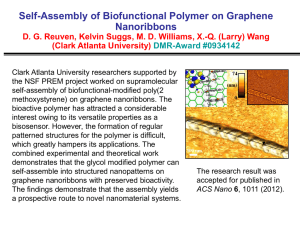
Synthetic procedures - Royal Society of Chemistry
advertisement

Supplementary Material for Faraday Discussions
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2004
Organisation in two series of low-dimensional polymer electrolytes with high ambient
lithium salt conductivity.
Jianguo Liu, Yungui Zheng, Yen-Po Liao, Xiangbing Zeng, Goran Ungar and
Peter V. Wright
Dept. of Engineering Materials, University of Sheffield, Mappin St.,Sheffield, UK S1 3JD
Electronic supplementary information.
Table S!. X-ray data for C16On polymers and complexes with LiBF4 and LiClO4
Polymer or complex
d- spacing (/ Å, 26oC)
d- spacing (/ Å, 50oC)
C16O1
4.16, 15.91, 32.00
4.51, 33.88 (amorphous)
C16O1:LiBF4 (1:1)
3.87, 4.17, 6.09, 16.18, 32.54
3.88, 4.16, 6.07, 33.29
C16O2(100%)
4.16,8.25, 16.59, 33.68
4.60, 33.10 (amorphous)
C16O2(100%):LiBF4 (1:1)
3.87, 4.17, 4.84, 6.12, 8.39, 16.88, 34.28
3.87, 4.16, 4.83, 6.12, 33.88
C16O3(100%)
4.19,9.20, 12.14, 18.49, 37.64
4.45, 32.73
C16O3(100%):LiBF4 (1:1)
4.19, 4.83, 12.86, 19.49, 39.44
4.84, 41.13
C16O4(100%)
3.97, 4.19, 4.47, 9.33, 12.72, 18.73, 38.39
4.41, 32.18 (amorphous)
C16O4(100%):LiBF4 (1:1)
4.22, 14.31, 43.62
4.46, 43.62
C16O5(40%):LiBF4 (1:1)
3.89, 4.16, 19.69, 39.44
3.87, 4.14, 44.63
C16O5(100%)
4.17, 37.64
4.44, 33.29 (amorphous)
C16O5(100%):LiBF4 (1:1)
4.22, 14.93, 46.06
4.39, 42.97
LiBF4
4.06, 4.35
C16O1:LiClO4 (2:1)
3.90, 4.20, 6.76, 16.73, 33.88
3.89, 4.27, 35.55
C16O1:LiBF4 (2:1)
4.18, 16.36, 32.73
4.41, 33.29
C16O1X
4.23, 36.92
4.62, 35.12
C16O1X:LiClO4 (2:1)
4.25, 37.15
3.96, 4.33, 38.40
C16O1X:LiBF4 (2:1)
4.22, 36.45
4.24, 36.92
Numbers in bold indicate sharp reflections.
Table S2. X-ray data for C16O5-C16O1 copolymers and complexes
Polymer or complex
d- spacing (/ Å, 26oC)
d- spacing (/ Å, 50oC)
C16O5(100%)
4.17, 37.64
4.44, 33.29
C16O5(100%):LiBF4 (1:1)
4.22, 14.93, 46.06
4.39, 42.97
C16O5(75%)
4.18, 12.80, 18.73, 38.65
4.47, 33.68
C16O5(75%):LiBF4 (1:1)
4.18, 13.80, 21.20, 41.72
4.40,44.63
C16O5(40%)
4.18, 17.98, 36.92
4.47, 32.54
C16O5(40%):LiBF4 (1:1)
3.89, 4.16, 19.69, 39.44
3.87, 4.14, 44.63
LiBF4
4.06, 4.35
Numbers in bold indicate sharp reflections.
Supplementary Material for Faraday Discussions
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2004
Synthetic Procedures
Dimethyl sulphoxide (DMSO) was dried and distilled before use. Other reagents were
used without further purification.
