Population Dynamics
advertisement

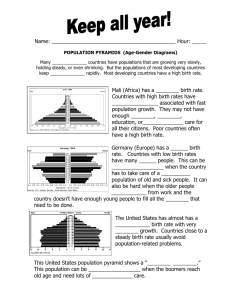
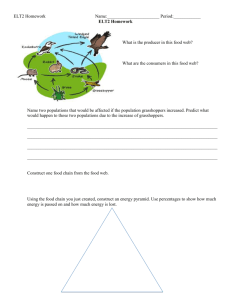
Science 20F Population Dynamics Changes in population size occur when individuals are added to or removed from a population. If increases in population are balanced by decreases in populations, the population growth is zero. This balance is called dynamic equilibrium. Factors that affect Population Sizes 1) Births – number of offspring of a species born in one year. 2) Deaths (mortality) – number of individuals of a species that die in one year. 3) Immigration – number of individuals of a species moving into an existing population. 4) Emigration – number of individuals of a species moving out of an existing population. Open Populations – If all four factors mentioned above are acting on populations, these populations are classified by Ecologists are open populations. Closed Populations – If only births and deaths affect populations, these populations are classified as closed populations. The global population of any species is considered a closed population. The human population is not in dynamic equilibrium. Population Histograms Histograms are useful when studying populations of long-lived organisms such as humans. The shape of the histogram pyramid allows you to predict changes in the population. A wide base indicates a rapidly growing population. When the base of the pyramid is narrower than the middle, a declining population is indicated. A gradually growing histogram pyramid indicates a stabilized population.