Food Webs and Pyramids of Biomass
advertisement

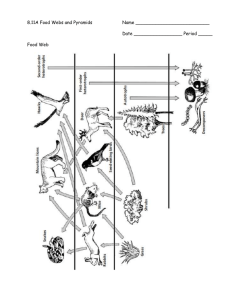
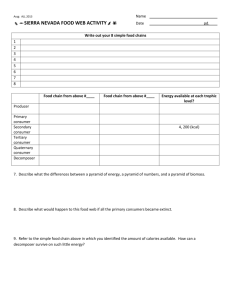
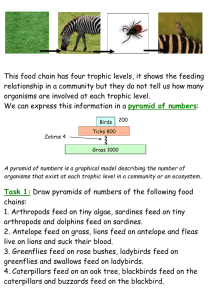
Food Webs and Pyramids of Biomass L.O: To be able to construct food chains, pyramids of number and biomass Visit the website: http://www.gould.edu.au/foodwebs/kids_web.htm Choose a food web to have a go at – you have to put the organism into its correct category e.g. producer. The food web is then built for you. Using your food web write out 2 food chains in your book. Now visit this website: http://www.ecokids.ca/pub/eco_info/topics/frogs/chain_reaction/index.cfm Play the game making the 2 food chains. Discuss the answers about the foodweb. Finally visit this site: http://www.bbc.co.uk/nature/blueplanet/webs/flash/main_game.shtml Complete the 5 challenges Draw out the pyramid of number When you complete this do some research to find out what a pyramid of biomass is, explain this in your book and draw out a few examples that you find. Activities For each of the following ecosystems draw out a food chain, pyramid of number and pyramid of biomass. 1. In a freshwater lake in Scotland, 3 million individual cells of photosynthetic plankton provide food for 10 000 pond shrimps. These are the primary consumers. The pond shrimps are eaten by 100 filter-feeding fish. These fish provide food for a pair of breeding swans that live on the lake. Organism Dry mass (estimate) in g found in 1m2 Photosynthetic plankton: 1000 Pond shrimps: 150 Fish: 50 Swans: 25 2. In the first trophic level of a deciduous woodland ecosystem, there are three beech trees. The beech trees provide food for 200 000 aphids, the primary consumers in the food chain. At the third trophic level there are 110 ladybirds. These provide food for the tertiary consumers, three sparrows. The top predator, a kestrel, eats the three sparrows. The kestrel is at the fifth trophic level. Organism Dry mass (estimate) in g found in 1 m2 Beech trees: 5000 Aphids: 100 Ladybirds: 40 Sparrows: 25 Kestrel: 10