Glaciers: 2 Types
advertisement

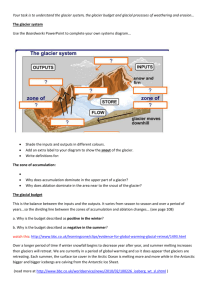
GLACIERS NOTES!! Glaciers: 2 Types ____________________ GLACIERS: long, slowmoving, streams of ice found in _______________ (high elevation) occupying former river valleys ___________________ GLACIERS (ICE SHEETS): very ________ (1000’s of years), thick (1000’s of meters) mass of ice ________________________________________________ _____________________: 1.7 Million SQ MI , 3 KM thick _____________________: 12.5 Million SQ MI, 5 KM thick WHERE DO THEY FORM? • AREAS OF ________________________ OR ______________________________ WHERE THEY HAVE _______ SUMMERS • PRESENTLY OCCUPY ________% OF WORLD’S TOTAL LAND AREA (COMPARED TO ______% DURING THE PLEISTOCENE EPOCH) How long ago was this? _______ HOW DO THEY FORM? • MORE SNOW MUST FALL THAN ______________ • ZONE OF ______________________ – SNOW TURNS TO ICE AT UPPER PART OF GLACIER • ZONE OF ____________________ (_________________) – LOWER PART • SNOW LINE (_________________________ LINE) LINE WHERE SNOW IS ________________________________ Process of Glacier Formation 1) SNOWFLAKES ______________ 2)SNOWFLAKES ______________ 3)FIRST INTO _________ (LIKE PACKED SNOWBALLS) 4)LOWER LAYERS TURN INTO GLACIAL _______ (SOLID ICE – NO AIR) UNDER THE WEIGHT OF OVERLYING FIRN AND SNOW Firn • ________ is an intermediate stage between ______ and _________________________ • When _________ snow is accumulated than is melted, the snow clumps together and will ultimately become glacial ice HOW DO GLACIERS MOVE? • UNDER THE INFLUENCE OF ___________________ • _________________________ IS THE DRIVING FORCE • UNDER PRESSURE THE DEEPER ICE BEHAVES LIKE A THICK ________________ (CALLED PLASTIC FLOW) AND __________ DOWNHILL OR _____________ OUT IN ALL DIRECTIONS (when glacier is about 300 ft. thick) GLACIER MOVEMENT • GLACIER ADVANCES SNOWFALL _____ MELTING • GLACIER RETREATS SNOWFALL _______MELTING • STATIONARY GLACIER SNOWFALL ______ MELTING GLACIER FLOW • SPEED IS LIKE A STREAM – ____________ IN THE MIDDLE / LESS FRICTION • fastest movement after 1) __________________, 2) ________________, and 3) in _______________ • WHY??? ______________________ form along ______________ slopes because upper zone of glacier is ______________ (rarely go deeper than 120ft. ) HOW DO GLACIERS ERODE? ____________________________ erosional agent because of their great size and weight Glaciers erode by: • __________________ – wearing, grinding, scraping rock surface because rock fragments are frozen into the ice at the bottom (ROCK FLOUR) • _________________ – rock fragments loosened, picked up and carried by glaciers EROSIONAL FEATURES • _______________ - Grooves carved into the bedrock by pebbles and cobbles carried at the bottom of a glacier – can show direction of glacial movement • __________________________ • __________________ - TILL - is angular to sub-round and NOT SORTED AND NOT LAYERED ERRATIC – EVIDENCE OF GLACIER EROSION • A ______________-sized rock dumped by a glacier. The rock is usually of a _______________________ that the surrounding rock… VALLEY GLACIERS VALLEY GLACIER EROSIONAL FEATURES ___________________ that were scenic to begin with are now jagged, angular peaks GLACIERS MODIFY RIVER VALLEYS BY… TURNING THE V-SHAPE RIVER VALLEYS INTO ________________ GLACIATED VALLEYS EROSIONAL LANDSCAPE FEATURES OF VALLEY GLACIERS ________________________: semi-circular shaped bowl created as a glacier scours back toward the mountain (1st place snow and ice accumulate) _____________________: steep-sided, sharp-edged bedrock ridge formed by two glaciers eroding away on opposite sides of ridges ____________________: 3 or more cirques adjacent to one another _____________________: glacial lakes produced by glacial scouring- often found in cirques _____________________: valley eroded by a small tributary glacier; floor is at a higher elevation that valley it feeds into… VALLEY GLACIER DEPOSITIONAL FEATURES _______________________ – unsorted, un-layered pile of till There are many types of moraines ________________ – till along side of glacier ___________________ – 2 glaciers come together and the lateral moraines join in a single ridge ____________________ – farthest advance of glacier __________________ – glacier retreats, pauses, deposits – will be parallel to terminal moraine f05_07a_pg84 CONTINENTAL OR ICE SHEET GLACIERS • MOST FLOW OVER RELATIVELY FLAT AREAS SO LANDSCAPE FEATURES ARE LESS DRAMATIC – ROUNDED HILLS (valley glaciers sharpen and continental glaciers round) • LAKES AND SWAMPS GREAT LAKES FINGER LAKES CONTINENTAL GLACIER DEPOSITIONAL FEATURES ____________________ – glacially formed accumulation of debris ______________________ - ground moraine that is mounded into a stream-lined oval shape hill (inverted spoon) – steep side points in direction the glacier came from _____________________ – large, buried ice blocks melted and left depressions. Ex. Lake Ronkonkoma ______________________ - deposits made by streams after glaciers melt (sorted/stratified) The Milankovitch Cycle • Changes in the tilt of the Earth’s axis from 21.5º - 24.5º (obliquity – every 41,000 years), changes in the shape of Earth's orbit (eccentricity – every 100,000 years) and axis pointing to Vega instead of Polaris (precession – + or - 21,000 years). • Bottom line – about a 100,000 year cycle • Since then however, fears of global warming as a result of man-made greenhouse gas pollution have dominated the environmental agenda – hard to predict