Data-Driven Instruction and Assessment Rubric
advertisement
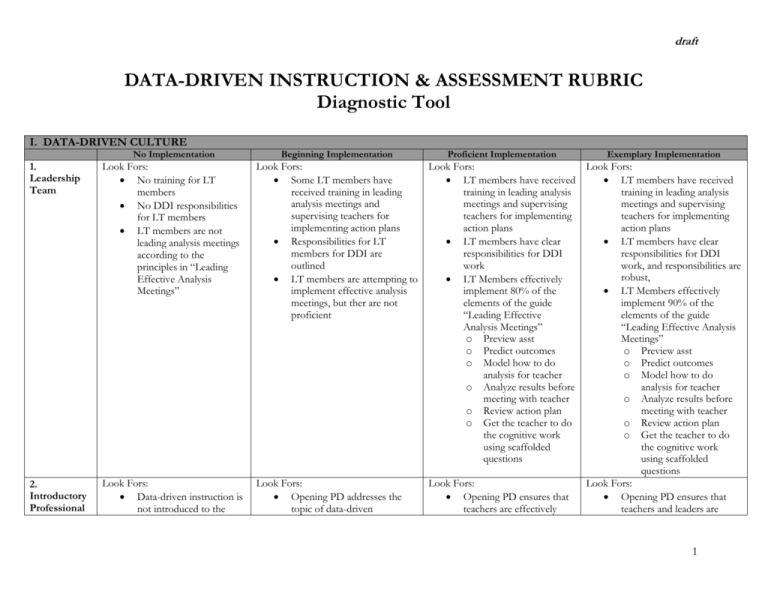
draft DATA-DRIVEN INSTRUCTION & ASSESSMENT RUBRIC Diagnostic Tool I. DATA-DRIVEN CULTURE No Implementation 1. Leadership Team Look Fors: No training for LT members No DDI responsibilities for LT members LT members are not leading analysis meetings according to the principles in “Leading Effective Analysis Meetings” 2. Introductory Professional Look Fors: Data-driven instruction is not introduced to the Beginning Implementation Proficient Implementation Exemplary Implementation Look Fors: Look Fors: Look Fors: Some LT members have LT members have received LT members have received received training in leading training in leading analysis training in leading analysis analysis meetings and meetings and supervising meetings and supervising supervising teachers for teachers for implementing teachers for implementing implementing action plans action plans action plans Responsibilities for LT LT members have clear LT members have clear members for DDI are responsibilities for DDI responsibilities for DDI outlined work work, and responsibilities are robust, LT members are attempting to LT Members effectively implement effective analysis implement 80% of the LT Members effectively meetings, but ther are not elements of the guide implement 90% of the proficient “Leading Effective elements of the guide Analysis Meetings” “Leading Effective Analysis o Preview asst Meetings” o Predict outcomes o Preview asst o Model how to do o Predict outcomes analysis for teacher o Model how to do o Analyze results before analysis for teacher meeting with teacher o Analyze results before o Review action plan meeting with teacher o Get the teacher to do o Review action plan the cognitive work o Get the teacher to do using scaffolded the cognitive work questions using scaffolded questions Look Fors: Look Fors: Look Fors: Opening PD addresses the Opening PD ensures that Opening PD ensures that topic of data-driven teachers are effectively teachers and leaders are 1 draft Development staff instruction, but teachers leave without the opportunity to fully understand and apply the tenets of assessment, analysis and action 3. Calendar introduced to data-driven instruction—they understand how interim assessments define rigor Teachers effectively and efficiently analyze results in a common way based on the expectations of the principal Principal ensures that teachers have a clear expectation and format for action plans aligned to the needs as defined by the data effectively introduced to data-driven instruction— they understand how interim assessments define rigor Teachers and leaders effectively and efficiently analyze results in a common way based on the expectations of the principal Principal ensures that teachers and leaders have a clear expectation and format for action plans aligned to the needs as defined by the data No Implementation Beginning Implementation Proficient Implementation Exemplary Implementation Look Fors—Calendar includes: Few or none of the items needed for proficient implementation Other Look Fors: Calendar is not in place to launch the school year Look Fors—Calendar includes: Some but not all of the items needed for proficient analysis & action Other Look Fors: Calendar is partially in place from the start of the year. Calendar is not very explicit within the culture of the school Look Fors—Calendar includes: Assessment administration Time for scoring Somewhat sufficient paidtime for teachers to analyze results Somewhat sufficient paidtime for teachers/teams to plan new lessons based on data analysis Re-teaching time in pacing charts Time for assessment creation/adaptation (if needed) Look Fors—Calendar includes: Previewing upcoming assessment & predicting performance Assessment administration Time for scoring Paid-time for teachers to analyze results Paid-time for teachers/teams to plan new lessons based on data analysis Re-teaching time in pacing charts Time for assessment creation/adaptation (if 2 draft Other Look Fors: Calendar is fully in place from the start of the school year Calendar is front and center in the mind of the principal All core teachers know the calendar is the guide for the DDI work during the year 4. Ongoing Professional Development Look Fors: There is no ongoing PD around data analysis, action planning or reteaching after the first training of the year Look Fors: A couple of professional development sessions are offered throughout the year that are aligned with the datadriven cycle PD is delivered with quality, but some participants may not have skills needed following the session PD may lack sufficient modeling and application so that teachers have the skills needed to do analysis and action Look Fors: Professional development ensures all teachers have skills needed to analyze data and act based on data Professional development is delivered “real time” so that needs are seen and met throughout the year Professional development is organized and led by principal or key leaders in the building Professional development provides ample time for practice and feedback based on performance needed) Other Look Fors: Calendar is fully in place from the start of the school year