Care of the Patient Experiencing Problems with the Gastrointestinal
advertisement

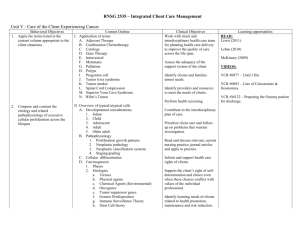
RNSG 2535 – Integrated Client Care Management Unit IV - Care of the Client Experiencing Problems with the Gastrointestinal System and its Accessory Organs 1. 2. 3. Behavioral Objectives Apply the terms listed in the content column appropriate to the client situations. Compare and contrast the normal anatomy and physiology to the pathophysiology of the disease processes in the gastrointestinal system across the lifespan. Analyze factors included in the assessment of the client experiencing complex problems of the gastrointestinal system, including the developmental and cultural considerations. I. Content Outline Application of terms A. Anasarca B. Anastomosis C. Asterixis D. Bariatric E. Biliary atresia F. Celiac disease G. Esophageal atresia H. Fistula I. Gluten free diet J. Hernias K. Interstitial edema L. Ileus M. Obstipation N. Osmolatity O. Steatorrhea P. Tenesmus Q. Third spacing R. Volvulus II. Anatomy & Physiology of the Gastrointestinal/ accessory organ system A. Developmental considerations 1. Infant 2. Child 3. Adolescent 4. Adult 5. Older adult B. Pathophysiology of gastrointestinal system and accessory organs III. Gastrointestinal/accessory organs assessment A. Interview 1. Chief complaint 2. History of present illness 3. Prior medical history Clinical Objectives Apply knowledge of how changes in clients’ personal behavior improve client’s health. Learning opportunities READ: Lewis (2011) Lehne (2010) Identify client’s unmet needs from a holistic perspective. Participate in peer review and quality improvement processes. Communicate plan of care to nurses and other interdisciplinary health care team members. McKinney (2009) VIDEO: #0159-Dealing With Problems During Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy #0164-Laparoscopic Treatment of Common Duct Stones Promote a safe, effective environment conducive to the optimal health and dignity of the client. #0107-Nurse’s View of Endoscopy Select and carry out safe and appropriate activities to assist client to meet basic physiologic needs, including: circulation, nutrition, oxygenation, activity, elimination, comfort, rest and sleep. #1113-The Operation: Colon Resection Use interdisciplinary resources within the institution to address ethical and legal concerns. #1112-The Operation: Liver Transplant COMPUTER SIMULATION: #5027-Physical Examination of the Abdomen #5041-Apply Critical Thinking to Nursing Skills: Nutrition and Elimination Use current technology to enhance client care MEDCOM ONLINE FILMS: VIDM216-T Caring for the Stoma, Caring for the Patient: Enterostomal RNSG 2535 – Integrated Client Care Management Unit IV - Care of the Client Experiencing Problems with the Gastrointestinal System and its Accessory Organs Behavioral Objectives 4. 5. 6. 7. Content Outline Medication history (prescription/nonprescription) Family/social/occupational history Knowledge of health maintenance Identify risk factors Clinical Objectives Identify and communicate reasons and rationales for deviation from plan of care to interdisciplinary health care team. Learning opportunities Nursing VIDM231-T Diabetes in Clinical Practice VIDM140-T Nasogastric Intubation, Balloon Gastronomy Tube Replacement VIDM133-T Nurses' Guide to Enteral Feeding Tubes Review Level II Gastrointestinal medications B. Physical exam 1. Bowel sounds 2. Size, shape, and abdominal girth 3. Tenderness/rebound tenderness 4. Pain 5. Nausea/vomiting 6. Hydration status 7. Vital signs 8. Skin color 9. Fluid wave (tympanic wave) C. Diagnostic tests 1. Laboratory studies a. Stool b. Electrolytes c. Complete blood count (CBC) d. Liver function tests (LFT) e. Amylase/lipase f. Serum albumin g. Gastric analysis h. H pylori i. Serum ammonia j. Bilirubin 2. Radiology/Imaging a. Upper GI with/without small bowel follow through