FUNCTIONAL BEHAVIORAL ASSESSMENT CONSIDERATIONS
advertisement
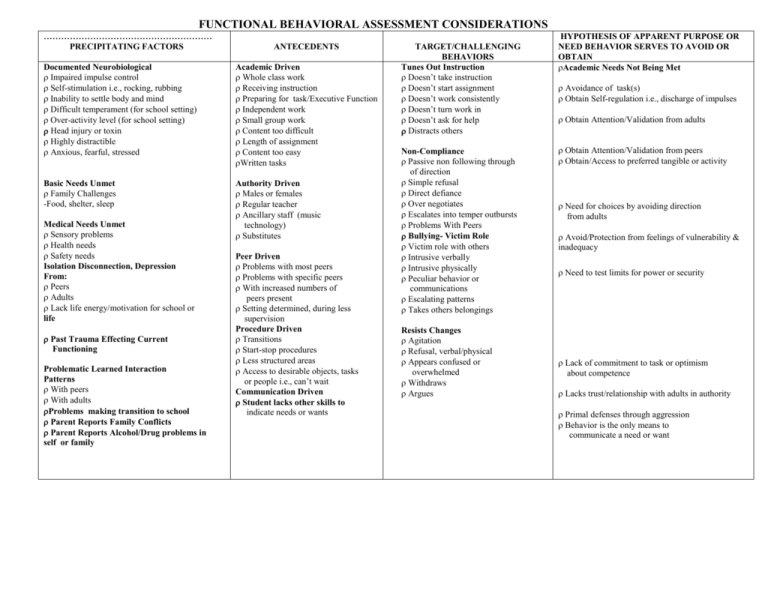
FUNCTIONAL BEHAVIORAL ASSESSMENT CONSIDERATIONS ...................................................................................................................................................................... PRECIPITATING FACTORS ANTECEDENTS Documented Neurobiological Impaired impulse control Self-stimulation i.e., rocking, rubbing Inability to settle body and mind Difficult temperament (for school setting) Over-activity level (for school setting) Head injury or toxin Highly distractible Anxious, fearful, stressed Academic Driven Whole class work Receiving instruction Preparing for task/Executive Function Independent work Small group work Content too difficult Length of assignment Content too easy Written tasks Basic Needs Unmet Family Challenges -Food, shelter, sleep Authority Driven Males or females Regular teacher Ancillary staff (music technology) Substitutes Medical Needs Unmet Sensory problems Health needs Safety needs Isolation Disconnection, Depression From: Peers Adults Lack life energy/motivation for school or life Past Trauma Effecting Current Functioning Problematic Learned Interaction Patterns With peers With adults Problems making transition to school Parent Reports Family Conflicts Parent Reports Alcohol/Drug problems in self or family Peer Driven Problems with most peers Problems with specific peers With increased numbers of peers present Setting determined, during less supervision Procedure Driven Transitions Start-stop procedures Less structured areas Access to desirable objects, tasks or people i.e., can’t wait Communication Driven Student lacks other skills to indicate needs or wants TARGET/CHALLENGING BEHAVIORS Tunes Out Instruction Doesn’t take instruction Doesn’t start assignment Doesn’t work consistently Doesn’t turn work in Doesn’t ask for help Distracts others Non-Compliance Passive non following through of direction Simple refusal Direct defiance Over negotiates Escalates into temper outbursts Problems With Peers Bullying- Victim Role Victim role with others Intrusive verbally Intrusive physically Peculiar behavior or communications Escalating patterns Takes others belongings Resists Changes Agitation Refusal, verbal/physical Appears confused or overwhelmed Withdraws Argues HYPOTHESIS OF APPARENT PURPOSE OR NEED BEHAVIOR SERVES TO AVOID OR OBTAIN Academic Needs Not Being Met Avoidance of task(s) Obtain Self-regulation i.e., discharge of impulses Obtain Attention/Validation from adults Obtain Attention/Validation from peers Obtain/Access to preferred tangible or activity Need for choices by avoiding direction from adults Avoid/Protection from feelings of vulnerability & inadequacy Need to test limits for power or security Lack of commitment to task or optimism about competence Lacks trust/relationship with adults in authority Primal defenses through aggression Behavior is the only means to communicate a need or want PRECIPITATING FACTORS --Interventions Neurobiological Involve family to obtain developmental history MD appointment with specific concerns communicated Assess with family for community services Basic needs unmet Connect with family to offer community “Strength Based” assistance YST or Community staffing team Medical/Sensory Facilitate referral to MD Utilize district nurse Trauma Facilitate services of trauma specialist Reassure safety frequently Modify settings to insure sense of safety Coordinate with community agent i.e., Mental Health Worker Isolation/disconnection/depression Assess cause Increase students perceived support base Teach social skill for inclusion, asking for assistance Offer small group for academic tasks or social opportunities Peer assistance Cross age tutoring Opportunities to build status with peers Refer if remains unable to have energy for life or school Involve student in decision making Transition to School Task analysis-break down steps to beginning school day and modify as such Increase structure and support with preferred adult or peer Begin day with incentive schedule Picture schedule or organizing activity Daily check in group or with “coach” Learned Antisocial Interaction Patterns Identify clear expectations for positive behaviors Cost/benefit program for acceptable and non-acceptable choices Assess if early or late onset Early onset requires full participation by parents, and community professionals Late onset may be responsive to goal setting and reinforcement for positive and negative behaviors, monitoring peer influences PREDICTORS --Interventions Academic Driven Pinpoint specific problem task analysis, breakdown steps for problematic task expectation Create a strengths-needs scale* Modify content, length, time to perform tasks Modify seating Increase or decrease movement options Stimulate interest areas for student Allow peer help Teach organization skills Teach positive self-talk Teach communications skills: How to get help, how to ask for a break, a quieter place To recognize when help is needed Over-teach classroom skill required Pre-teach academic expectation* Authority Driven Evaluate quality of relationship Increase rapport Goal setting for specific expectations Identify positive and negative adults for student-increase access to former Look for ways to reinforce expected behaviors – 3:1 positive to negative statements Response Cost Plan* Allow limited (2) choices when giving directives Increase “Alpha” vs. “Beta” directives Reinforce small steps toward compliance Peer Driven Increase time with positive peers Decrease time with negative peers Cooperative learning options Teach social skill to improve peer interaction Teach verbal skill to meet social need or want Teach conflict management skills Communication Driven Teach social skill to verbalize or signal need or want Teach multimode expression of need or want* (h) Over-teach skill of communication of need or want* (i) Prepare adults to recognize attempts to communicate* (j) Procedure Driven Pre-teach steps to procedure Specify behavioral expectation Prepare for all changes Picture schedule of procedures Reassure verbally if fearful of change Over request tasks with high degree of success prior to difficult procedure* (k) Allow peer assistance, e.g. “Hall Buddy”