Rendell - Genetics
advertisement

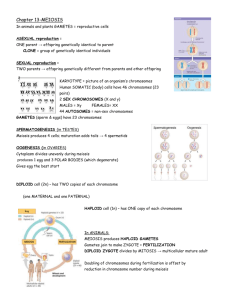
Rendell/Walz Period 2 Chapter 6 Introduction to Genetics Key Words Heredity Notes Set of characteristics an organism receives from its parents. Genetics Study of heredity. Gregor Mendel Pioneer of genetics Traits Characteristic that distinguishes one individual from another. Hybrid P generation Offspring of parents with different characteristics. F1 generation (F = filusson ) Parentis of the parent F1 generation First generation of offspring from the P generation F2 generation Second generation which is produced when the F1 generation are crossed among themselves. Gene Unit that determines traits. Alleles Different forms of a gene. Dominant allele Form of allele that is expressed. Recessive allele Form of allele that is not expressed. Phenotype Form of trait that it displays (physical appearance). Genotype Genetic composition of organism. Homozygous Organisms with identical pair of alleles, ex. TT or tt . Heterozygous Organisms with mixed pair of alleles, ex. Tt. Segregation Process that separates the two alleles of gene. Independent assortment Genes that segregate independently, ex. Genes for seed shape and color do not influence each other’s inheritance. Notes Key Words Gametes Reproductive cell Contain half the number of chromosomes (one set) Human cells 46 chromosomes Human gametes (sperm and egg cells) 23 chromosomes Haploid cell Diploid cell Contains only one set of chromosomes (n). Contains a double set of chromosomes (2n). Meiosis Process of cell division. Number of chromosomes in a diploid cell is reduced by half. End products Four haploid cells Meiosis I Meiosis II Meiosis I 1. Each chromosome is replicated. Duplicate chromatids are formed. Chromatids are joined at centromeres. 2. Prophase I - like prophase of mitosis. Chromosomes uncoil. Spindle apparatus forms. Crossing over 3. Metaphase I homologous chromosomes (corresponding chromosomes) pair together. Chromosomes line up in center of cell. Paired chromosomes form structures called tetrads. Independent Assortment occurs here 4. Anaphase I Homologous chromosomes are pulled toward opposite sides of cell. 5. End products of meiosis I two haploid (n) daughter cells. Meiosis II Two daughter cells undergo a second round of cell division. 1. Metaphase II Chromosomes line up as in metaphase of mitosis. 2. End products of meiosis II four haploid cells. Crossing Over Switches alleles from one chromosome to another. Probability and Genetics Probability applies to genetics because formation of gametes depends on random events. Notes Key Words Incomplete Dominance Heterozygote phenotype is somewhere between the two homozygous phenotypes. Example: (RR) x (rr) (Rr) Red x white pink Codominance Both alleles affect phenotype. Example: roan horses have 2 colors in their coats. Multiple Alleles Genes with more than two alleles. Example: genes for blood group and eye color. Polygenic Traits Traits controlled by more than one gene. Answer the Following 1. _____ What type of allele is always expressed? a. dominant allele c. recessive allele 2. b. homologous allele d. incomplete allele _____In pea plants, the tallness or shortness is known as a. genotype c. dominance 3. _____ The haploid number of chromosomes for a human is a. 23 4. b. phenotype d. gametes b. 26 c. 46 d. 92 _____ Cells that contain only a single set of chromosomes are a. homologous c. diploid b. haploid d. heterozygous 5. _____ Which process reduces the number of chromosomes in a diploid cell by half to produce gametes? a. mitosis b. codominance c. crossing-over d. meiosis 6. _____An identical pair of alleles for a trait(TT or tt) has what type of genotype? a. homologous b. homozygous c. heterozygous d. segregation 7. _____ Crossing different true-breeding(purebred) stocks produces offspring called a. P generation b. 8. a. traits 9. F2 generation c. cross-overs d. hybrids _____ The different forms of a gene are called b. alleles c. gametes d. hybrids _____Crossing over is the exchange of genetic information between a. reproductive cells c. any 2 chromosomes b. diploid cells d. homologous chromosomes 10. In a pea plant, axial flower position is dominant over terminal flower position. What genotype and phenotype ratios will result if a heterozygous axial pea plant is crossed with a pea plant with terminal flowers? (Show work) 11. During metaphase I of meiosis, homologous chromosomes line up at the equator of a cell. A) Diagram this in a cell with four chromosomes. B) Label: chromosome, chromatid, spindle fiber, pole, centromere, tetrad C) Explain what happens next. 12. 13. A female horse that is pure black and a pure trotter is crossed with a male horse that is hybrid for both traits. A) What are the genotypes of the parents? B) What gametes are produced by each of the parents? C) Draw a Punnet square representing this cross. D) What are the genotypic and phenotypic ratios that result? Genotype: Phenotype: During which phase(s), does following occur? Write the correct answer on the line provided. For some, there may be more than one answer. S phase of Interphase Metaphse II Prophase I Anaphase I Prophase II Anaphase II Metaphase I Telophase I Telophase II 1. __________ The chromosomes line up as a tetrad at the equator. 2. __________ The chromosomes move to the poles. 3. __________ The spindle fiber shortens. 4.__________ DNA synthesis occurs. 5. __________Homologous chromosomes pair up at the equator. 6. __________The cell membrane pinches forward. 7. __________ The sister chromatids divide and move apart. 8.__________Chromosomes lined up at the equator is not in a tetrad. 9.__________ Homologous chromosomes BEGIN to pair up. 10.__________ Sister chromatids, still joined, move toward the poles.