University of Salahaddin
advertisement

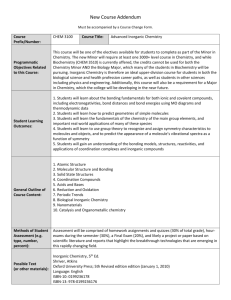
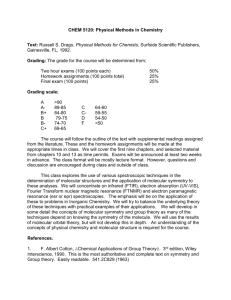
University of Salahaddin College of Science Department of Chemistry Course Book Inorganic Chemistry (Coordination Chemistry) Third Year Chemistry Academic Year: 2013-2014 Professor Dr.Ali Ismail Abdullah Ph.D. in Inorganic Chemistry E-mail: ali_h51@yahoo.com Dr. Azad H. Mahdy Ph.D. in Inorganic Chemistry azad_mahdy@ yahoo.co.uk Course Objective This course includes a detailed overview of historical development of coordination chemistry, hypothesis and theories which proposed for interpreting the nature of coordinating bonds between metal ions and ligands, such as VBT ,CFT and MOT, Coordination numbers and isomers ,Transition metals, VSEPR rule for determination of the shape and geometries of the covalent compounds ,Electronic spectra of the complexes , Kinetic and reaction mechanism of the coordination compounds. Grading The students are required to do two closed examinations at the course besides other assignments, for example daily quizzes and other activities which may held 5% of total grades ( 5 marks), final examination which bears 50% from the total degrees. Over all degrees 75% theory( 3 hours per week) and 25% practical. Quizzes In class every week, the students should already have knowledge of subject that they had taken before, and ready for any quizzes. Syllabus of Coordination Chemistry 3 Hours/week (theory)+( practice) 3hours/week 1 An Introduction to Coordination chemistry: (4 weeks) 1- The Historical Development of Coordination Compounds: Hypothesis and theories proposed for explaining the nature of coordinating bonds. 2- The Blomstrand-Jorgensen Chain Theory. The Werner Coordination Theory. 3- Sidgwick (EAN) rule and Pauling principle of Coordination Bonds. 4- Nomenclature of ligands and coordination complexes (IUPAC) rule. Bonding Theories for Coordination Compounds : (3 weeks). The Lewis Acid-Base Difination Valence Bond Theory(VBT) : Coordination number , Hyberdization and geometrical structure , Origin of Magnetic properties ,weakness points of VBT (Crystal Field Theory (CFT): ( 4 weeks). Shapes of 3d orbitals Degenerate of d-orbitals , properties, Splitting of d-orbitals in different fields : Octahedral (O.h) , Tetragonally distorted O.h, (sq.pl.) and Tetrahedral(T.H) fields. Squarq planar Crysyal Field Stabilazation Energy(CFSE): Magnetic Measurements , High-spin and low-spin , Strong field and weak field . crystal field stabilization energy, spin complexes, high spin and low pairing energies, factors affecting the magnitude of CF splitting energies. spectrochemical series, Jahn-Teller effects, limitations of Jahn-Teller theor Coordination Number and Isomers :( 4 weeks). 1-Structural Isomers: , ionization isomerism, linkage isomerism, coord.isomers ,etc. determination of cis-trans isomers. 2 2-Stereoisomers: a. Optical isomers or enantiomers b. Geometric isomers Effect of d-orbital splitting on structure and thermodynamic of the complexes i-Ionic radii ii-Heat of hydration Ligand Field Theory (Adjusted CFT): i-NMR spectra ii-ESR spectra iii-Nephelauxic effect iv-D-d transition Molecular orbital theory : (3 weeks): Linear combination of atomic orbitals ( LCAO): S , p and d orbital overlaps : Basic principle, -bonding and -bonding in octahedral complexes, effects of -bonding on stability of the complexes. MOT in tetrahedral and octahedral complexes, limitations of MOT, comparison of different approaches to bonding in coordination compounds . Books Recommended: 1. S. Z. Haider, Advanced Inorganic Chemistry. 2. James E. Huheey, Inorganic Chemistry. 3. Cotton, Wilkinson and Gaus, Basic Inorganic Chemistry. 4. Shriver, Atkins and langford, Inorganic Chemistry. 5. Douglas. McDaniels and Alexander, Concepts and Models of Inorganic Chemistry. 