Molar Mass - Mounds Park Academy
advertisement

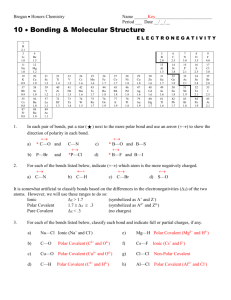
Bonding Types of Bonds Electron Dot Diagrams Shapes of Molecules (VSEPR) Intermolecular Forces James In Your Textbook Types of Bonds: pp. 419-424 and 437-446 and 462 Electron Dot Diagrams: pp. 441 Shapes of Molecules (VSEPR): pp. 455-456 Intermolecular Forces: pp. 463-466 Types of Bonds Covalent Definition Example Electronegativity Difference Conductivity Melting/Boiling Points Solubility in Water Assignment 1: Types of Bonds Ionic Determine the type of bonding between each pair of elements. If bonds formed are ionic, draw an electron dot diagram. If the bonds are covalent, determine if they are pure or polar. If polar, show the direction of the polarity. Cl and Br (3.16 – 2.96 = 0.20) Li and Cl (3.16 -0.98 = 2.18) Pure covalent Ionic +1 Li (Lithium chloride) . . -1 : Cl : .. H and Cl (3.16 – 2.2 = 0.96) Al and O (3.44 – 1.61 = 1.83) Polar covalent Ionic (Aluminum oxide) H – Cl +3 Al +3 Al +3 Al . . -2 : O: .. . . -2 : O: .. Ca and N (3.04 – 1.00 = 2.04) Li and O (3.44 – 0.98 = 1.83) Ionic (Calcium nitride) Ionic ( Lithium oxide) +2 Ca . . -3 :N: .. +2 . . -3 Ca :N: .. . . -3 :N: .. +1 Li Cl and Cl (3.16 – 3.16 = 0) Sr and Br (2.95 – 0.98 = 2.46) . . -2 : O: .. +1 Li Pure covalent Ionic (Strontium bromide) +2 Sr . . -1 : Br : .. . . -1 : Br : .. Ca and F (3.98 – 1.00 = 2.98) Si and O (3.44 – 1.90 = 1.54) Ionic (calcium fluoride) +2 . . -1 Sr : Br : .. . . -1 : Br : .. Polar covalent Si - O Name the ionic compounds above. Is potassium nitrate ionic or covalent? Try to draw a dot diagram. Ionic +1 K .. . . -1 :O:N::O: .. :O: .. Assignment 2: Electron Dot Diagrams Draw the electron dot diagram for the following covalent compounds. Determine if the bonds are polar and the direction of polarity: 1. hydrosulfuric acid wants 12 .. has 8 H:S:H share 4 ‘‘ 2. carbon tetrachloride wants 40 .. has 32 : Cl : share 8 .. .. .. : Cl : C : Cl : .. .. .. : Cl : .. polar covalent bonds toward Cl polar covalent bonds toward S 3. aluminum bromide (Al wants 6) wants 30 .. has 24 : Br : share 6 .. .. .. : Br : Al : Br : .. .. 4. dicarbon dihydride (ethyne) wants 20 has 10 H:C:::C:H share 10 polar covalent bonds toward C polar covalent bonds toward Br 5. oxygen gas wants 16 .. .. has 12 :O :: O: share 4 6. sulfur difluoride want 24 .. .. .. has 20 : F : S : F : share 4 .. .. .. pure covalent bonds polar covalent bonds toward F 7. sulfur trioxide want 32 .. .. 8. carbon monoxide wants 16 has 24 share 8 : O : S :: O : .. .. : O : . . polar covalent bonds toward O 9. hydrofluoric acid wants 10 .. has 8 H : F : share 2 .. highly polar (essentially ionic) toward F has 10 share 6 : C ::: O: polar covalent bonds toward O 10. nitrogen trihydride wants 14 .. has 8 H : N : H share 6 .. H polar covalent bonds toward N Assignment 3: Types of Bonds Determine whether each statement below is true or false? F 1. All bonds are the same. F 2. Chemical bonds form when nuclei of two atoms are attracted to each other. Nuclei are both positive and would not attract. T 3. In a covalent bond, orbitals overlap and a pair of electrons is shared. F 4. An oxygen atom could overlap an orbital with one hydrogen atom and have a stable electron configuration. Oxygen needs 2 electrons, so 2 H F 5. All covalent bonds are the same. T 6. Electrons shared in a bond will spend more time orbiting the nucleus of the atom with the higher electronegativity. T 7. Electrons shared in a bond between a hydrogen atom and an astatine atom are shared equally. They have the same electronegativity. F 8. Electrons shared in a bond between a boron atom and a nitrogen atom are shared equally. N has a higher electronegativity (difference =1.0) T 9. Electrons are shared unequally in a polar covalent bond. F 10. F 11. T 12. The more electronegative element in a polar covalent bond will be the negative dipole of the molecule. T 13. In the compound aluminum sulfide, sulfur is the negative dipole. T 14. The bond in KCl is ionic. T/F 15. T 16. T 17. T 18. Electrons are shared equally in an ionic bond. In an ionic bond, electrons not shared at all. The bond between a lithium atom and a fluorine atom will be covalent. Polar molecules have higher melting points. Higher than pure, lower than Ionic In bonds between K and Br, one electron is transferred from a potassium atom to a bromine atom. Ionic compounds tend to form crystalline solids. Elements that form ionic bonds with each other are usually far apart on the periodic table. Determine the type of bonding and draw electron dot diagrams for each of the following compounds. If the compound is polar, show the direction of polarity (negative pole). phosphorous trichloride polar bonds carbon dioxide polar bonds wants 