Grade 2 - Farmington River Regional School District
advertisement

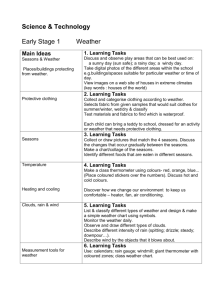
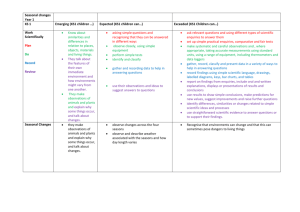
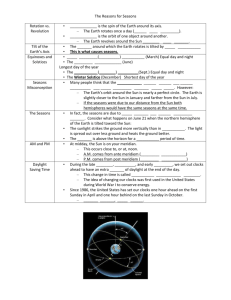
FARMINGTON RIVER REGIONAL SCHOOL DISTRICT – SCIENCE MAP GRADE TWO Month Content September WEATHER AND SEASONS 1. Seasons 2. Temperature October WEATHER AND SEASONS 1. Seasons 2. Temperature Skills 1a. Describe the four seasons and their characteristics. 1b. Explain some ways people can warm up or cool off. 1c. Describe how people adjust to weather conditions during different seasons. 1d. Describe some ways that animals or plants change in response to seasonal weather conditions. 2a. Demonstrate that materials absorb varying amounts of the sun's heat. 2b. Identify different surfaces and communicate the fact that they absorb varying amounts of the sun's heat. 1a. Describe the four seasons and their characteristics. 1b. Explain some ways people can warm up or cool off. 1c. Describe how people adjust to weather conditions during different seasons. 1d. Describe some ways that animals or plants change in response to seasonal weather conditions. Standards MA_Curriculum_Frameworks Science and Technology/ Engineering (2001) : p-2 • Learning Standard 1.3 Describe the weather changes from day to day and over the seasons. Introduced • Topic The Sun as a Source of Light and Heat Introduced • Topic Periodic Phenomena Introduced • Learning Standard 2.7 Recognize changes in appearance that animals and plants go through as the seasons change. Introduced • Learning Standard 2.8 Identify the ways in which an organism's habitat provides for its basic needs (plants require air, water, nutrients, and light; animals require food, water, air, and shelter). Introduced MA_Curriculum_Frameworks Science and Technology/ Engineering (2001) : p-2 • Topic The Weather Developed • Topic Periodic Phenomena Developed • Strand 2 Life Science (Biology) Developed • Topic Living Things and Their Environment Developed • Topic Earth's Materials 2a. Demonstrate that materials absorb varying amounts of the sun's heat. 2b. Identify different surfaces and communicate the fact that they absorb varying amounts of the sun's heat. 1 of 6 Month November FARMINGTON RIVER REGIONAL SCHOOL DISTRICT – SCIENCE MAP GRADE TWO Content Skills WEATHER AND SEASONS 1. Wind 1a. Demonstrate that wind or moving air can make objects move. 1b. Infer that wind can move fast or slow. 2. Water and Water Cycle 2a. Infer that water changes from water vapor to liquid water when warm air touches a cold surface. 2b. Identify a variety of weather conditions involving water in different forms. 3. Light 3a. Identify sources of light. 3b. Classify sources of light as natural or made by people. 3c. Conclude that the sun is the most important source of light. 3d. Observe that a light source gives off both heat and light. 3e. Observe that light travels in a straight line. 3f. Classify objects according to how well light can pass through them. 3g. Identify an object by the shadow that is cast when the object is placed in a beam of light. Standards MA_Curriculum_Frameworks Science and Technology/ Engineering (2001) : p-2 • Learning Standard 1.2 Understand that air is a mixture of gases that is all around us and that wind is moving air. • Topic The Sun as a Source of Light and Heat Developed • Topic Periodic Phenomena Developed • Strand 2 Life Science (Biology) • Topic Living Things and Their Environment Developed • Strand 3 Physical Sciences (Chemistry and Physics) • Topic Observable Properties of Objects Introduced • Topic Position and Motion of Objects • Learning Standard 3.3 Describe the various ways that objects can move, such as in a straight line, zigzag, back-and-forth, round-andround, fast, and slow. • Strand 3 Physical Sciences (Chemistry and Physics) Introduced • Learning Standard 3.3 Describe the various ways that objects can move, such as in a straight line, zigzag, back-and-forth, round-andround, fast, and slow. Introduced • Strand 3 Physical Sciences (Chemistry and Physics) Introduced • Topic Observable Properties of Objects • Learning Standard 3.1 Sort objects by observable properties such as size, shape, color, weight, and texture. Introduced • Topic Position and Motion of Objects Introduced • Learning Standard 3.3 Describe the various ways that objects can move, such as in a straight line, zigzag, back-and-forth, round-andround, fast, and slow. Introduced 2 of 6 Month December FARMINGTON RIVER REGIONAL SCHOOL DISTRICT – SCIENCE MAP GRADE TWO Content Skills Standards 1. LIGHT AND 1a. Observe that a light source gives MA_Curriculum_Frameworks Science and Technology/ COLOR off both heat and light. Engineering (2001) : p-2 1b. Observe that light travels in a straight line. • Topic The Sun as a Source of Light and Heat Developed 1c. Classify objects according to how well light can pass through them. • Learning Standard 1.4 Recognize that the sun supplies heat and 1d. Identify an object by the shadow light to the earth and is necessary for life. Developed that is cast when the object is placed in a beam of light. • Learning Standard 3.3 Describe the various ways that objects can 1e. Observe how the shadow cast by an move, such as in a straight line, zigzag, back-and-forth, round-andobject changes when the position of the round, fast, and slow. Developed light source changes. 1f. Predict where shadows would be at • Learning Standard 3.1 Sort objects by observable properties such different times of the day. as size, shape, color, weight, and texture. Developed 2a. Produce the colors of the spectrum. 2b. Identify the colors of the spectrum. 2c. Identify the colors resulting from the mixture of two colors. January LIGHT AND COLOR 1a. Observe that a light source gives off both heat and light. 