Calendar is front and center in the mind of the principal and the leadership team All teachers know the calendar is the guide for the DDI work during the year Calendar is easily adjustable if district changes require it Look Fors: Professional development ensures all teachers have skills needed to analyze data and act based on data Professional development is delivered “real time” so that needs are seen and met throughout the year Professional development not only matches the needs of the staff to implement DDI, but the needs of the staff as defined by the student weaknesses Professional development is organized and led by key leaders in the building. Not just the principal Professional development provides ample time for practice and feedback based on performance 3 draft 5. Build By Borrowing Look fors: No evidence of sharing best practices across teachers/schools Look fors: Some leaders and teachers are borrowing ideas from their peers and from other schools, but that does not translate to schoolwide action Many teachers work in complete isolation Look fors: Leaders are leveraging the performance of the best teachers in the school to improve teaching practices in the remaining classrooms With encouragement, teachers seek out resources & support from other teachers with stronger results Look fors: School leaders/teachers have visited other high-achieving schools to acquire best practices Leaders are leveraging the performance of the best teachers in the school to improve teaching practices in the remaining classrooms Teachers actively seek out resources & support from other teachers with stronger results 4 draft II. Assessments No Implementation Beginning Implementation Proficient Implementation Exemplary Implementation 1. Common Interim Look Fors: Sporadically administered Not common across grade level Math & Literacy assessments given only at certain grade levels Look Fors: Administered 2-3 times per year Common for grade and content area Only given in math and literacy at every grade level 311 Look Fors: Administered 4-6 times per year Common for grade and content area Given in Math & Literacy at every grade level 3-11 Look Fors: Administered 4-6 times per year Common for grade and content area Goes beyond math and reading to minimally include science and social studies (ES) Have interim assessments for grades K-2 2. Transparent Starting Point Look fors: Teachers do not see the assessment in advance Look fors: Teachers see assessments weeks before the administration or at a minimum, teachers are able to see the assessment before it is administered Look Fors: At the end of each assessment cycle, the next assessments are available to define the academic expectations Look fors: At the start of the year, all assessments are available to define the academic expectations Teachers back map their planning from the assessments without utilizing the exact assessment questions 3. Alignment State and College Look fors: Assessment items and tests match the state test level of rigor less than 50% of the time College readiness is unaddressed Look fors: Assessment items and tests match the state test level of rigor at least 50% of the time Alignment to college readiness is understood by leaders, but little action has occurred to make this alignment happen in the assessments Look fors: Look fors: Assessment items and tests Assessment items and tests match the state test level are at least at the level of of rigor at least 75% of the rigor of the state test time Assessment items have been Alignment to college designed to ensure alignment readiness is understood by with college readiness leaders, but little action has expectations occurred to make this alignment happen in the assessments 5 draft 4. Aligned to Instructional Sequence Look fors: Assessments are not aligned to scope & sequence Look fors: Grade level or content area has a clearly defined scope and sequence of standards, but assessments only partially match that the scope and sequence. What is taught is assessed Look fors: Look fors: Grade level or content area Grade level or content area has a clearly defined scope has a clearly defined scope and sequence of standards and sequence of standards Assessments align to 90% All assessments are aligned of the scope and to the scope and sequence sequence. Teachers follow the scope What is assessed is aligned and sequence to what is taught 5. Reassess Look fors: Assessments are unitbased; they do not reassess standards from previous units Look fors: Assessments sporadically reassess standards throughout the year Look fors: Assessments reassess the most important standards throughout the year Assessments are cumulative in nature, and build in rigor and length Look fors: Assessments reassess the most important standards throughout the year Assessments are cumulative in nature, and build in rigor and length Assessments are flexible, adjusting the emphasize standards that need reassessment based on student performance 6 draft III. Analysis No Implementation 1. Results Turnaround 2. Data Reports 3. Teacher Owned Beginning Implementation Proficient Implementation Exemplary Implementation Look fors: Results take longer than a week to be made available Teachers not involved in scoring Look fors: