Organic Compounds
advertisement

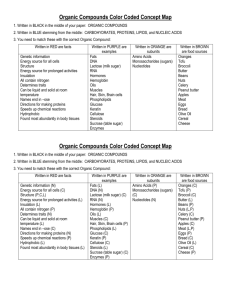
1 Chapter 3 – Biochemistry and Organic Compounds Characteristics of organic compounds: All organic compounds are derived from living things or are products of living things Examples of organic compounds:_____________________________________ Over ______________________ organic compounds have been identified ALL organic compounds contain _______________________ There are only 2 known compounds that contain C and are not organic:________________ Carbon has an atomic number of _______ This means that it has ________ electrons 4 of these electrons are in the outer shell and are able to form bonds Carbon needs to form _______ covalent bonds to be stable Carbon can bond with __________ or also with _____________________ Carbon is well suited to make the backbone of many compounds because it can bond in _________________ or ______________________ or ___________ Functional Groups: In most organic compounds there are additional clusters of atoms called functional groups. These groups influence the ________________ of the compound and also influence the _______________________________________ they can undergo. Large Carbon Molecules: __________________ are single, simple molecules - ________________ __________________ are the larger compounds made by joining together many monomers. __________________ very large polymers _________________ is the process of joining together monomers to make polymers. In order to form the bond to hold the monomers together a water molecule must be removed. One water molecule is removed for every bond that is formed. Can also be called ____________________ _____________________ is the process of breaking apart polymers to get individual monomers. This process requires water to be added for every bond that will be broke. ____________________ shows the makeup of a compound using symbols and numbers Ex: _________________ shows the makeup of compound by drawing its physical arrangement Ex: __________________ when 2 compounds have the same molecular formula but different structural formulas There are 4 types of organic compounds we will be studying: 2 Carbohydrates Are composed of ______________________ Always in a ratio of _______________________ Should compose ____________ of our diet Usually have names that end in _______________ Used for ___________________________________________ Monosaccharides -- ______________________ Are the building blocks (monomers) of carbohydrates 3 most common are: o _________________ - produced by plants during photosynthesis. Is the main ___________________ for organisms. This is the primary type of sugar that is carried in your blood to all your cells. It is regulated by insulin. Your brain neurons rely entirely on glucose for their energy. In order to have enough energy your body usually breaks down other sugars to get the glucose. Sometimes this sugars is also called ____________________ o ___________________ - found in _______________and ______________is the __________________ sugar and tastes twice as sweet as regular table sugar. o ______________________ - found in ____________________. Draw a picture of each of the 3 monosaccharides: These 3 monosaccharides have the same formula ___________________ but they are all structurally different. So they are __________________ Disaccharides -- ______________________ These sugars are formed when you join 2 monosaccharides together. They are bonded together by the process of _______________________. 3 most common are: o ______________ (_______________) – found in sugar cane and sugar beets. Made when a ________________ is bonded to a ___________________ o _________________ (_______________) – found in mammal milk. Made when a ______________________ is bonded to a ____________________. The human body must break this sugar apart with a special enzyme called lactase. All human infants have this enzyme. However some people do not produce this enzyme as 3 adults. They are called ___________________________________. If a person continues to eat lactose they will suffer intestinal cramping, gas and acid. o ___________________ ( ________________) – found in barley and used to make beer and malted milk drinks. Made when a _________________ is bonded to a ________________. These 3 all have the same formula ____________________ o Explain why their formula not the doubling of the formula of a monosaccharide? Draw a picture of a disaccharide here: Polysaccharides -- ______________________ Complex carbohydrates composed of 3 or more monosaccharides Three most common types: o _________________ ( __________________) - how plants store their excess sugar made from photosynthesis. Made by 100s of sugars all bonded in the same direction. Examples are:__________________________________ o _____________________ (__________________) – consists of hundreds of glucose molecules bonded together in a highly branched chain. Stored in an animal’s ________________ and ______________ tissue. The human body stores enough glycogen to provide sugar to the blood for 24-36 hours. o _____________________ - consists of glucose molecules bonded in long straight chains with the sugars being bonded going in opposite directions. Gives strength, rigidity and support to plant cells. Humans cannot digest this type of polysaccharides and get energy because we do not have the proper enzyme to break the bonds. Some animals have this enzyme and can survive entirely on plants. Humans eat foods containing cellulose because they are a good source of _______________ , _______________and ______________________. To use disaccharides or polysacahrides your body must break them apart using __________________. The _____________________ can then be used for energy. In our diet we divide our carbohydrates into simple carbs and complex carbs. 