Plate Tectonics Continued
advertisement

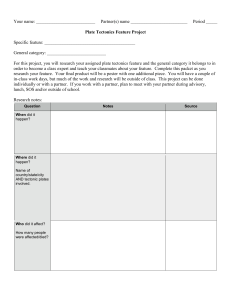
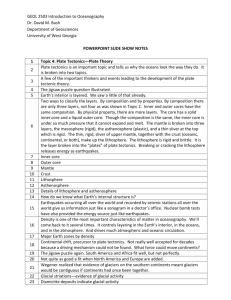
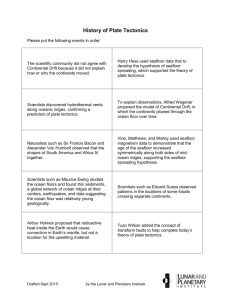
Plate Tectonics Continued Earth Science 3a. Students know features of the ocean floor (magnetic patterns, age, and seafloor topography) provide evidence of plate tectonics. Section 22.5 1. What is the mid-Atlantic ridge and where is it found? 2. What is a rift valley and where is it found in relation to underwater ridges? 3. What is an ocean trench? 4. Where is oceanic crust the newest? Why? 5. Where is oceanic crust the oldest? Why? 6. These two features provided evidence for seafloor spreading. What is seafloor spreading? 7. How does seafloor spreading produce underwater ridges? Underwater ridges are produced by seafloor spreading when… 8. How does seafloor spreading produce ocean trenches? Ocean trenches are produced by seafloor spreading when… 3 This picture shows seafloor spreading. Draw where the ridges and ocean trenches form. Magnetic Stripes (22.5) 9. What is magnetic reversal and how often does it occur? 10. Magnetite is a naturally occurring mineral contained within lava. When lava emerges from the mantle as a liquid through the divergent plate boundary, the magnetite is able to orient with the earth’s magnetic field (think of a compass needle). The lava hardens shortly after emerging from the mantle and the magnetite gets stuck in its orientation. Therefore it reflects the magnetic field that was present when it came out of the mantle. Explain how this has caused magnetic striping. Used the sentence starters provided. Magnetic striping is ___________ that are present on the ocean floor. The earth’s magnetic field has reversed many times throughout history. This creates magnetic stripes because _______________. 4 Activity: Magnetic Stripes Place two pieces of green paper together; these represent the continents at the time of Pangaea. As we travel through history, the continents move apart and new oceanic crust is formed between the continents. The earth’s magnetic polarity is reversing throughout history as well. Magnetite in the rock will orient with the earth’s polarity until the rock hardens. Show magnetite’s orientation with an up arrow if the earth’s north magnetic pole is at the geographic north pole and a down arrow if the earth’s magnetic north pole is at the geographic sound pole. Draw what happens. Explain what happens in complete sentences. As the continents move apart, ______... Section 22.6 11. What is a tectonic plate? 5 12. List and describe the three types of plate boundaries. 13. List 3 possible causes of plate tectonic movement. Break down the standard: Students know features of the ocean floor (magnetic patterns, age, and sea-floor topography) provide evidence of plate tectonics? What is plate tectonics? Plate tectonics is a theory. What does that mean? How do we know tectonic plates are moving? 1. Magnetic Patterns Magnetic patterns support the theory of plate tectonics because ___(state the evidence/observations)___ shows that ___(state what it proves)___. 2. Age The age of the seafloor supports the theory of plate tectonics because ___(state the evidence/observations about seafloor age)__ shows that __(state what it proves)___. 6 3. Sea-floor topography (ridges and trenches) Ridges and trenches support the theory of plate tectonics because ridges were formed by ____(state how plate tectonics formed ridges)___ and ocean trenches were formed by ___(state how plate tectonics formed trenches)___. Because we have all of this evidence, plate tectonics is a well accepted theory. Answer the focus question: What evidence do we have to support the theory of plate tectonics? Use your answers to the above questions to help you write a synthesized answer. You may also include the evidence provided in section 22.4 that supports continental drift (which is a part of plate tectonics). 7