Look fors: Look fors: Results available within a week Results available within 2-3 Results available within 48 days hours Teachers not involved, or minimally involved in scoring Teachers somewhat Teachers involved in scoring involved in scoring of of constructed responses constructed responses Look fors: Look fors: Look fors: Look fors: Reports are difficult to Reports either have too little Concise reports: 1-2 pages Concise reports: 1 page per understand or too much information per classroom classroom Little data or Reports might not include Reports include item Reports includes item overwhelming amounts of item analysis or overall results analysis and overall results analysis, standard analysis data and overall results Reports are understandable Reports are mostly No item analysis for leaders but require some understandable for Data reports are color coded interpretation for teachers teachers & leaders Reports are understandable for teachers & leaders Look fors: Look fors: Look fors: Look fors: Teachers have no Teachers do little of the Teachers show some Teachers show strong ownership at all of the analysis; analysis mostly done initiative in analysis initiative in analysis analysis of their results by principal, instructional meetings meetings, suggesting leader or a “data team” preparation prior to the Teachers lack knowledge Leaders effectively meeting and skill to effectively and Teachers may lack knowledge facilitate analysis meetings efficiently analyze results and skill to effectively and to ensure that teachers do Teachers express ownership efficiently analyze results most of the analysis; for results and immediately Teachers expressly do not occasionally they intervene begin thinking about how to find value in analyzing Teachers analyze, but may to model good analysis improve results results blame test or students for poor results Teachers express Teachers are eager to see ownership for result results Teachers understand Leaders actively participate results and fluently talk in analysis, and strongly about them facilitate when needed Teachers completely understand results, and fluently talk about them 7 draft 4. Test in Hand Look fors: No test-in-hand analysis Look fors: Teachers or leaders have the assessments in hand during analysis, but not both Teachers look mostly at the assessment questions, and do not focus strongly on the student responses 5. Deep Analysis Deep analysis: only answers what students got wrong Deep analysis: mostly answers what students got wrong; infrequently answers why they got it wrong Look fors: Analysis is mostly broad generalizations like “students need to read more” or “students need to practice problemsolving” Teachers mostly just discuss what was wrong Look fors: Teachers look at student constructed responses and begin to diagnose student challenges Teachers look at wrong answer choices, and begin to diagnose student misunderstandings Teachers reach actionable conclusions with analysis, but often conclusions are general and not fully based on a deep understanding of results Analysis includes some generalizations like “students need to read more” or “students need to practice problem-solving” Look fors: Observe interim assessment in the hands of leaders and teachers during analysis meetings Assessments items are occasionally referenced throughout analysis meetings Teachers use the assessment when analyzing results Deep analysis: frequently, but not always, moves beyond what students got wrong and answers why they got it wrong Look fors: Teachers and leaders are fairly knowledgeable about the wrong answer choices, and what they demonstrate about student misunderstandings Teachers and leaders focus analysis on specific student misunderstandings based on wrong answer choices Look fors: Observe interim assessment in the hands of leaders and teachers during analysis meetings Assessment items are referenced throughout analysis meetings Teachers use the assessment when analyzing results Deep analysis: always moves beyond what students got wrong and answers why they got it wrong Look fors: Teachers and leaders are fully knowledgeable about the wrong answer choices, and what they demonstrate about student misunderstandings Teachers and leaders focus analysis on specific student misunderstandings based on wrong answer choices Teachers and leaders fully diagnose student challenges based on constructed responses Teachers and leaders combine the analysis with knowledge of the scope and sequence to drive action 8 draft steps 9 draft IV. Action No Implementation Beginning Implementation 1. Lesson Planning Look fors: No evidence of new lessons connected to data analysis Teacher teams do not plan collaboratively around data Look fors: Teacher teams problem solve and plan together based on data, but often not focused on specific student needs or don’t have specific lesson plans as a result Planning conversations often focus on teaching it again, and less on how to teach it differently Look fors: Evidence of new lessons that respond explicitly to data analysis Evidence of “flex time” or “reteach weeks” that are built into schedule Most teacher teams plan new lessons together using an effective protocol such as the Results Meeting Protocol Proficient