4 Lipids Composed of large amounts of ___________ and very few ________ Examples are _______________________ Are ____________________ in water Is essential for the proper functioning of the body – but must be right type Have many uses: o Chief _____________________ molecule. Concentrated energy for ____________. They body will start to burn fats after 30 minutes of exercise when they have used up all the glycogen that was previously stored. o o Provide _______________________ Protective padding around ____________________ o Composes __________________ making an outer barrier of the cell o __________________ for plants and animals o o ____________________ for aquatic animals Maintains healthy _________ and _________________ o Helps in the absorption and transport of ______________________ The building blocks or monomers of lipids are ______________ and _________________ Types of fatty acids 1. ________________________ All carbon are single bonded to all the other C’s. These fats are __________________ at room temperature. They usually come from animal fat. They are ______________ for your health, increase the bad cholesterol in your bloodstream and should be limited in your diet. Examples: 2. ___________________________- have several C to C double bonds. They are better for you than saturated fats and come from plants. They are still high in calories so you need to limit/watch them in your diet. Examples: 3. _________________________ have one C to C double bond. This means that they are ________________ at room temperature. They better for you than the poly unsaturated fats, help to lower cholesterol because they also come from plant sources. Examples: 4. _________________________ - come from fish and walnuts. Are the BEST type of fat to eat in your diet. Have many beneficial effects including protecting against heart disease. 5. ______________________________ - are chemically processed fats. They are the WORST type of fatty acid and should be avoided completely in your diet. They raise bad cholesterol levels and lower good levels and are linked to heart disease. On labels they are called hydrogenated oils. 5 Types of Lipids 1. Triglycerides - - type of lipid composed of ______ molecules of a fatty acid bonded to _______ molecule of _____________. a. _____________ - are triglycerides that are ________ at room temperature. Produced by plants. Also produced by animals for their hair and skin. Important because they help with waterproofing. b. _____________ - are triglycerides that are _________ at room temperature. Found in animals. Important to protect vital organs and store excess food. 2. ________________ - are a long fatty acid chain joined to a long alcohol chain. This makes them extremely ________________. 3. _________________- are composed of 4 carbon rings. Are present in hormones, nerve tissue, plant poisons and toad venom. Abnormal amounts lead to liver disease, intestinal bleeding and sterility. 4. _____________ - a large lipid that can build up in blood vessels and clog the blood flow. Amount must be controlled or can lead to heart attacks and strokes. There are 2 types: a. ___________ which is the bad type, is slow and sticks in your arteries/veins and b._________________ which is the good type and moves fast through the blood – this type is needed to stay healthy. Proteins Are composed of __________________ Are the ___________________________________ for cells and body parts such as: Are the _________________________________needed for essential life processes of organisms. Examples would be: Are found in foods such as: Made from monomers of __________________ There are ____________ amino acids. All organisms use the same 20 amino acids (aa) to make proteins. Amino acids can be used in different numbers and combinations to make millions of different proteins. Each amino acid has the same basic structure – they are only different in the R group –there are 20 different amino acids so there are 20 different R groups that could be bonded there. 6 Each individual is unique because of their __________________. The order of the amino acids in your proteins makes each one different. These different proteins make up your unique body. Your proteins are determined by your ___________________. Our bodies can make many of the amino acids that we need to live The ones we can make are called _________________________ because we don’t have to get them from our food. The amino acids we can’t make are called _____________________ and must be obtained in our diet. There are _______ that are essential to children and ______ that are essential for adults. If you eat animal proteins (meat, milk etc) you will get all the amino acids you need. Plant proteins lack some amino acids so vegetarians must be careful to eat a variety of foods to get all their amino acids. Amino acids can be recycled through the food chain and reused over and over to make different proteins for different organisms. Proteins are formed by joining amino acids together through the process of _______________________. The chains have between ____ and ________ amino acids The special bond between amino acids is called a _________________ bond because it joins a C to a N. Two amino acids bonded together is a _______________. Many amino acids bonded in a chain is a _______________ When one or more polypeptide chains are joined and folded up it makes a complete and functional protein Special type of proteins: o ___________________ are proteins that act as catalysts and speed up the rate at which chemical reactions occur. They lower the activation energy needed for the reaction to start. o Enzymes are not part of the reaction and can be reused over and over again. o Enzymes are very specific and will work only on a specific reaction o _________ is the reactant in the chemical reaction that is catalyzed by the enzyme – what the enzyme works on o ________________ is the place on the enzyme that bonds to the substrate. o Can think of enzymes as a lock and key o If an enzyme is heated or exposed to strong acids or bases it can denature. This means that the bonds holding the protein together break and the protein will unfold and can no longer do its job. (This can be lethal to humans in some cases). o Examples of enzymes: 7 Nucleic Acids Nucleic Acids are the ________________________ of the cell. They contain the directions that allow all cells to function properly. There are 2 types of nucleic acids: o ________________ – (deoxyribonucleic acid) – this molecule is found in the nucleus of cells. The job of DNA is ________________________________ o ________________ - (ribonucleic acid) – this molecules is found in cells. There are 3 types. Their job is to _____________________________________ . The monomer of a nucleic acid is a ________________________. o Nucleotides are very small – there are 3 billion DNA nucleotides in the nucleus of every human cell. o They have 3 parts ____________________ _____________________ ____________________ Summary POLYMER Carbohydrate Lipid Protein Nucleic Acid MONOMER USES