Big Idea - Moore Public Schools
advertisement

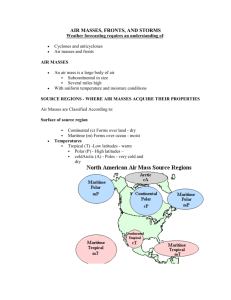
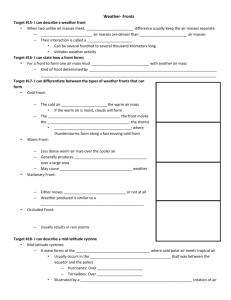
Section 15.1 Air Masses and Fronts 5. It may take ____________ or ___________ for changes to spread thru the entire air mass. 1. What are the characteristics of an Air Mass? 6. Weather changes where air masses meet. When a cold, dense air mass pushes warmer air it is a ____________ front. Cold fronts can move It is a large _______________. It is ______________ than other types of fronts. It often produces tall __________________________ clouds and Temperature and humidity are ______________. After the storms the air is cooler and ______________. 7. When a warm air mass pushes colder air it is a ______________ front. It moves _______________. Warm air moves up and over dense, colder air which produce ________-____________ skies. When the warm front An air mass can cover approaches first you see high ___________ clouds then high ___________ clouds. Warm fronts bring hours of steady ___________ or ___________. 8. Continental Fronts form over ______ _______. Maritime Fronts form over _________. __________________ fronts occur when air masses first meet or _______ moving. Clouds may cover the sky for ______________. 9. From page 503 which city will the cold front affect next?_______________ 10. Suppose you heard that a front was approaching your town. What type of weather would you expect? ______________________________________ 2. Air Mass categories _____________________________________________________________ st 1 word describes ____________________ 2nd word describes ____________________ 11. High and Low Pressure Systems At a ________ pressure center, air sinks slowly down and spreads out toward areas of ___________ pressure. Most high pressure systems are __________ and change Tropical Masses form near the ___________. Polar Masses form far ___________________. ____________. Most weather from a high pressure system is _________ and ______________. 12. A _______ pressure system’s air moves upward to ___________ altitudes. 3. 4. The Latin prefix “mare” as is the word marine, means ___________. Movement of an Air Mass When a continental polar air mass moves over warm water, the air slowly becomes ___________ and gains ___________________. As the air moves higher it also moves ____________. This movement usually produces _____________ weather. 13. Fronts and Weather Draw the symbol for each type of front based on the 1. picture on page 503. front: ________ 15.2 front: _________ front: _________ Low Pressure and Storms Hurricanes form over warm ocean water. Compare and contrast tropical storms and hurricanes by filling in the chart. Tropical Storms Hurricanes Wind speed Forms where? Gets energy from? 14. In which state(s) is the warm front?_____________________________ . 2. Draw a diagram of a hurricane and label its parts. 3. From the picture on p. 508 how does the size of the hurricane compare to What direction is it traveling from? ____________ 15. In which state(s) is the cold front?_____________________________ What direction is it traveling from? ____________ 16. In which state(s) is the stationary front?___________________________ What direction is it traveling from? ____________ the size of Florida? ____________________________________________ 4. Describe the path of the center of the storm. It began in the __________ Ocean, moved ________________________ toward Florida. It then headed _____________ following the ______________ coast. 5. 6. Why do hurricanes strike the eastern United States most often between August and October? ___________________________________________________________ Where does a hurricane gain its energy. __________________________ ___________________________________________________________ 7. Where does a hurricane lose its energy. __________________________ ___________________________________________________________ 8. List things you can do to prepare for a hurricane while on vacation. _____________________________________________________________ 15.3 Vertical Air can cause severe storms. 1. Fill in the concept web below about thunderstorms. 2. A funnel is not called a tornado until _____________________________. 3. List three effects of a large tornado. ____________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ 9. Effects of Hurricanes Complete the cause-and-effect diagram. Effect Cause Hurricane 10. 10 POINTS EXTRA CREDIT – Name a hurricane, the year, and location that was a category 5 when it made landfall in the United States. _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ 11. Complete the chart. Write yes, no, or maybe for each type of winter storm. Blizzard Lake-effect snowstorm Ice storm Snow Ice Strong winds Very cold __________________________ 4. List things you can do to prepare for a tornado. _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ 12. List things you can do to prepare for a Winter storm. _____________________________________________________________ ____________________________ _____________________________________________________________ 5. What is the difference between a Tornado WATCH and a WARNING? _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ 6. Fill in the table about tornadoes. Use R64 to determine strength of tornados. F 2. Which two of these sources report conditions for wide areas? __________________________ ____________________________ 3. Which technology provides data for one place? ____________________ Characteristics Most common tornadoes 4. WEATHER MAP Use the p R61 in the appendix and tell what each of the 4 station symbols are for 1) cloud cover,2) temperature, 3) wind and About 20 percent of tornadoes 4) where each is located, approximately. (Weather map on p 520) About 1 percent of tornadoes DATA STA 1 STA 2 STA 3 STA 4 Cloud cover 7. With your lab partner, brain storm a list of items that you may need for your tornado shelter. _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ 15.4 Weather Forecasting 1. Look at the picture on page 519 in your textbook. Label each box with a source of weather data. Temperature Wind Location 5. H represents _______ __________________ L represents __________ ____________________________ 6. What do the colored patches mean? _____________________ 7. If two places are on the same isobar, what do you know about their weather? _____________________________________ 8. Iso means ____________ bar means ____________________ 9. Satellite Images and Special Maps Why are infrared satellite images useful? ____________________________________ 10. Forecasters use computer models to predict weather. List two ways that meteorologists use computers when forecasting the weather. ________________________________________________ ________________________________________________ 11. Which are more accurate, short or long-range forecasts? Why? _________________________________________ The map below shows isobars around two different air systems. Use what you know about weather maps to answer the questions that follow. ________________________________________________ 12. Predict the weather prediction for each set of conditions. Conditions Prediction A cold front is moving into an area that has warm, moist air. A warm front is moving into an area that has cold, dense air. A cool sea breeze is blowing inland, causing warm, humid air to rise. Air pressure is falling and the temperature is rising. Air pressure is increasing and the temperature is steady. A thunderstorm is developing spinning winds at its center A low-pressure center is over the Atlantic Ocean where the water temperature is above 27ºC (81ºF). Cold air is pushing warm air where the air is 2ºC (36ºF) and the ground is -3ºC (27ºF). 13. What kind of pressure system is indicated at 1? _______________ 14. Does the air here move upward or downward? _______________ 15. What kind of pressure system is indicated at 2? _______________ 16. Does the air here move upward or downward? _______________ Turn to page 529 and answer the questions about the Map. 1. _____________ 4. _____________ 2. _____________ 5. _____________ 3. _____________ 6. _____________ 7. __________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________ 8. Do you think scientists should work to control the weather, or is it better to let nature take its course? Why? _____________________________ _____________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________