Synthesis of poly[2,5,8,11,14-pentaoxapentadecamethylene(5-hexadecyloxy-1,3phenylene)] (C16O5 copolymer (method X)
5-hexadecyloxy benzene-1,3-dimethanol (i) and 1,11-dichloro-3,6,9-trioxaundecane
(tetraethyleneglycol dichloride) were prepared as described previously12. The polymer
C16O5X(50%) was prepared by heating 1.89g (0.005mol) 5-hexadecyloxy benzene1,3-dimethanol (i), 1.16g (0.005mol) tetraethylene glycol dichloride and 2.24g
(0.04mol) potassium hydroxide in 5ml dimethyl sulphoxide for 7 days with gentle
stirring at 90C under a nitrogen atmosphere. The polymer was precipitated in water
and the mixture was neutralized by addition of concentrated acetic acid. The polymer
was separated and washed with hot water several times to remove inorganic salts and
finally with hot methanol several times to remove monomer. The product is yellow.
1
H NMR: H(400MHz; solvent CDCl3; standard SiMe4) 0.86 (3H, t, CH3), 1.25 (25H,
s, 12CH2), 1.45 (2H, m, -CH2), 1.75 (2H, m, -CH2), 3.65 (7.5H, t (broad), 4CH2
ethoxy), 3.92 (2H, t, -CH2), 4.45 (2H, s, -CH2, benzyl), 6.85 (2.5H, m,
C6H3aromatic). 1H NMR results show that the molar proportion of the tetraethoxy
segments (= 3.65ppm) is ca. 50% of the side chain groups. The 2 benzylic
hydrogens are only half of the 4 expected and the FTIR spectrum shows medium ester
C=O at 1720 cm-1 suggesting that the polymer is an ether-ester. GPC gave molar mass
averages <Mn> = 29,224, <Mw> = 257,711, <Mz> = 677, 074. DSC of C16O5
indicates that the polymer melts at 33C.
Synthesis of C12C18O5X (method X)
The copolymer, abbreviated as C12C18O5X(18%), was prepared by heating 0.81g
(0.0025mol) 5- dodecyloxybenzene -1, 3-dimethanol, 1.02g (0.0025mol) 5octadecyloxybenzene -1, 3-dimethanol, 1.16g (0.005mol) tetraethylene glycol
dichloride, 2.24g (0.04mol) potassium hydroxide and 2.24g potassium carbonate in
30ml dimethyl sulphoxide for 7 days with gentle stirring at 90C under nitrogen
atmosphere. The polymer was precipitated in water and the mixture was neutralized
by addition of concentrated acetic acid and extracted into chloroform. After
evaporation of the chloroform, the residue was washed with hot water several times to
remove inorganic salt and finally with hot methanol several times to remove the
monomer. The product is pale brown. 1H NMR H(400MHz; solvent CDCl3; standard
SiMe4) 0.86 (3H, t, CH3), 1.25 (23H, s, 11.5CH2), 1.45 (2H, m, -CH2), 1.75 (2H, m,
-CH2), 3.65 (3H, t (broad), CH2 ethoxy), 3.92 (2H, t, -CH2), 4.45 (2H, s, CH2
benzyl), 6.85 (3H, m, C6H3 aromatic). 1H NMR results suggest 15.5 side chain -CH2which is consistent with an equimolar mixture of -C12H25 and -C18H37 side chains. The
results also show that the molar proportion of the tetraethoxy segments (= 3.65ppm)
is only ca. 18% of the side chain groups and the 2 main chain benzylic -hydrogens
are only 50% of the expected 4 hydrogens. The FTIR spectrum shows a medium ester
C=O band at 1720 cm-1 indicating that the polymer C12C18O5X(18%) is an etherester. GPC gave molar mass averages <Mn> = 2,614, <Mw> = 52,541 and <Mz> =
1,069,798.
Synthesis of 1,3-bis (bromomethyl) -5- hexadecyl -oxybenzene (ii)
Supplementary Material for Faraday Discussions
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2004
Under a dry atmosphere, 5 g(13.2mmol) of 5- hexadecyloxybenzene -1, 3dimethanol (i) was suspended in 20 ml dry diethyl ether and cooled to 0°C with
stirring. Into the suspension, 3.18g(11.7mmol) of phosphorous tribromide was added
dropwise whilst keeping the temperature of the mixture below 5°C. After completion
of the addition, the solution was stirred for 10 hours at room temperature, and then
refluxed for 12 hours. The reaction mixture was then poured into a crushed ice bath.