Implementation Look fors: Evidence of new lessons that respond explicitly to data analysis Evidence of “flex time” or “reteach weeks” that are built into schedule Teacher teams plan new lessons together using an effective protocol such as the Results Meeting Protocol; the tone of the meetings are always solutions focused Exemplary Implementation 2. Teacher Action Plans Look fors: No evidence of teacher action plans Look fors: Teachers plan for reteaching, but often planning is not specific regarding goals, time, and strategy Differentiation is present in planning, but often only superficial Look fors: Teacher action plans are clearly implemented across 90% of the school Action plans include strategies for whole-group and small group instruction/pull-out Action plans include some supports for struggling students Action plans have clear timeline for implementation 3. Ongoing Look fors: Look fors: Look fors: Look fors: Teacher action plans are clearly implemented across the school Action plans include strategies for whole-group and small group instruction/pull-out Action plans include explicit supports for struggling students: creative use of extra time before, during or after typical school day Action plans have clear timeline for implementation Look fors: 10 draft Assessment Little evidence of ongoing assessment/checking for understanding Teachers assess at least weekly based on previous data and standards currently being taught Teachers link weekly assessment to reteaching, but often fail to act based on reassessment results Ongoing assessment efforts rarely take into account the different levels of proficiency present in the class Assessment/checking for understanding is present each week Everything retaught is reassessed Teaches are fairly knowledgeable about individual student performance and can fluently speak to it Assessment/checking for understanding is present in every class, everyday Assessment is differentiated based on current student proficiency levels Everything retaught is reassessed, and subsequent actions are driven by the new proficiency levels Assessment types are differentiated to ensure application in different formats Teaches are always very knowledgeable about individual student performance and can fluently speak to it Teachers are able to accurately predict how students will perform on next interim assessment 11 draft No Implementation Beginning Implementation Proficient Implementation Exemplary Implementation 4. Accountability Look fors: Leaders are not observing classes or reviewing lesson plans/action plans Leader is not able to articulate action steps being taken by teachers as a result of data analysis Look fors: Leaders are aware of action plans but don’t have much personal knowledge of their content Leader is only periodically observing for reteaching and rarely focused on specific reteaching efforts Leaders follow up with teachers after observing, but often this follow up is not specifically linked to the data and instructional practice Follow up by leader often lacks clear, actionable changes sought to classroom instruction Look fors: Leaders are knowledgeable about action plans, and how they link to specific needs of a class and grade/content area as defined by the data Leaders are observing most of the teaching each assessment cycle with the action plan in mind Observations by leaders are somewhat linked to the action plans Feedback from leaders to teachers is mostly linked to student needs, and fairly actionable Ongoing assessment information is utilized when observing 5. Engaged Students Look fors: Students are unaware of their performance on the assessments Look fors: Students are aware of their performance on the assessments Students can articulate why the interim assessments are important Students know they are working during class time to develop mastery toward Look fors: Most students you speak to know their specific performance levels on the interims Students generally can articulate the actions they are taking to improve their performance Students know that the Look fors: Leaders fully knowledgeable about action plans, and how they link to specific needs of a class and grade/content area as defined by the data Leaders are observing teaching each assessment cycle with the action plan in mind Observations by leaders are explicitly linked to the action plans, and whether the students are gaining mastery on specific standards Feedback from leaders to teachers is clearly linked to student needs, and immediately actionable Ongoing assessment information is utilized when observing Look fors: Any student you speak to knows their specific performance levels on the interims Students know where they are strong and weak, and then can articulate the specific actions they are taking to improve their 12 draft standards interims provide them with feedback they desire on their performance, and therefore engage in the taking of the interims fully performance in specific areas Students know what mastery looks like Students know that the interims provide them with feedback they desire on their performance, and therefore engage in the taking of the interims fully Students participate in the creation of their own action plan & tracking their performance 13