Genetics 1 – Meiosis and Recombination
advertisement
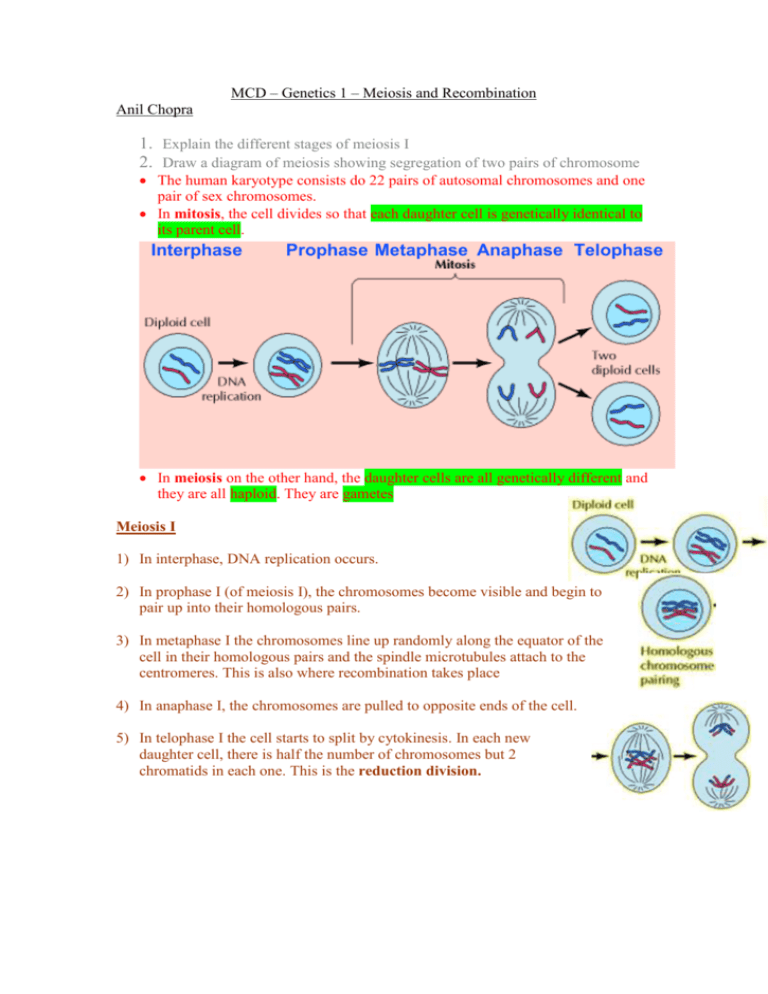
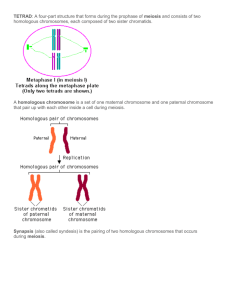
MCD – Genetics 1 – Meiosis and Recombination Anil Chopra 1. Explain the different stages of meiosis I 2. Draw a diagram of meiosis showing segregation of two pairs of chromosome The human karyotype consists do 22 pairs of autosomal chromosomes and one pair of sex chromosomes. In mitosis, the cell divides so that each daughter cell is genetically identical to its parent cell. Interphase Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase In meiosis on the other hand, the daughter cells are all genetically different and they are all haploid. They are gametes Meiosis I 1) In interphase, DNA replication occurs. 2) In prophase I (of meiosis I), the chromosomes become visible and begin to pair up into their homologous pairs. 3) In metaphase I the chromosomes line up randomly along the equator of the cell in their homologous pairs and the spindle microtubules attach to the centromeres. This is also where recombination takes place 4) In anaphase I, the chromosomes are pulled to opposite ends of the cell. 5) In telophase I the cell starts to split by cytokinesis. In each new daughter cell, there is half the number of chromosomes but 2 chromatids in each one. This is the reduction division. 3. Explain what occurs at meiosis II Meiosis II This is essentially the same as mitosis, only that there is half the number of chromosomes to split. Therefore altogether the process of meiosis: 4. Explain how recombination of chromosomes occurs. Recombination is the crossing over of genetic material between chromosomes. This means that genes, at particular loci can change place during metaphase of meiosis I. The recombination fraction is the chance that two different marked alleles on separate chromosomes will be inherited together. This increases as the two different alleles marked are further away on the chromosomes. Linkage is when the recombination fraction is more than 50% or 0.5.