The organic solid was washed with a 10% aqueous sodium carbonate and then with
water. The product was extracted into diethyl ether and the solution was dried over
MgSO4. The solvent was evaporated to yield 6.3g white crystals, m.p. 68C. 1H NMR
H(400MHz; solvent CDCl3; standard SiMe4) 0.86 (3H, t, CH3), 1.25 (24H, s, 12
CH2), 1.43 (2H, m, -CH2), 1.76 (2H, m, -CH2), 3.98 (2H, t, -CH2), 4.70 (4H, d, 2
-CH2 benzyl ), 6.87 (2H, s, 2H aromatic). 6.96 (1H, s, H aromatic). Elemental
analysis: Br, required 31.68%, found 31.49%. IR: 3050cm-1, 2849cm-1, 1600cm-1,
1590cm-1, 1500cm-1, 680cm-1.
Synthesis of poly{[2,5,8,11,14-pentaoxapentadecamethylene(5-hexadecyloxy-1,3phenylene)]0.75 - co- [ 2-oxatrimethylene(5-hexadecyloxy-1,3-phenylene)]0.25,
}C16O5 (75%) ( method Y)
The polymer C16O5(75%) was prepared by heating 1g (0.002mol) of bis-1,3(bromomethyl) -5- hexadecyloxybenzene (ii), 0.385g (0.002mol) tetraethylene glycol,
and 0.89g (0.016 mol) potassium hydroxide in 2ml dimethyl sulphoxide for 5 hours
with gentle stirring at 30 ~ 60C. The polymer was precipitated in water and the
mixture was neutralized by addition of concentrated acetic acid. The polymer was
separated and washed with hot water several times to remove inorganic salt and
finally with hot methanol several times to remove monomer. The product was pale
yellow. The yield was 0.45g (42%). 1H NMR H(400MHz; solvent CDCl3; standard
SiMe4) 0.86 (3H, t, CH3), 1.25 (24H, s, 12CH2), 1.45 (2H, m, -CH2), 1.75 (2H, m, CH2), 3.65 (12H, m, 6CH2 ethoxy), 3.92 (2H, t, -CH2), 4.45 (4H, s, -CH2 benzyl),
6.85 (3H, m, C6H3 aromatic). The 1H NMR shows that molar proportion of
tetraethoxy segments (= 3.65ppm) is 75% of the molar equivalent of side chain
groups. However, the full compliment of 4 benzyl hydrogens suggests that the main
chain structure is entirely polyether. GPC molar mass averages Mn = 9,335, Mw =
61,305, Mz = 260,113. The DSC of C16O5(75%) indicates that the polymer melts at
28.30C.
Synthesis of poly{[2,5,8,11,14-pentaoxapentadecamethylene(5-hexadecyloxy-1,3phenylene)]0.40
co[
2-oxatrimethylene(5-hexadecyloxy-1,3phenylene)]0.60}C16O5 (40%) (method Y)
The polymer C16O5(40%) was prepared by heating with gentle stirring at 50 ~ 60C
of 1g (0.002mol) 1, 3-bis (dibromomethyl) -5- hexadecyloxybenzene, 0.2888g
(0.0015mol) tetraethylene glycol, 0.1876g (0.0005 mol) 5-hexadecyloxy benzene-1,3dimethanol and 0.44g (0.008mol) potassium hydroxide in 1ml dimethyl sulphoxide
and 1 ml tetrahydrofuran (THF) for 3days. The polymer was precipitated in water and
the product isolated using the same procedure as above. The product is white. 1H
NMR spectrum was identical to that above with the exception of the peak at 3.63
ppm (6.5H, m, 3.3 CH2 ethoxy), corresponding to 40% tetraethoxy segments in the
Supplementary Material for Faraday Discussions
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2004
polymer backbone. GPC gave molar mass averages Mn = 7,176, Mw = 14,194, Mz =
24,089. DSC indicates that the polymer melts at 35.76C.
