ICEL Factors to Consider for Hypothesis Generation
advertisement

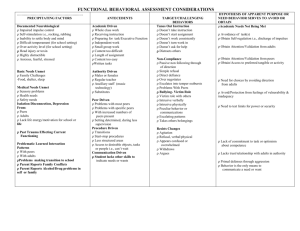
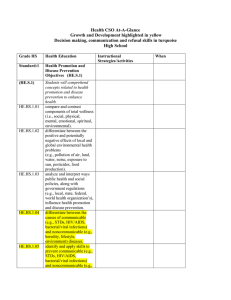
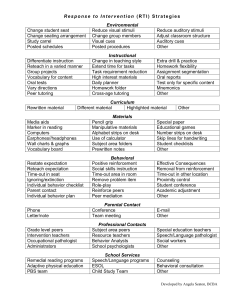
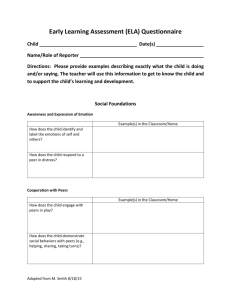
ICEL Factors to Consider for Hypothesis Generation Remember Focus on Alterable Hypotheses First To Change Student Behavior you Must Change Adult Behavior Instruction (I) • Instructional approach or method(s) e.g., instruction presented in a way that relates to child’s weaknesses (e.g., lecture/auditory etc.) • Expectations/objectives • Clarity of instruction . Organization of instruction • Pace (instruction presented too fast for student’s learning rate) • Opportunities for practice (insufficient opportunity to practice skills, lack of teacher guided practice) • Duration of continuous instruction (length of instruction/assignments too long for attention/concentration skills of the student) • Nature & frequency of feedback (e.g., feedback to student not frequent enough) • Academic engaged time • Classroom Management . Expectations too high for the skills of the student (e.g., reinforcers at the end of the week, student needs daily). . Rate of reinforcement too low for student needs .Other??? Curriculum (C) Philosophy of the curriculum presented (e.g., too narrow such as phonics only) Content of materials • Difficulty level of materials (too easy or too difficult) • Sequencing • Organization • Perceived relevance (curriculum not relevant to child’s experiences/understanding . Other? Environment (E) . Arrangement of the room (e.g., student and teacher physically too far apart, student too close to peers, student near window or distractions etc.) . Temperature • Furniture/equipment • Rules (rules/expectations in class/building far exceed skills of the student to be successful) . Level of supervision (frequency/rate) too low for student needs, too many areas in the building that are not supervised adequately) • Management plans (e.g., inconsistent discipline programs/philosophies/differences between staff who interact with the same student) • Routines (Schedule of daily activities) • Expectations • Peer context-Peers reinforce inappropriate behavior; Peers do not provide appropriate/adequate models); Social/Academic skills of peers significantly higher (lower) than student; Peers taunt/instigate student to engage in inappropriate behavior; Expectations/values of peer group influence student • Peer (e.g., attention) . Task pressure . Bus ride (length, problems on the bus carry over to school, etc.) . Family/Neighborhood/Community Characteristics/Conditions including different values/expectations between home and school; parent discipline inadequate/too severe/teaches child aggression; lack of or low levels of supervision; parent academic skills too low to assist their child; reading and related behaviors do not occur in the home; parent difficulties (substance abuse etc.) result in inconsistent parenting, low levels of supervision, negativity; parent unwilling or unable to reinforce school-related academic/behavioral strategies in the home; Parent permits the child to be around inappropriate adults/peers in the community; parent expectations too high for child/too much pressure; parent unwilling/unable to meet health/nutrition/basic needs of the child resulting in absences, inability of the child to concentrate on tasks, tardiness etc. Other?? Learner (Last Area to Consider) (L) • Perception of learning environment • Academic skills (e.g., lacks prerequisite skills for task) • Attributions (beliefs-others out to get me, parents do not want me to do well in school, I expect to fail, if I do not fight first then I will be hurt, my parents want me to fight back, etc.) . Social Skills (e.g., ability to initiate contact, play behaviors) • Adaptive behavior skills (e.g., self-help,) • Motivation . Organization . Adequate short and long term memory (auditory and visual) . length of attention span . Self-monitoring skills . Impulsivity (inability to delay long enough to think/behave) . Inability to integrate visual/motor/auditory tasks . Other social/behavioral skills . Health Areas including: Hearing, motor, vision skills; Specific health conditions related to problem behaviors/academic concerns; Side effects of medication; Speech/language difficulties; Fatigue results in higher activity and less ability to focus etc., Medication cycle not appropriate for school day/activities; . Excessive absences . Language other than English