32 has 26 shares 6 wants 24 has 16 shares 8 .. .. .. : Cl : P : Cl : .. .. .. : Cl : .. .. .. :O::C::O: (electrons pulled toward each Cl) (electrons pulled toward each O) carbon tetrabromide calcium oxide ionic bonds wants 40 has 32 shares 8 .. : Br .. polar bonds .. : Br : .. : C : .. : Br : .. +2 Ca . . -2 : O : .. .. Br : .. (electrons pulled toward each Br) calcium chloride ionic bonds +2 Ca . . -1 : Cl : .. ethyne (C2H2) slightly polar bonds wants 20 has 10 shares 10 . . -1 : Cl : .. H: C ::: C :H (electrons pulled toward C a little) sulfur dichloride polar bonds wants 24 has 20 sodium oxide ionic bonds +1 .. .. .. Na .. -2 shares 4 : Cl : S : Cl : .. .. .. +1 : O : .. Na (electrons pulled toward each Cl) selenium dihydride polar bonds oxygen dichloride polar bonds wants 12 has 8 shares 4 wants 24 has 20 shares 4 .. H : Se : H .. (slight) .. .. .. : Cl : O : Cl : .. .. .. (electrons pulled toward Se) (electrons pulled toward O) Ethane (C2H6) slightly polar bonds potassium chloride ionic bonds wants 28 has 14 shares 14 H H .. .. H:C : C :H .. .. H H +1 K . . -1 : Cl : .. (electrons pulled toward C a little) Assignment 4: Predicting Shapes of Molecules Compound H2 O Electron Dot Diagram .. H : O : H .. want 12 has 8 shares 4 Electron Pairs Lone Pairs Shape 4 2 angular 2 0 linear 3 0 Trigonal planar H : Be : H BeH2 BF3 wants 8 has 4 shares 4 .. .. : F : B : F : .. .. .. :F: .. want 30 has 24 share 6 want 40 have 32 share 8 4 0 tetrahedral SiCl4 .. : Cl : .. .. .. : Cl : C : Cl : .. .. .. : Cl : .. want 24 have 20 share 4 4 2 Angular OCl2 .. .. .. : Cl : O : Cl : .. .. .. Compound HCl Electron Dot Diagram .. H : Cl : .. want 10 has 8 shares 2 Electron Pairs Lone Pairs Shape n/a n/a linear 4 (acts like 2) 0 linear want 28 have 20 share 8 4 0 tetrahedral want 32 have 26 share 6 4 1 pyramidal 4 (acts like 2) 0 linear H : C:::N: HCN CH2Cl2 PF3 want 18 has 10 shares 8 .. : Cl : .. H : C : H .. : Cl : .. .. :F: .. .. .. :F :P : F: .. .. .. .. .. : S ::C::S: CS2 want 24 have 16 share 8 Polarity of compounds on the next page: H2O polar bonds and angular shape = polar compound Oxygen is the negative pole. BeH2 polar bonds and linear shape (uneven pull is dispersed) = pure compound BF3 polar bonds and trigonal planar shape (uneven pull is dispersed) = pure compound SiCl4 polar bonds and tetrahedral shape (uneven pull is dispersed) = pure compound OCl2 polar bonds and angular shape = polar compound Oxygen in the negative pole. HCl polar bonds and linear shape with Cl pulling the electrons toward itself = polar compound Cl is the negative pole. HCN polar bonds and linear shape with N pulling electrons toward itself = polar compound N is the negative pole. CH2Cl2 polar bonds and tetrahedral shape (uneven pull probably dispersed) = pure compound PF3 polar bonds with pyramidal shape = polar compound F end of molecule is the negative pole. CS2 non polar (pure) bonds, so molecule is pure. Assignment 5: Molarity problems Compound Electron Dot Diagram .. .. : I : Al : I : .. .. .. :I: .. want 30 has 24 share 6 AlI3 .. :F: S : F: .. SF2 Al AlF3 . . -1 :F: .. . . -1 :F: .. .. : Cl : .. .. .. : Cl : C : Cl : .. : Cl : .. .. H : Cl : .. HBr Lone Pairs Shape 3 0 Trigonal Planar 4 2 Angular n/a n/a Ionic Forms Crystals not molecules 4 0 Tetrahedral 1/3 0/3 Linear want 24 has 20 share 4 +3 CCl4 Electron Pairs . . -1 :F: .. want 28 have 20 share 8 want 10 have 8 share 2 Compound BeF2 Electron Dot Electron Diagram Pairs .. .. : F : Be : F : .. .. want 20 2 has 16 share 4 Lone Pairs Shape 0 Linear Pure .. : O .. .. : S:: O : .. :O: .. want 32 has 24 share 8 3 electron groups 0 Trigonal Planar pure .. : Cl .. 3 electron groups 0 CCl2O .. : C:: O : .. : Cl : .. want 32 has 24 share 8 Trigonal Planar Slight polarity 4 1 Pyramidal Polar AsCl3 .. .. .. : Cl : As : Cl : .. .. .. : Cl : .. want 32 has 26 share 6 4 2 Angular Polar SO3 .. H : Se : H .. SeH2 want 12 has 8 share 4 Assignment 6: Bonding Review You should be able to: Describe atomic structure in terms of valence electrons How do bonds form? (two ways) How are ions formed specifically? Describe what type of bond is seen in a compound. Describe the characteristics seen in compounds with each type of bond. (ex: would the compound be soluble in water?) Describe the octet rule as applied to covalent compounds. How many electrons do atoms want? How many bonds form? Draw electron dot diagrams for covalent compounds. Draw structural diagrams for covalent compounds. Describe the shape of a molecule using VSEPR Theory. Determine the polarity of a molecule using the electron dot diagram and shape. Relate the polarity of a molecule of a covalent compound to characteristics seen by that compound. Look over all your worksheets and labs for the unit!