Synthesis of poly[2,5,8,11,14-pentaoxapentadecamethylene(5-hexadecyloxy-1,3phenylene)] C16O5(100%) (method Y)
The polymer C16O5(100%) was prepared by heating with gentle stirring at 50
~ 60C 1g (0.002mol) 1, 3-bis (dibromomethyl) -5- hexadecyloxybenzene, (ii) 0.385g
(0.002mol) tetraethylene glycol, and 0.44g (0.008mol) potassium hydroxide in 1ml
dimethyl sulphoxide and 1 ml tetrahydrofuran (THF) for 3 hrs. The polymer was
precipitated in water. The mixture was neutralized by addition of concentrated acetic
acid. The polymer was separated and washed with hot water (T >50C) several times
to remove inorganic salt and finally with hot methanol several times to remove
monomer. The product is white. 1H NMR: H(400MHz; solvent CDCl3; standard
SiMe4) 0.86 (3H, t, CH3), 1.25 (25H, s, 12CH2), 1.45 (2H, m, -CH2), 1.75 (2H, m,
-CH2), 3.65 (16H, m, 8CH2 ethoxy), 3.92 (2H, t, -CH2), 4.45 (4H, s, -CH2,
benzyl), 6.85 (3H, m, C6H3aromatic). GPC gave molar mass averages Mn = 15,753,
Mw = 37,992, Mz = 77,258. DSC of C16O5 indicates that the polymer melts at
22.89C.
Synthesis
of
poly[2,5,8,11-tetraoxadodecamethylene(5-hexadecyloxy-1,3phenylene] (C16O4(100%) (method Y)
The polymer C16O4(100%) was prepared as above but the molar equivalent
of triethylene glycol was used. The yield is (75%). 1H NMR: H(400MHz; solvent
CDCl3; standard SiMe4) 0.86 (3H, t, CH3), 1.25 (24H, s, 12CH2), 1.45 (2H, m, CH2), 1.75 (2H, m, -CH2), 3.65 (12H, m, 6CH2 ethoxy), 3.92 (2H, t, -CH2), 4.45
(4H, s, -CH2, benzyl), 6.85 (3H, m, C6H3aromatic). GPC: molar mass averages Mn =
8,369, Mw = 21,555, Mz = 39,720. DSC of C16O4 indicates that the polymer melts at
28.07C.
Synthesis of poly[2,5,8,-trioxanonamethylene(5-hexadecyloxy-1,3-phenylene,
C16O3(100%) (method Y)
The polymer C16O3(100%) was prepared as above but the molar equivalent
of diethylene glycol, was used. The yield was 79%. 1H NMR: H(400MHz; solvent
CDCl3; standard SiMe4) 0.86 (3H, t, CH3), 1.25 (25H, s, 12CH2), 1.45 (2H, m, CH2), 1.75 (2H, m, -CH2), 3.65 (8H, m, 4 CH2 ethoxy), 3.92 (2H, t, -CH2), 4.45
(4H, s, -CH2, benzyl), 6.85 (3H, m, C6H3aromatic). GPC molar mass averages Mn =
8,174, Mw = 17,409, Mz = 29,000. DSC of C16O3 indicates that the polymer melts at
32.53C.
Synthesis
of
poly[2,5-dioxahexamethylene(5-hexadecyloxy-1,3-phenylene,
C16O2(100%) (method Y)
The polymer C16O2(100%) was prepared as above but the molar equivalent of
ethylene glycol was used. The yield was 64%. 1H NMR: H(400MHz; solvent CDCl3;
standard SiMe4) 0.86 (3H, t, CH3), 1.25 (25H, s, 12CH2), 1.45 (2H, m, -CH2), 1.75
(2H, m, -CH2), 3.65 (4H, m, 2 CH2 ethoxy), 3.92 (2H, t, -CH2), 4.45 (4H, s, -
Supplementary Material for Faraday Discussions
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2004
CH2, benzyl), 6.85 (3H, m, C6H3aromatic). GPC molar mass averages Mn = 9,110, Mw
= 74,063, Mz = 284,061. DSC of C16O2 indicates that the polymer melts at 37.76C.
