Eng_Civil_Al-Shamrani, M.
advertisement

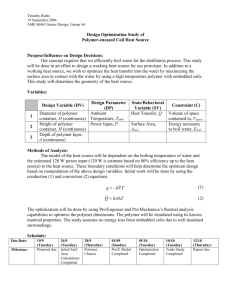
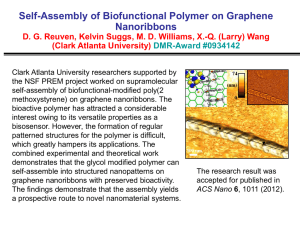
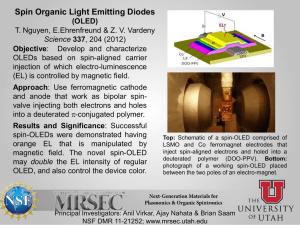
Eng-CE- Al-Shamrani, M. 3 Title General analytical concept and design methodology to producing a clay-based polymer nanocomposite Author-s Contact lnfo El-Sheikhy, R.A., Al-Shamrani, M.A. Prof. Mosleh A. Al-Shamrani Geotechnical Engineering College of Engineering Dept. of Civil Engineering Office: 2A54 shamrani@ksu.edu.sa P.O. Box 800 Riyadh Saudi Arabia Department Major citation Civil Engineering Department Soil -structure interactions, Computational geomechanics Year of Publication Publisher Sponsor Type of Publication ISSN 2010 Ceramic Transactions Volume 219, 2010, Pages 165-174 Book series 10421122 URI/DOI Full Text (Yes,No) Key words Yes Bonding process; Clay platelets; Commercial applications; Design Methodology; Environmentally-friendly; Fiber distribution; Fiber orientations; High aspect ratio; Interfacial bond strength; Large surface area; Low costs; Material preparation; Matrix materials; Methods of analysis; Nano clays; Nano-materials; Nanocomposite materials; Natural properties; New approaches; New mechanisms; Polymer nanocomposite; Reinforcing materials; Voids and inclusions Abstract area, clay platelets are very convenient filler and reinforcing materials in matrix materials such as polymers to produce advanced nano-composites with unique properties. Claybased polymer nano-composites can have new and different properties that make them suitable for many different industrial and commercial applications, such as in automotive, medicine, electronics, sensors, construction, packaging, coatings, drugs, biomedical engineering, and others. Production of these nano-composite materials involves several steps of material preparation, mixing, and processing. Basically, the design of these nanocomposites depends on a simple concept and the mechanism of strengthening a material with weak properties by adding a small amount of another material with strong properties. Reinforcing the main material (polymer) with a certain ratio (5%- 15%) of filler (nano-clay), will transform the polymer into an advanced functional material. The morphology, characterization, and analysis of these materials are based on that concept. There have been problems and difficulties in manufacturing these nano-composites. In the current study, a new point of view is taken involving a new concept, a new mechanism, new techniques for mixing and processing, and new methods of analysis and characterization. This study utilizes a new approach to understand and control the interfacial bond strength between the clay nano-fibers and the polymer, voids and inclusions, the de-bonding process between the fibers and the polymer, fiber orientation, fiber distribution and intensity, fracture, and cracks. This study uses natural Saudi nano-clay and polymers to solve the problems and difficulties with clay/polymer nano-composites that previous studies encountered.