Chapter 4- Aqueous Reactions
advertisement

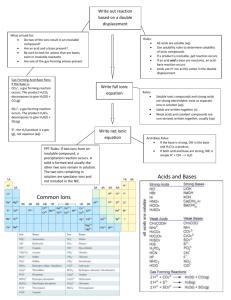
AQUEOUS REACTIONS A solution is a homogeneous mixture of two or more substances. All aqueous solutions can be classified in terms their ability to conduct electricity. If a substance forms ions in solution, it is an electrolyte and will conduct electricity. Ie. NaCl If a substance does not form ions in solution, it is a nonelectrolyte and does not conduct electricity.Ie. sugar Compounds whose aqueous solutions conduct electricity well are strong electrolytes. Compounds whose solutions conduct electricity poorly are weak electrolytes. Exchange (metathesis) reactions involve the exchange of ions in solution. Ionic equations: 2KI(aq)+Pb(NO3)2(aq)PbI2(s)+2KNO3(aq) Both potassium iodide and lead nitrate are colorless solutions. When mixed they form lead iodide, a yellow precipitate. The molecular equation lists all species in their molecular form The complete ionic equation lists all strong soluble electrolytes as ions:Pb2+(aq)+2NO3-(aq)+2K+(aq)+2I(aq)PbI2(s)+2K+(aq)+2NO3-(aq) The net ionic equation lists only those ions not common on both sides of the reaction:Pb2+(aq)+2I-(aq)PbI2(s) The spectator ions that are present in the solution , but play no direct role in the reaction are eliminated in the net equation. Acids are substances that ionize in aqueous solutions to form H+. Acids are proton donors. Bases are proton acceptors. Bases react with the H+ to form water. Strong acids and bases are strong electrolytes. They ionize completely in solution. Strong bases include Group1A metal hydroxides, Ca(OH)2, Ba(OH)2, and Sr(OH)2 Strong acids include HCl, HBr, HI, HClO3, H2SO4, and HNO3 Weak acids and weak bases are weak electrolytes. They partially ionize in solution. A neutralization reaction occurs when an acid and base react. The result is the formation of a salt and water Acids react with carbonates and hydrogen carbonates to form carbon dioxide and water H+(aq)+ HCO3-(aq)H2O(l)+CO2(g) Reaction of sulfides with acid generate hydrogen sulfide 2H+(aq)+S2+(aq)H2S(g) When a substance loses electrons, it undergoes oxidation(OIL): Ca(s)+2H+(aq)Ca2+(aq)+H2(g). When a substance gains electrons, it undergoes reduction(RIG): 2Ca(s)+O2(g)2CaO(s) The reaction of a metal with an acid or a metal salt is called a displacement reaction: A+BXAX+B It is common for metals to produce hydrogen gas when they react with acids. Mg(s)+2HClMgCl2(aq)+H2(g) molecular Mg(s)+2H+Mg2+(aq)+ H2(g) net ionic The metal is oxidized and the H+is reduced. It is possible for metals to be oxidized in the presence of a salt:Fe(s)+Ni(NO3)2(aq)Fe(NO3)2(aq)+Ni(s) molecular Fe(s)+ Ni2+(aq)Fe2+(aq)+Ni(s) net ionic In this case, iron is oxidized and nickel is reduced. If one substance is oxidized, another substance must be reduced. Molarity=moles of solute/liters of solution When an ionic compound dissolves, the relative concentration of ions depends on the chemical formula For 1M NaCl, the solution is 1M in Na+ ; 1M in Cl For 1M Na2SO4, the solution is 2M in Na+; 1M in SO4 When making dilutions, MinitialVinitial=MfinalVfinal