1b. Observe that light travels in a straight line. 1c. Classify objects according to how well light can pass through them. 1d. Identify an object by the shadow that is cast when the object is placed in a beam of light. 1e. Observe how the shadow cast by an object changes when the position of the light source changes. 1f. Predict where shadows would be at different times of the day. MA_Curriculum_Frameworks Science and Technology/ Engineering (2001) : p-2 • Strand 3 Physical Sciences (Chemistry and Physics) Developed • Learning Standard 3.1 Sort objects by observable properties such as size, shape, color, weight, and texture. Developed • Topic The Sun as a Source of Light and Heat Developed 2a. Produce the colors of the spectrum. 2b. Identify the colors of the spectrum. 2c. Identify the colors resulting from the mixture of two colors. 3 of 6 Month February FARMINGTON RIVER REGIONAL SCHOOL DISTRICT – SCIENCE MAP GRADE TWO Content Skills 1. INTERACTIONS OF LIVING THINGS Habitats: Woodland Swamp Rainforest Pond Desert Arctic Mountain March INTERACTIONS OF LIVING THINGS Habitats: Woodland Swamp Rainforest Pond Desert Arctic Mountain 1a. Classify objects into two groups: living and nonliving. 1b. Describe what living things need to survive. 1c. Compare objects from the schoolyard environment and a woodland environment. 1d. Identify plants and animals found in Woodland and Swamp habitats. 1e. Describe how an animal uses living and nonliving resources to make a home for itself and its young. 1f. Generalize that body parts help animals to survive in their environment. 1g. Observe how some animals can change their environment to better meet their needs. Standards Continues through April MA_Curriculum_Frameworks Science and Technology/ Engineering (2001) : p-2 • Strand 2 Life Science (Biology) Introduced • Topic Characteristics of Living Things • Learning Standard 2.1 Recognize that animals (including humans) and plants are living things that grow, reproduce, and need food, air, and water. Introduced • Learning Standard 2.2 Differentiate between living and nonliving things. Group both living and nonliving things according to the characteristics that they share. Introduced • Learning Standard 2.3 Recognize that plants and animals have life cycles, and that life cycles vary for different living things. Introduced • Learning Standard 2.6 Recognize that people and other animals interact with the environment through their senses of sight, hearing, touch, smell, and taste. Introduced • Learning Standard 2.7 Recognize changes in appearance that animals and plants go through as the seasons change. Introduced 1a. Identify plants and animals found in Rainforest, Pond, Desert and Arctic habitats. 1b. Describe how an animal uses living and nonliving resources to make a home for itself and its young. 1c. Generalize that body parts help animals to survive in their environment. 1d. Observe how some animals can change their environment to better meet their needs. 1e. Differentiate between woodland and desert plants and justify why each is suited to their environment. 4 of 6 Month April FARMINGTON RIVER REGIONAL SCHOOL DISTRICT – SCIENCE MAP GRADE TWO Content Skills INTERACTIONS OF 1a. Identify plants and animals found Continues through June LIVING THINGS in a mountain habitat. -----------1b. Describe how an animal uses living Habitats: and nonliving resources to make a Woodland home for itself and its young. Swamp 1c. Generalize that body parts help Rainforest animals to survive in their Pond environment. Desert 1d. Observe how some animals can Arctic change their environment to better Mountain meet their needs. 1e. Compare physical features of living things from different environments. 1f. Describe how people and natural forces can change the environment. Standards 5 of 6 Month May/June FARMINGTON RIVER REGIONAL SCHOOL DISTRICT – SCIENCE MAP GRADE TWO Content Skills Standards SOLIDS LIQUIDS 2a. Describe the properties of solid MA_Curriculum_Frameworks Science and Technology/ AND GASES objects. Engineering (2001): p-2 2b. Group solid objects on the basis of Matter properties such as size, shape, texture • Topic Observable Properties of Objects Introduced and color. 1a. Describe the properties of liquids. • Learning Standard 3.1 Sort objects by observable properties such Group liquids on the basis of properties as size, shape, color, weight, and texture. Introduced such as color and texture. 1b. Conclude that a solid has a definite • Topic States of Matter Introduced shape and that liquids take the shape of the container it is in. • Learning Standard 3.2 Identify objects and materials as solid, 1c. Describe the properties of a gas and liquid, or gas. Recognize that solids have a definite shape and that conclude that gas does not have a liquids and gases take the shape of their container. Introduced definite size and shape and is usually colorless and odorless. 1d. Conclude that solids, liquids, and gases occupy space. 1e. Discover that heat can change a solid into a liquid and liquid changes into a gas when heat energy is applied. 1f. Conclude that when gas is cooled enough, it chances into a liquid. 1g. Classify objects and substances as a solid, liquid and gas. Germs How germs affect our health. MA_Curriculum_Frameworks Comprehensive Health (1999) : p-5 • Learning Standard 8.1 Describe how the body fights germs and disease naturally and with medicines and immunization. • Learning Standard 8.2 Identify the common symptoms of illness and recognize that being responsible for individual health means alerting caretakers to any symptoms of illness. • Learning Standard 8.3 Apply skills to prevent and control the spread of disease, including those that help promote cleanliness (such as correct handwashing, regular bathing, and washing clothes). 6 of 6