Promote the effective coordination of client-centered health care. Identify priorities and make judgments concerning the needs of multiple clients in order to organize care. RNSG 2535 – Integrated Client Care Management Unit IV - Care of the Client Experiencing Problems with the Gastrointestinal System and its Accessory Organs Behavioral Objectives 4. Differentiate between the etiology, pathophysiology, and clinical manifestations of selected complex gastrointestinal/accessory problems Content Outline b. Barium swallow c. Barium enema d. Gall bladder series e. Gall bladder sonogram f. Sonogram g. Flat plate of the abdomen h. Computed axial tomography (CT) i. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) 3. Invasive a. Liver biopsy b. GI biopsy 4. Endoscopic a. Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) b. Endoscopicretrogradecholangiopancreatgram (ERCP) c. Colonoscopy (sigmoidoscopy, proctoscopy, anoscopy) D. Cultural influences 1. Hereditary 2. Environmental 3. Health beliefs/practices E. Developmental 1. Age specific assessment data a. Muscle tone b. Vital signs c. Fluid /electrolytes d. Nutritional 2. Behavioral/emotional response to health care providers IV. Complex Gastrointestinal/accessory organ problems A. Peptic ulcer disease B. Gallbladder disease C. Inflammatory bowel disease 1. Regional enteritis (Crohn’s) Clinical Objectives Learning opportunities RNSG 2535 – Integrated Client Care Management Unit IV - Care of the Client Experiencing Problems with the Gastrointestinal System and its Accessory Organs Behavioral Objectives 5. Discuss analysis, planning, implementation and evaluation for the nursing management of clients with complex gastrointestinal problems/accessory organs. Content Outline 2. Ulcerative colitis D. Diverticulosis/diverticulitis E. Diabetes Mellitis F. Hepatitis G. Liver Failure H. Pancreatitis I. Morbid Obesity V. Selected nursing diagnoses/selected nursing implementation A. Fluid and electrolyte imbalance 1. Independent interventions a. Abdominal assessment b. Age related hydration status c. Intake and output d. Monitor pertinent diagnostic tests e. Maintain skin integrity 2. Collaborate interventions a. Administer replacement fluid (1) Intravenous therapy (2) Total parenteral nutrition (TPN) b. Administer medications and monitor for desired effects/adverse effects/side (1) Antidiarrheal (2) Steroids (3) H-2 receptor antagonist (4) Antisecretory (5) Mucosal barriers (6) Antacids (7) Antibiotics (8) Vitamins (9) Stool softeners (10) Laxatives (11) Anticholinergic (12) GI stimulant (13) Antiemetic (14) Proton pump inhibitors Clinical Objectives Learning opportunities RNSG 2535 – Integrated Client Care Management Unit IV - Care of the Client Experiencing Problems with the Gastrointestinal System and its Accessory Organs Behavioral Objectives 3. 4. Content Outline (15) Pancreatic enzymes (16) Insulins (17) Antidiabetics c. Gastric therapy (1) Lavage (2) Nasogastric (3) Sengstaken-Blakemore d. Paracentesis Recognition of complications a. Hemorrhage b. Portal hypertension (1) Esophageal varices (2) Ascites (3) Anasarca c. Hepatic encephalopathy d. Clotting disorders e. Paracentesis f. Pernicious anemia g. Perforation/peritonitis h. Hypovolemic shock i. Hyperglycemia j. Hypercalcemia k. Malnutrition l. Bowel obstruction m. Impaired skin integrity n. Infection o. Septic shock p. Skin excoriation q. Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) r. Hyperglycemic hyperosmolar nonketotic coma (HHNK) The client will have improved fluid and electrolyte balance as evidenced by a. Demonstrate no signs and symptoms of dehydration b. Improved laboratory studies c. Increase intake of fluids to a Clinical Objectives Learning opportunities RNSG 2535 – Integrated Client Care Management Unit IV - Care of the Client Experiencing Problems with the Gastrointestinal System and its Accessory Organs Behavioral Objectives Content Outline specified d. amount according to age and metabolic e. needs f. Maintains adequate bowel elimination g. Vital signs B. High risk for post op complications 1. Surgical modalities a. Cholecystectomy b. Gastrectomy c. Pyloroplasty d. Colostomy e. Ileostomy f. Colon resection /Colectomy g. Peritoneal venous shunt h. Inguinal herniorrhaphy i. Porta-caval anastomosis j. Liver transplant k. Gastric by-pass surgery 2. Independent interventions a. Review all pertinent assessments b. NG tube maintenance / mouth care c. I &0 d. V/S e. Foley care f. Anti embolic stockings g. Ankle exercises; ROM h. Incentive spirometry i. Monitor IV / site care j. Position for comfort k. Assessment wound; wound care l. See NCP for pain m. Encourage activity as tolerated n. Safety considerations o. Monitor pertinent lab values p. Colostomy care Clinical Objectives Learning opportunities RNSG 2535 – Integrated Client Care Management Unit IV - Care of the Client Experiencing Problems with the Gastrointestinal System and its Accessory Organs Behavioral Objectives Content Outline q. Report unexpected observations 3. Collaborative interventions a. Administer medications and monitor for desired effects/adverse effects/ side effects (1) Antibiotics (2) Narcotics (3) Prophylactic heparin / lovenox b. Collaborate with enterostomal therapist c. Collaborate with registered dietitian d. Oxygen support 4. Recognition of complications a. Hemorrhage b. Infection: wound and systemic c. Paralytic ileus d. Peritonitis e. Delayed wound healing: dehiscence, evisceration f. Malnutrition g. Dumping syndrome h. Bowel obstruction i. Adhesions j. Pernicious anemia 5. The client will not experience post-op complications as evidenced by: a. Wound healing b. Vital signs c. Bowel sounds d. Abdominal girth e. Homans sign f. Tolerates diet g. Laboratory studies C. Altered health maintenance: Knowledge deficit 1. Client teaching a. Assess readiness to learn, ability, Clinical Objectives Learning opportunities RNSG 2535 – Integrated Client Care Management Unit IV - Care of the Client Experiencing Problems with the Gastrointestinal System and its Accessory Organs Behavioral Objectives Content Outline knowledge b. Avoid aggravating factors c. Promotion of alleviating factors avoid activities that increase intra-abdominal pressure (lifting) d. Reportable signs/symptoms e. Wound care f. Ostomy care g. Medication teaching h. Rest/activity i. Risk factors j. Life style modifications k. Nutritional (1) High fiber / high residue (2) Low fiber/low residue (3) High protein (4) Regular diet (5) Low fat l. Maintenance of fluid balance (age specific) m. Diabetic teaching 2. Community Resources a. American Ostomy Association b. National Foundation for Ileitis and Colitis c. Alcoholics Anonymous d. Public Health Department e. Home health f. American Diabetes Association g. Juvenile Diabetes Association h. National Bariatric Association 3. The client will have improved health maintenance as evidenced by: a. Identifying aggravating and alleviating factors b. Identifying reportable signs and symptoms Clinical Objectives Learning opportunities RNSG 2535 – Integrated Client Care Management Unit IV - Care of the Client Experiencing Problems with the Gastrointestinal System and its Accessory Organs Behavioral Objectives Content Outline Describing the purpose, correct administration and side effects of meds d. Ability to discuss diagnosis, surgical procedure, and post care e. Demonstrates osmotic care f. Increasing activity as tolerated g. Achieves optimum level of nutrition through prescribed diet h. Utilizing community resources D. Ineffective Individual coping: anxiety, fear powerlessness, dependence. Review Unit III-Care of the Client Experiencing Respiratory Problems E. Body Image Disturbance. Review Unit V-Care of the Client Experiencing Cancer Clinical Objectives Learning opportunities c. n:soph\fall\Unit IV Gastro Revised 07/11