive-colored mineral made of independent silicon tetrahedra, with Fe+2 and Mg+2 to balance the charge. It is the first mineral to crystallize out of a basaltic melt. 26) ___________ are silicate minerals where the silicon tetrahedra are bonded together in a sheet structure. 27) The mineral shown just above has (choose: one (1) / two (2) / three (3)) planes of cleavage 28) Quartz, with a hardness of 7, will scratch a knife blade, hardness 5.5. True or False? 29) A calcium-rich plagioclase feldspar forms at a higher temperature than a sodium-rich plagioclase feldspar. True or False? Hint: Check your Bowens Reaction Series 30) Given: This Cambrian transgression shows lines where Glossopleura and Olenellus have been found. Everything is right-side-up. Question: Glossopleura is younger than Olenellus. True or False? Southwest Northeast 31) In this diagram, the presence of three species of index fossils is shown for two measured sections. The sandstone marked A on the left is the same age as (a) chert 1 (b) mudstone 2 (c) sandstone 3 (d) sandstone 4 32) This picture shows the Glarus Thrust Fault in the Alps near Elm, Switzerland. Thrust Faults are typical of: (a) divergent margins (b) convergent margins (c) transform margins (d) plumes 33) The upthrown block is: (a) darker in color (b) lighter in color 34) The map view below shows bedrock boundaries between folded rock layers, and strike and dip symbols. Assume like-colored areas are the same layer. This is a a. non-plunging anticline b. plunging anticline c. non-plunging syncline d. plunging syncline 35) The youngest rocks are a. green (center) b. yellow c. red (outermost) d. all of the above 36) The map view below shows bedrock boundaries between folded rock layers, and strike and dip symbols. Assume like-colored areas are the same layer. This is a (a) (b) (c) (d) non-plunging anticline plunging anticline non-plunging syncline plunging syncline 37) The youngest rocks are (a) (b) (c) (d) green yellow red all of the above 38) The map view below shows bedrock boundaries between folded rock layers, and strike and dip symbols. Assume like-colored areas are the same layer. This is a a. non-plunging anticline b. plunging anticline c. non-plunging syncline d. plunging syncline 39) The youngest rocks are a. green (center) b. yellow c. red (outermost) d. all of the above. 40) These are ammonite shells, a type of Cephalopod Mollusk. These cannot be younger than (a) (b) (c) (d) the end of the Permian the Ordovician the end of the Cretaceous the Miocene 41) This is a partial lower jaw and teeth of a large mammal, Oreodon. This fossil is (a) (b) (c) (d) Cenozoic Mesozoic Paleozoic Precambrian 42) These folds visible in a hillside are (choose one: overturned/recumbent) 43) These folds viewed from space are (choose one: non plunging/plunging). 44) The aerial photo below shows bedrock boundaries between folded rock layers, and strike and dip symbols. These folds plunge (choose: towards the top / towards the bottom of the picture.