Philosophers
advertisement

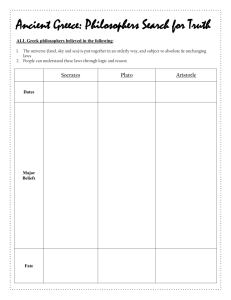
THEORY OF KNOWLEDGE TNeal SPRING 2010 PHILOSOPHERS Your student team has been assigned a group of philosophers. Learn about these philosophers, especially the theories for which they are famous. Particularly, consider theories regarding epistemology. Be prepared to compare and contrast your philosophers to each other’s theories and philosophers who came before them—especially Plato and Aristotle. Each member of the student team should understand all philosophers in the assigned group. Do not divide the research up with each student responsible for one philosopher. You may, however, divide up the categories listed below so that each of you are looking for a specific focus for all of the philosophers in your group. Due date: Create a PowerPoint presentation using GoogleDocs so that each group member can participate actively. Share your information with each other, so every group member has both input and knowledge. Be prepared to present your philosophers with the class on the date that corresponds with the Sophie’s World reading assignments. Check the website for tentative dates. Your presentation should include the following: Provide an overview of each of the philosophers’ theories on epistemology. Summarize the theory for which each philosopher is most famous. Share biographical information but only details that shed light on the philosophers’ theories Explain how each philosopher relates to previous philosophy—how is it similar and how does it differ? Point out observations made by Gaarder in Sophie’s World. Do these philosophers tend to relate better to Plato or to Aristotle? Defend your answer. Discuss at least one significant knowledge issue that relates to these philosophers’ theories. State the knowledge issue as a question, then explain how it relates to the various philosophers’ theories. The Hellenistic/Roman Period: The Cynics, Diogenes of Sinope The Stoics, Seneca Marcus Aurelius The Sceptics, Empiricus Romanticims and Idealism: Jean-Jacques Rousseau (father of Romanticism) George Berkeley (idealist) Immanuel Kant (idealist) George Hegel (idealist) Toward Christian Theology Plotinus (neoplatonists) St. Augustine of Hippo (Christian) Aquinas (Scholasticism) Thomas More (Christian Utopia) Liberalism and Pragmatism in the Nineteenth Century John Stuart Mill (liberal) Mary Wollstonecraft (liberal) William James (pragmatist) Rationalism in the Age of Reason: Francis Bacon (Scientific Revolution) Rene Descartes (rationalist) Benedict de Spinoza (rationalist) Gottfried von Leibniz (rationalist) Empiricism and the Enlightenment: John Locke (empiricist) David Hume (empiricist) Voltaire (empiricist) Materialism Karl Marx (materialist) Carl Jung (materialist) Sigmund Freud (materialist) Existentialism and Postmodernism Soren Kierkegaard (existentialist) Friedrich Nietzsche (existentialist) Claude Levi-Strauss (postmodernist) Michel Foucault (postmodernists)