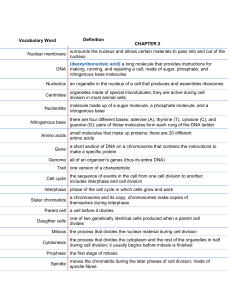
What is the main thing that happens during interphase? Is it
advertisement

1. What is the main thing that happens during interphase? Is it necessary for mitosis? 2. Division of the nucleus, called ________________, occurs before division of the cytoplasm, called __________________________. 3. During anaphase, __________________________________, which are genetically (identical/different), are separated. 4. What is the product of mitosis? Are they genetically identical or different? 5. Why does a cell become a cancer cell? What is a cancer cell’s main characteristic? 6. There are 5 things that contribute to genetic variation, 2 of which happen during meiosis. What are they? Define them. 7. What are homologous chromosomes? Are they genetically identical or different? 8. During anaphase I, __________________________________, which are genetically (identical/different), are separated. 9. During anaphase II, __________________________________, which are genetically (identical/different), are separated. 10. When does synapsis occur? Crossing over? 11. What is the product of meiosis? Are they genetically identical or different? Haploid or diploid? 12. What are the Laws of Segregation and Independent Assortment? 13. A brown-eyed man does not know what his (genotype/phenotype) is because brown is the dominant trait. If he undergoes a ________________, he might know. 14. What is incomplete dominance? Does it support the blending or particulate hypothesis? 15. What was the main discovery Morgan made after his experiments with flies? What was the wild type? Mutant type? 16. What does the Chromosome Theory of Heredity state? Did Morgan’s discovery support this? 17. A dog that is heterozygous for two traits (i.e. BbHh) mated with a dog with recessive genes (bbhh). The majority of the puppies (90%) had the phenotypes of their parents. What does this suggest about the two traits? How did some puppies NOT have the phenotypes of their parents? These puppies are called _________________ offspring. 18. Lamarck’s Theory of Evolution had two ideas. What were they? Are either valid? 19. What are Darwin’s two main ideas of his Theory of Evolution? Are either valid? 20. Natural selection limits the population of salmon; only some live to ______________. Why is this important? 21. Natural selection acts on the (individual/population). Evolution acts on the (individual/population). 22. Name some key evidence supporting Darwin’s theory. 23. In microevolution, ________________—a localized group of organisms of the same species—is studied by looking at their __________________, or total composition of genes (for all time/at that time). 24. What is allelic frequency? Why do we analyze it over and over for a population? 25. What does the Hardy-Weinberg theory state? Are his conditions realistic? 26. There are 2 main causes for microevolution. Describe each and how it affects populations/causes evolution. 27. Sexual reproduction (increases/decreases) (phenotypic/genetic) diversity within a population. (Do you know how?) 28. Natural selection works on that diversity, (increasing/decreasing) (phenotypic/genetic) diversity within a population. (Do you know how?)