6. Sharpe, Inorganic Chemistry. 7. W. L. Jolly, Inorganic Chemistry 3 1. Electronic Spectra of metal complexes : (4 weeks). Term symbols, selection rules, Hund's rule and ground state term, splitting of electronic energy levels and spectroscopic states, Energy level diagrams of the electronic spectra of d1-9 , complexes in O.h and T.H fields. Orgel-diagram. charge transfer spectra. 2. Stability of coordination compounds: (3weeks). Thermodynamics and kinetic stability, factors influencing the stability of complexes. 3. Reaction mechanism : (3 weeks). A Brief survey of reaction types. Types of substitution reactions, introduction to ligand substitution reactions-lability and inertness, substitution reaction in octahedral compleses—(SN1.) Reaction mechanism. Effect of Charge / radius ratio on kinetic behavior of Coordn.Com pounds. types of mechanism of ligand substitution reactions, acid hydrolysis and base hydrolysis reaction, effect of charge, leaving group, nonleaving group, solvents, steric effect, etc. on reaction rates, substitution without breaking the metal- ligand bond, recimization reaction. Ligand substitution reaction on square planar complexes--general features, significance of the rate law, (SN2) Reaction mechanism Trans-Effect Theories of trans effect : i-polarity ii--bonding . Redox reactions-, inner and outer sphere reactions and their mechanism, theory of redox reactions, , d-d and charge transfer reactions. 4 Books Recommended : 1. Purcell and Kotz : Advanced Inorganic Chemistry 2. J. E. Huheey : Inorganic Chemistry 3. J. D. Lee : Inorganic Chemistry 4. M.L. Tobe : Inorganic Reaction Mechanism 5. Shriver, Atkins and Langford : Inorganic Chmistry 6. Douglas, McDaniels and Alexander : Concepts and Models of Inorganic Chemistry 7. Katakis and Gordon : Mechanism of Inorganic Reactions 5 University of Salahaddin College of Science Department of Chemistry Course Book Advanced Inorganic Chemistry M.Sc. Students First Course Academic Year: 2012-2013 Professor Dr.Ali Ismail Abdullah Ph.D. in Inorganic Chemistry E-mail: ali_h51@yahoo.com Mob: 0750 4624174 Course Objective This course includes a detailed overview of periodic table properties, Transition metals, VSEPR rule for determination of the shape and geometries of the covalent compounds , Russel-Saunder states and Electronic spectra of the complexes , Hard and Soft Acid-Base (Pearson Principle) and reaction types. Grading The students are required to do a closed examination at the course 30% and final examination which bears 70% from the total degrees. Over all degrees 100% . Syllabus of Coordination Chemistry 3 Hours/week ( 7 weeks from total 15 weeks) : 1- A detailed overview of periodic table properties (Groups and periods), Number of elements in each period. 2- Valence Shell Electon Pair Repulsion (VSEPR), for Determination of actual Shapes and Geometres of the covalent compounds. 3- Electronic Spectra of the Coordination compounds. Terms ande Russel-Saunde states, selection rules Energy level diagrams of the electronic spectra of d1-9 , complexes in an O.h and T.H fields. Orgel-diagram. 4-Hard and Soft Acid-Base (Pearson Principle). 5- Types of reactions , Classification of reactions for coordination complexes as: Addition, Substitution ,Dissosiation, Elimination and Oxidative addition. 6- Outer-sphere and Inner-sphere reactions. References: 1-Inorganic Chemistry, Principles of Structure and reactivity by ; James Huheey. 2-Advancd inorganic Chemistry by; Cotton and Wilkinson. 3-The Molecular Nature of Matter and Change bu; Martin Silberberg, Madelyn E, Logan. 4-Descriptive Inorganic, Coordination and Solid Chemistry by; Glen e.Rodgers. 5- Inorganic Chemistry by ; Gtherine E.Housecroft and Alan glan g. Sharppe. 6- Complexes and First-Row Transition Elements. David Nicholls.