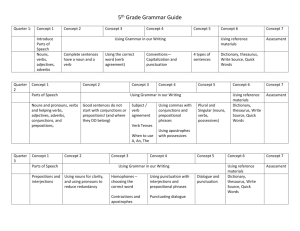
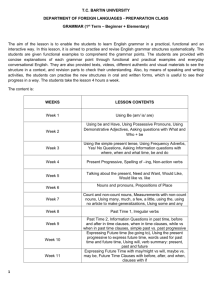
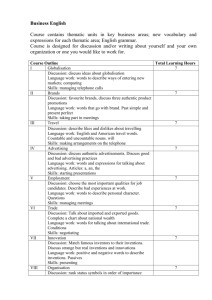
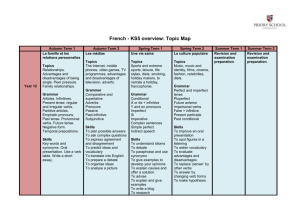
Grammar at the word level checklist - K
advertisement

English K–6 Support Materials for Students with Special Education Needs Form 4: Grammar at the word level checklist Name: Age: Date: Overview Age of acquisition Grammatical feature Example(s) 3 years Present progressive [ing] running 3 years Prepositions – in/on in box/on table 3 years Regular plural [s] cats 3½ years Irregular past tense swam 3 ½ years Possessive [s] Mum’s shoes 3½ years Articles [a, the] A book/The car 3½ years Regular past tense [ed] walked 3½ years Third person singular [s] He swims 3½ years Copula verbs [is/are] It is happy 4 years Auxiliary verbs [is/are and (verb)-ing] She is going 4 years Superlatives biggest 5 years Comparatives smaller, taller 6 years Noun derivations painter, cyclist 7 years Adverbs easily, gently 12/02/2016 Tick if there is evidence of the grammatical feature Form 4: Grammar at the word level checklist 1 English K–6 Support Materials for Students with Special Education Needs In-depth word level analysis Nouns reflect vocabulary development. Students may have specific difficulty recalling words rapidly or lack flexibility in the types of nouns used. List the nouns used by the student. Note: • any difficulty finding words (this may indicate difficulty with recall) • the accuracy and appropriate use of words and plural forms • the variety of nouns used Can the student use a variety of nouns and recall these easily? Yes No Can the student use the plural form of nouns? Yes No Record the non-specific words used by the student, eg something, thingy, it or that one Consider the frequency (circle): 12/02/2016 Low Moderate High Form 4: Grammar at the word level checklist 2 English K–6 Support Materials for Students with Special Education Needs Adjectives: use of descriptive language reflects concept development eg colour, size, shape. List the adjectives used by the student Order of acquisition (Wigg & Semmel 1984) Attribute Adjective examples Size big, little, small Colour red, blue, green Colour and size big red/small blue Shape round, square Length long, short Temperature hot, cold Height tall, short Width wide, narrow, thin Age new, old, young Taste sweet, sour Odour sweet, nice, awful, foul, yuk Attractiveness pretty, ugly, beautiful, nice Time first, last, early, late Speed fast, slow Texture hard, soft, smooth, rough Affect happy, sad, angry, fearful Distance near, far, distant Are adjectives evident and sufficient? 12/02/2016 Used by the student? Yes No Yes No Form 4: Grammar at the word level checklist 3 English K–6 Support Materials for Students with Special Education Needs Verbs (main verbs) tell what is happening or what is. Each clause must have a verb. Classify and list the types of main verbs used by the student. Action eg take, live, slip, look, get, run Relating eg be, have, look, include Sensing (feeling and thinking) eg think, believe, forget, wish, want, know Saying eg said, shouted, yelled, whisper, asked, cried Verb tense Circle the tenses used accurately by the student. Tense Present examples Past examples Future examples Simple I work I worked I will work Continuous I am working I was working I will be working Perfect I have worked I had worked I will have worked Perfect continuous I have been working I had been working I will have been working Third person singular[s] He works Does the student use verb tense accurately and consistently? Yes No Does the student use irregular past tense verbs eg swam, rode, spoke Yes No Helper verbs (auxiliary) are often vulnerable as they are less stressed parts of speech. Circle the helper verbs that are used by the student. am are can could is may might will have Others Does the student use helper (auxiliary) verbs accurately and consistently? 12/02/2016 Yes No Form 4: Grammar at the word level checklist 4 English K–6 Support Materials for Students with Special Education Needs Conjunctions: used to indicate a connection in a sentence or between sentences. Order of acquisition 1 2 3 4 5 Type Examples Early developing Late developing Adding information and, then, too addition, along, also, as well, in with Condition but, or although, anyway, however, if, otherwise, unless, when Cause and effect because, so, then as a result, consequently, therefore Time after, before, first, last, later, next, soon, then as, finally, for a start, in conclusion, then, to begin, until, while Condition for example, for instance, I mean, in fact, in other words, or rather, that is, to be more precise, to put it another way Additional conjunctions used: Personal pronouns: used to give language cohesion. Circle the pronouns used by the student Singular Plural Subject Object Subject Object 1st person I me we us 2nd person you you you you 3rd person he she it him her it they them Does the student use pronouns accurately to refer to number and gender? Yes No Possessive pronouns Circle the pronouns used by the student 1st person mine our 2nd person yours yours 3rd person his/hers theirs Does the student use possessive pronouns accurately? 12/02/2016 Yes No Form 4: Grammar at the word level checklist 5 English K–6 Support Materials for Students with Special Education Needs Prepositions: used in adjectival and adverbial phrases to provide extra information. The following prepositions are used in adverbial phrases to provide more information about where, when and how things occur. Circle the prepositions used by the student about above across after ahead all over along among around at away away from before behind below beneath beside between by close by close to down during for from in in front of inside into like near near to next to of off on on top of out out of past through to towards under until up with within Additional prepositions used: Examples of prepositions in order of acquisition Age of acquisition Prepositions 2 years in, off 2 ½ years on, under, out, away 3 years towards, up 3 ½ years in front, next to, around 4 years beside 4 ½ years down 5 years ahead, behind Reference: Owens, R (1991) 12/02/2016 Form 4: Grammar at the word level checklist 6