Female Reproductive System 12th Grade Health
advertisement

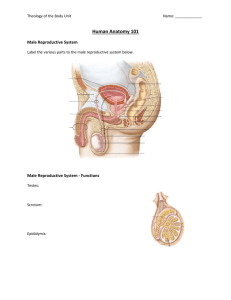
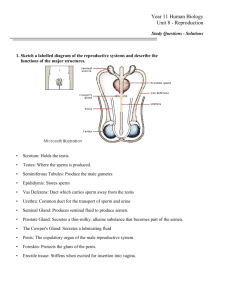
Female Reproductive System 12th Grade Health Function(s) Production of female sex hormones – estrogen & progesterone Production and storage of female sex cells – ovum/ova Preparation for implantation and development of fertilized ovum - menstruation Structure (pathway of the ovum through female reproductive system) INTERNAL STRUCTURE: Ovaries – female sex glands (gonads); produce estrogen and progesterone; house the ova (eggs). Fallopian Tubes – tubes that lead the ova from the ovaries to the uterus; place where fertilization takes place. Uterus – strong elastic pear-shaped muscle; size of a fist; also called the “womb;” development of embryo/fetus occurs here. Cervix – “narrow” opening between the uterus and the vagina. Vagina – “birth canal;” elastic tube where sperm is deposited during sexual intercourse. EXTERNAL STRUCTURE (VULVA): Clitoris – small knob of tissue in front of the vaginal opening which produces sexual arousal. Labia Majora – outer folds of tissue on either side of vaginal opening providing protection from pathogens. Labia Minora – inner folds of tissue on either side of the vaginal opening providing protection from pathogens. Mons Pubis – rounded fatty pad of tissue located directly on top of the pubic bone. Female Reproductive System 12th Grade Health Problems with the Female Reproductive System Menstrual Cramps – abdominal cramps that sometimes occur in the beginning of the menstrual period. Premenstrual Syndrome (PMS) – A variety of symptoms sometimes experienced up to two weeks before each menstrual period which include nervous tension, anxiety, irritability, bloating, weight gain, depression, mood swings, and fatigue; thought to be caused by a hormonal imbalance or nutritional deficiency. Toxic Shock Syndrome (TSS) – a bacterial disease usually found in menstruating females who use tampons characterized by sudden high fever, vomiting, diarrhea and dizziness. Vaginitis / Yeast Infection / Trichomoniasis – infections of the vagina caused by a bacteria, fungus and protozoa respectively. Symptoms include discharge from vagina, itching and a burning sensation during urination. Sterility – inability for a woman to reproduce; can be caused by a blocked fallopian tube, failure of the ovaries to produce fertile ova or an untreated sexually transmitted infection. Endometriosis – abnormal presence of the endometrium in the abdominal cavity. Breast Cancer – found in about 1 out of 9 females at sometime in their lives; heredity plays a major role in terms of risk; can be found early through Breast Self-Exam (BSE) and a regular mammography. Ovarian Cysts – growth on the outside of an ovary; surgery may be require if cyst is large. Cancer of the Cervix, Uterus and Ovaries – more common in older women with a history of cancer in their family. Regular checkups are recommended for early detection. Amenorrhea – cessation of a menstrual cycle or Dysmenorrhea – an irregular menstrual cycle. Causes very low percentage of body fat or poor diet. Female Reproductive System 12th Grade Health Care for the Female Reproductive System cleanliness, protection, self-examination and regular medical examinations Additional Information and Terminology Ovulation – the release of a mature ovum from the ovaries once every 28 days. Endometrium – the lining of the uterus. Menstruation – the passing of the endometrium through the vagina and out the body due to uterine contractions. Gynecologist – doctor specializing in caring for females. The Menstrual Cycle Generally a 28-day cycle. Begins with menstruation; 2 – 3 fluid ounces of blood and tissue leave the body. Menstrual flow usually lasts about 3 – 5 days. Endometrium once again thickens, preparing for the possibility of a fertilized egg. On about the 14th day (half way through the cycle) the female will ovulate and release a mature ovum from her one of her ovaries. If ovum is not fertilized by the time it reaches the uterus, the endometrium will once again break down and flow out of the body during menstruation. Male Reproductive System 12th Grade Health Function(s) Production of male sex hormone – testosterone Production of male sex cells – sperm Production of fluid in which sperm travels – semen Transfer of sperm to female body during sexual intercourse for procreative purposes. Structure (pathway of the sperm through male reproductive system) Scrotum – sac of skin that holds the testes and regulates temperature for sperm production (just under 98.6F). Testes – male sex glands (gonads); produce sperm and testosterone. Epididymis – coiled tubes found above each testicle; store and mature sperm before ejaculation. Vas Deferens – tubes that carry sperm from the epididymis to the seminal glands. Seminal Vesicle – seminal gland that provides a fructose fluid to semen which helps to nourish sperm. Prostate – seminal gland that provides a basic solution to semen which helps to neutralize the acidity of the vagina which in turn protects sperm. Cowper’s Gland – seminal gland that secretes a lubricant that cleanses the urethra prior to ejaculation. Urethra – tube that exits the body through the penis; carries both urine and semen. Penis – external male reproductive organ made of spongy tissue; used for urination as well as for sexual intercourse. Male Reproductive System 12th Grade Health Additional Information and Terminology Erection – filling of blood in the spongy tissue of penis when aroused. Foreskin – skin covering the end of the penis. Circumcision – procedure whereby the foreskin is removed surgically. Ejaculation – release of semen from urethra/penis caused by involuntary muscular contractions (approximately 300 – 400 million sperm released). Nocturnal Emission – ejaculation of semen while sleeping; also called a “wet dream.” Problems with the Male Reproductive System Inguinal Hernia – when part of the intestines push through a tear in the abdominal wall into the scrotum. Sterility – condition whereby a male can not reproduce caused by malfunction of various parts of the system, producing too few sperm, poor quality sperm, temperature changes, smoking, exposure to certain chemicals or disease related. Enlarged Prostate – caused by age (over 50), tumor or infection; results in frequent urination. Prostate Cancer – usually in males over 50 years of age; 2nd leading cancer in males. Testicular Cancer – most common in men 15 – 34 years of age; characterized by dull ache and in groin, enlarged testicle and hard lumps/nodules on testes. Testicular Self-Exam (TSE) can help to detect early signs. Sexually Transmitted Infections – contracted during unprotected sex or sharing of needles. Care for the Male Reproductive System cleanliness, protection and self-examination