Synthesis of poly[ 2-oxatrimethylene(5-hexadecyloxy-1,3-phenylene)] (C16O1)
(method Y)
The polymer C16O1 was prepared as above but the glycol was replaced by the
molar equivalent of 5- hexadecyloxybenzene -1, 3-dimethanol (i). The product is
white and the yield was 63%. 1H NMR: H(400MHz; solvent CDCl3; standard SiMe4)
0.86 (3H, t, CH3), 1.25 (25H, s, 12CH2), 1.45 (2H, m, -CH2), 1.75 (2H, m, -CH2),
3.92 (2H, t, -CH2), 4.45 (4H, s, -CH2, benzyl), 6.85 (3H, m, C6H3aromatic). GPC
molar mass averages Mn = 4,272, Mw = 10,594, Mz = 17,510. DSC of C16O1
indicates that the polymer melts at 40.92C.
Synthesis of C16O1X (method X)
The polymer C16O1X was prepared by heating with gentle stirring at 60C of
1.00g (0.00264mol) 5- hexadecyloxybenzene -1, 3-dimethanol, and 3g (0.04mol)
potassium hydroxide in 5ml dimethyl sulphoxide for 7 days. The polymer was
precipitated in water; the mixture was neutralized by addition of concentrated acetic
acid and extracted into chloroform. After evaporation of the chloroform, the residue
was washed with hot water several times to remove inorganic salt and finally with hot
methanol several times to remove the monomer. 1H NMR: H(400MHz; solvent
CDCl3; standard SiMe4) 0.86 (3H, t, CH3), 1.25 (25H, s, 12CH2), 1.45 (2H, m, CH2), 1.75 (2H, m, -CH2), 3.92 (2H, t, -CH2), 4.45 – 4.9 (2H, s, -CH2, benzyl),
6.85 – 7.8 (3H, m, C6H3aromatic). FTIR showed a strong band at 1720 cm-1. GPC
molar mass average Mw =10,000. DSC of C16O1X indicates that the polymer melts at
42C.
Synthesis of polymer II (PTHFC12)
Polymer II (PTHFC12) was prepared by standard Williamson condensation of
hydroxy-terminated polytetrahydrofuran (Mn = 1688 g mol-1) with 1,12dibromododecane and excess powdered KOH (8 molar ratio) at 90oC. Polymer II
(PTHFC12) was purified by washing with dilute aqueous acetic acid followed by
water and dried under vacuum. The GPC result gave molar mass averages M w =
39,000. DSC of PTHFC12 indicates that the solution deposited polymer melts at 30C
whereas melt-recrystallised polymer melts at 24C.
Synthesis of ‘polymer’ III (DC18PTHF)
Polymer III (DC18PTHF) was prepared by standard Williamson condensation of
8.44g (0.005mol) hydroxy-terminated polytetrahydrofuran (Mn = 1688 g mol-1 ) with
3.33g (0.005mol) 1-bromododecane and excess powdered (8 molar ratio) 2.24g KOH
in 40ml dimethyl sulphoxide for 7 days at 90oC. Polymer III (DC18PTHF) was
purified by washing with dilute aqueous acetic acid followed by water and dried
under vacuum. 1H NMR: H(400MHz; solvent CDCl3; standard SiMe4) 0.86 (13H, t,
CH3), 1.25 (127H, s, 32 CH2), 1.6 (140H, m, 68 -CH2 butoxy, 2-CH2 ), 1.75 (2H,
m, -CH2), 3.4 (137H, t, 68 -CH2 butoxy), 3.6 (5H, s, 2 CH2). GPC molar mass
averages Mn = 3,250, Mw = 4724, Mz = 6,599. Polydispersity is 1.45. DSC of
DC18PTHF indicates that the polymer melts over the range 10 - 35C.
Supplementary Material for Faraday Discussions
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2004
Molecular Dynamics modelling using Cerius2 software
C16O5 (Polymer I) – Li salt complexes
anions
Lithium ions
End view
-
40 - 45Å
Side view
Modelling by G. Ungar
C16O1 :Li salt complex
33Å
C16O1 : LiBF4 (2 :1) dark grey spheres, carbon; light grey spheres, hydrogen; red,
oxygen; pink, lithium; purple, boron; green, fluorine. (atomic radii are not to scale)